Abstract
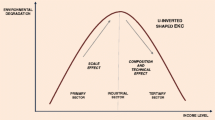
In the recent times, the issue of excessive carbon emission is a hot topic among the scholars and governors. In this context, it is necessary to examine the factors affecting the emissions level, particularly in emerging economy like China. Using the extended period from 1990 to 2021, this study analyzes the impact of energy efficiency, economic growth, and renewable energy along with the testing of environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) paradox. The empirical results validate the cointegration between the mentioned variables. Employing the novel non-parametric approaches, this study found the existence of the EKC hypothesis in the country as the economic growth initially increases environmental challenges, while reducing it after reaching a specific income level. On the other hand, energy efficiency and renewable energy consumption are found to be significant tools for improving environmental sustainability and reducing of carbon emissions. The robustness of the results is confirmed by the non-parametric (bootstrap quantile regression) and parametric (fully modified ordinary least square) approaches. Based on the outcomes, this study also revealed policy implications for the scholars and governors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Website, and the World Bank (WB).
References
Acaravci, A., & Ozturk, I. (2010). On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy, 35(12), 5412–5420.
Adebayo, T. S., & Rjoub, H. (2021). Assessment of the role of trade and renewable energy consumption on consumption-based carbon emissions: Evidence from the MINT economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(41), 58271–58283.
Adebayo, T. S., Oladipupo, S. D., Rjoub, H., Kirikkaleli, D., & Adeshola, I. (2022). Asymmetric effect of structural change and renewable energy consumption on carbon emissions: Designing an SDG framework for Turkey. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25, 528–556.
Adebayo, T. S., Rjoub, H., Akinsola, G. D., & Oladipupo, S. D. (2022). The asymmetric effects of renewable energy consumption and trade openness on carbon emissions in Sweden: New evidence from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(2), 1875–1886.
Akram, R., Chen, F., Khalid, F., Ye, Z., & Majeed, M. T. (2020). Heterogeneous effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions: Evidence from developing countries. Journal of cleaner production, 247, 119122.
Akram, R., Majeed, M. T., Fareed, Z., Khalid, F., & Ye, C. (2020). Asymmetric effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions of BRICS economies: Evidence from nonlinear panel autoregressive distributed lag model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(15), 18254–18268.
Alison. (2020). https://www.belfercenter.org/publication/china-now-worlds-largest-economy-we-shouldnt-be-shocked. Accessed 15 Feb 2021
Anser, M. K., Usman, M., Godil, D. I., Shabbir, M. S., Sharif, A., Tabash, M. I., & Lopez, L. B. (2021). Does globalization affect the green economy and environment? The relationship between energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(37), 51105–51118.
Banerjee, A., Dolado, J., & Mestre, R. (1998). Error-correction mechanism tests for cointegration in a single-equation framework. Journal of Time Series Analysis, 19(3), 267–283.
Bashir, M. A., Dengfeng, Z., Bashir, M. F., Rahim, S., & Xi, Z. (2022). Exploring the role of economic and institutional indicators for carbon and GHG emissions: Policy-based analysis for OECD countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(12), 32722–32736.
Bayer, C., & Hanck, C. (2013). Combining non-cointegration tests. Journal of Time series analysis, 34(1), 83–95.
Boswijk, H. (1994). Testing for an unstable root in conditional and structural error correction models. Journal of Econometrics, 63(1), 37–60.
Cai, X., Wang, W., Rao, A., Rahim, S., & Zhao, X. (2022). Regional sustainable development and spatial effects from the perspective of renewable energy. Frontiers in Environmental. Science, 10, 166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.859523
Chen, H., Tackie, E. A., Ahakwa, I., Musah, M., Salakpi, A., Alfred, M., & Atingabili, S. (2022). Does energy consumption, economic growth, urbanization, and population growth influence carbon emissions in the BRICS? Evidence from panel models robust to cross-sectional dependence and slope heterogeneity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(25), 37598–37616.
Dickey, D. A., & Fuller, W. A. (1979). Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. Journal of the American statistical association, 74(366a), 427–431.
Efron, B., & Tibshirani, R. J. (1994). An introduction to the bootstrap. CRC press.
Ehigiamusoe, K. U., & Dogan, E. (2022). The role of interaction effect between renewable energy consumption and real income in carbon emissions: Evidence from low-income countries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 154, 111883.
Engle, R. F., & Granger, C. W. (1987). Co-integration and error correction: Representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica: journal of the Econometric Society, 55(2), 251–276.
Hasanov, F. J., Khan, Z., Hussain, M., & Tufail, M. (2021). Theoretical framework for the carbon emissions effects of technological progress and renewable energy consumption. Sustainable Development, 29(5), 810–822.
He, Y., Fu, F., & Liao, N. (2021). Exploring the path of carbon emissions reduction in China’s industrial sector through energy efficiency enhancement induced by R&D investment. Energy, 225, 120208 https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/co2-emissions-by-country
Jarque, C. M., & Bera, A. K. (1987). A test for normality of observations and regression residuals. International Statistical Review/Revue Internationale de Statistique, 55(2), 163–172.
Jiang, S., Chishti, M. Z., Rjoub, H., & Rahim, S. (2022). Environmental R&D and trade-adjusted carbon emissions: Evaluating the role of international trade. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(42), 63155–63170.
Johansen, S. (1991). Estimation and hypothesis testing of cointegration vectors in Gaussian vector autoregressive models. Econometrica: journal of the Econometric Society, 59(6), 1551–1580.
Kirikkaleli, D., Güngör, H., & Adebayo, T. S. (2022). Consumption-based carbon emissions, renewable energy consumption, financial development and economic growth in Chile. Business Strategy and the Environment, 31(3), 1123–1137.
Koenker, R., & Bassett Jr, G. (1978). Regression quantiles. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 33–50.
Lee, C. T., Lim, J. S., Van Fan, Y., Liu, X., Fujiwara, T., & Klemeš, J. J. (2018). Enabling low-carbon emissions for sustainable development in Asia and beyond. Journal of Cleaner Production, 176, 726–735.
Leitão, N. C., Balsalobre-Lorente, D., & Cantos-Cantos, J. M. (2021). The impact of renewable energy and economic complexity on carbon emissions in BRICS countries under the EKC scheme. Energies, 14(16), 4908.
Li, G., & Wei, W. (2021). Financial development, openness, innovation, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Energy Economics, 97, 105194.
Li, K., Hu, E., Xu, C., Musah, M., Kong, Y., Mensah, I. A., Zu, J., Jiang, W., & Su, Y. (2021). A heterogeneous analysis of the nexus between energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from the Group of Twenty (G20) countries. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 39(3), 815–837.
Luan, S., Hussain, M., Ali, S., & Rahim, S. (2022). China’s investment in energy industry to neutralize carbon emissions: Evidence from provincial data. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(26), 39375–39383.
Machado, J. A., & Silva, J. S. (2019). Quantiles via moments. Journal of Econometrics, 213(1), 145–173.
Mahmood, N., Wang, Z., & Hassan, S. T. (2019). Renewable energy, economic growth, human capital, and CO2 emission: An empirical analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(20), 20619–20630.
Mirza, F. M., Sinha, A., Khan, J. R., Kalugina, O. A., & Zafar, M. W. (2022). Impact of energy efficiency on CO2 Emissions: Empirical evidence from developing countries. Gondwana Research, 106, 64–77.
Narayan, K., Saboori, B., & Soleymani, A. (2016). Economic growth and carbon emissions. Economic Modelling, 53, 388–397.
Phillips, C., & Hansen, B. E. (1990). Statistical inference in instrumental variables regression with I (1) processes. The Review of Economic Studies, 57(1), 99–125.
Qin, L., Hou, Y., Miao, X., Zhang, X., Rahim, S., & Kirikkaleli, D. (2021). Revisiting financial development and renewable energy electricity role in attaining China’s carbon neutrality target. Journal of Environmental Management, 297, 113335.
Qin, L., Raheem, S., Murshed, M., Miao, X., Khan, Z., & Kirikkaleli, D. (2021). Does financial inclusion limit carbon dioxide emissions? Analyzing the role of globalization and renewable electricity output. Sustainable Development, 29(6), 1138–1154.
Radmehr, R., Henneberry, S. R., & Shayanmehr, S. (2021). Renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth nexus: A simultaneity spatial modeling analysis of EU countries. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 57, 13–27.
Raihan, A., & Tuspekova, A. (2022). Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between economic growth, renewable energy use, forested area, and carbon emissions in Malaysia. Resources, Conservation & Recycling Advances, 15, 200096.
Sadiq, M., Kannaiah, D., Yahya Khan, G., Shabbir, M. S., Bilal, K., & Zamir, A. (2022). Does sustainable environmental agenda matter? The role of globalization toward energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emissions in South Asian countries. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25(1), 76–95.
Salman, M., Long, X., Dauda, L., & Mensah, C. N. (2019). The impact of institutional quality on economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from Indonesia, South Korea, and Thailand. Journal of Cleaner Production, 241, 118331.
Salman, M., Long, X., Dauda, L., Mensah, C. N., & Muhammad, S. (2019). Different impacts of export and import on carbon emissions across 7 ASEAN countries: A panel quantile regression approach. Science of the total environment, 686, 1019–1029.
Sarkodie, S. A., & Strezov, V. (2018). Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. Journal of Cleaner Production, 201, 98–110.
Shahbaz, M., Naeem, M., Ahad, M., & Tahir, I. (2018). Is natural resource abundance a stimulus for financial development in the USA? Resources Policy, 55, 223–232.
Shahzad, U., Radulescu, M., Rahim, S., Isik, C., Yousaf, Z. and Ionescu, S.A., 2021. Do environment-related policy instruments and technologies facilitate renewable energy generation? Exploring the contextual evidence from developed economies. Energies, 14(3), 690
State Council. (2022). Available at: http://english.www.gov.cn/statecouncil/ministries/202201/31/content_WS61f7cd4fc6d09c94e48a4953.html. Accessed 10 May 2022
Sufyanullah, K., Ahmad, K. A., & Ali, M. A. S. (2022). Does emission of carbon dioxide is impacted by urbanization? An empirical study of urbanization, energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions-Using ARDL bound testing approach. Energy Policy, 164, 112908.
Sun, H., Edziah, B. K., Kporsu, A. K., Sarkodie, S. A., & Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. (2021). Energy efficiency: The role of technological innovation and knowledge spillover. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 167, 120659.
Wei, J., Rahim, S., & Wang, S. (2022). Role of environmental degradation, institutional quality and government health expenditures for human health: Evidence from emerging seven countries. Frontiers in Public Health, 562. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.870767/pdf
World Bank (2022). World development indicators. Available at: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/worlddevelopment-indicators#
Wu, Y., Tam, V. W., Shuai, C., Shen, L., Zhang, Y., & Liao, S. (2019). Decoupling China’s economic growth from carbon emissions: Empirical studies from 30 Chinese provinces (2001–2015). Science of the Total Environment, 656, 576–588.
Yao, X., Yasmeen, R., Hussain, J., & Shah, W. U. H. (2021). The repercussions of financial development and corruption on energy efficiency and ecological footprint: Evidence from BRICS and next 11 countries. Energy, 223, 120063.
Ye, N., Yuan, L., & Xu, Y. (2022). Non-parametric research methods to measure energy efficiency and renewable energy nexus: Evidence from emerging economies. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 36(1), 2421–2442.
Zhao, S., Hafeez, M., & Faisal, C. M. N. (2022). Does ICT diffusion lead to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in emerging Asian economies? Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(8), 12198–12207.
Acknowledgements
Zhou Rong is grateful for the support of the Guangdong Planning Project of Philosophy and Social Science (GD22XGL63). Liu Li acknowledges the research support provided by the Anhui University of Finance and Economics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The idea of the original draft belongs to Rong Zhou and Li Zheng. Liu Li designed the experiment and collected the dataset. The introduction and literature review sections are written by Najaf Iqbal. Zeeshan Fareed constructed the methodology section and empirical outcomes in the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
We confirmed that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal. Ethical approval and informed consent are not applicable for this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, R., Zheng, L., Li, L. et al. Energy efficiency and China’s carbon emissions: evidence from non-parametric approaches. Energy Efficiency 16, 63 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-023-10142-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12053-023-10142-4