Abstract
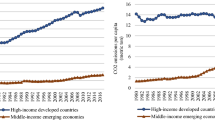
Most of the developed countries across the globe have targeted to attain sustainable economic growth. With this focus, the current study evaluated 29 OECD countries over the time period of 1990 to 2018 to analyze the influence of economic and environmental indicators, i.e., export diversification, institutional quality, macrocosmic variables on carbon dioxide, and greenhouse gas emissions. The current study used the quantile regression and generalized method of moments approach on the selected panel. Our comprehensive econometric approach allows us to reveal that export diversification negatively affects carbon emissions but promotes greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, institutional quality, economic growth, financial development, and economic growth helps to reduce carbon emissions but increase greenhouse emissions. In comparison, trade openness exhibits a positive influence on carbon emissions but a negative on greenhouse gas emissions. Besides, urbanization is found one of the major reasons for environmental degradation. In light of empirical fact findings, this study commends some innovative policy insights for scholars, governors, and policymakers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Researchers can contact corresponding author for data through email ID.
References
Acemoglu D, Naidu S, Restrepo P, Robinson JA (2019) Democracy does cause growth. J Polit Econ 127(1):47–100
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Lean HH (2015) The influence of economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, financial development, and renewable energy on pollution in Europe. Nat Hazards 79(1):621–644
Apergis N, Aye GC, Barros CP, Gupta R, Wanke P (2015) The energy efficiency of selected OECD countries: a slacks-based model with undesirable outputs. Energy Econ 51:45–53
Apergis N, Can M, Gozgor G, Lau CKM (2018) Effects of export concentration on CO 2 emissions in developed countries: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):14106–14116
Armeanu DŞ, Gherghina ŞC, Pasmangiu G (2019) Exploring the causal nexus between energy consumption, environmental pollution and economic growth: empirical evidence from central and Eastern Europe. Energies 12(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12193704.
Arslan H, Bilal, Bashir, MF (2021) Contemporary research on spillover effects of COVID-19 in stock markets. A systematic and bibliometric review. SCI Forum 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECERPH-3-09103
Bashir MF (2018) A class of multi-attribute auction transformed into single-attribute auction on Margin Bid. Bus Eco J 9(352)
Bashir MF, Shahzad U, Latif S, Bashir M (2015) The nexus between economic indicators and economic growth in Brazil. Nexus 13(1):1–8
Bashir MA, Sheng B, Doğan B, Sarwar S, Shahzad U (2020) Export product diversification and energy efficiency: empirical evidence from OECD countries. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 55:232–243
Bashir MF, Ma B, Shahbaz M, Jiao Z (2020) The nexus between environmental tax and carbon emissions with the roles of environmental technology and financial development. PLOS ONE 15(11):e0242412. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242412
Bashir MA, Sheng B, Farooq MU, Bashir MF, Shahzad U (2021a) The role of macroeconomic and institutional factors in foreign direct investment and economic growth: empirical evidence in the context of emerging economies. Global Local Econ Rev 24(2):67
Bashir MF, Benjiang MA, Shahbaz M, Shahzad U, Vo XV (2021b) Unveiling the heterogeneous impacts of environmental taxes on energy consumption and energy intensity: empirical evidence from OECD countries. Energy 226:120366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120366
Bashir MF, Ma B, Bashir MA, Shahzad L (2021c) Scientific data-driven evaluation of academic publications on environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(14):16982–16999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13110-6
Bashir MF, Ma B, Komal B, Bashir MA (2021d) Analysis of environmental taxes publications: a bibliometric and systematic literature review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(16):20700–20716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12123-x
Bashir MF, Ma B, Qin Y, Bashir, MA (2021e) Evaluation of One Belt One Road publications: a bibliometric and literature review analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(28):37016–37030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14621-y
Bashir MF, Ma B, Xia W, Shahzad U, Radulescu M (2022a) Do economic openness and institutional quality influence environmental patents? Empirical evidence from South Asia. Environ Eng Manag J 21(1):49–61
Bashir MF, Ma B, Shahzad L, Liu B, Ruan Q (2021f) China’s quest for economic dominance and energy consumption: Can Asian economies provide natural resources for the success of One Belt One Road? Manag Decis Econ 42(3):570–587. https://doi.org/10.1002/mde.3255
Bashir MF (2022a) Oil price shocks, stock market returns, and volatility spillovers: a bibliometric analysis and its implications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:22809–22828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18314-4
Bashir MF (2022b) Discovering the evolution of Pollution Haven Hypothesis: A literature review and future research agenda. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:48210–48232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20782-1
Bashir MF, Sadiq M, Talbi B et al (2022b) An outlook on the development of renewable energy, policy measures to reshape the current energy mix, and how to achieve sustainable economic growth in the post COVID-19 era. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:43636–43647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20010-w
Bashir MF, Benjiang MA, Hussain HI, Shahbaz M, Koca K, Shahzadi I (2022c) Evaluating environmental commitments to COP21 and the role of economic complexity, renewable energy, financial development, urbanization, and energy innovation: empirical evidence from the RCEP countries. Renew Energy 184:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.11.102
Bashir, MA, Dengfeng Z, Shahzadi I, Bashir MF (2022d) Does geothermal energy and natural resources affect environmental sustainability? Evidence in the lens of sustainable development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23656-8
Bashir MF, Ma B, Bashir MA, Radulescu M, Shahzad U (2022e) Investigating the role of environmental taxes and regulations for renewable energy consumption: evidence from developed economies. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 35(1):1262–1284. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1962383
Bilal, Bashir MF, Shahzad A, Komal B, Bashir M, Tan D (2021) Nexus between temperature and COVID-19 pandemic: a meta-analysis. In Sci Forum Proceedings pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECERPH-3-09098
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut Ü, Kuloğlu A (2017) The impact of urbanization on energy intensity: panel data evidence considering cross-sectional dependence and heterogeneity. Energy 133:242–256
Boutabba MA (2014) The impact of financial development, income, energy and trade on carbon emissions: evidence from the Indian economy. Econ Model 40:33–41
Cadot O, Celine C, Strauss-Kahn V (2011) Export diversification: what’s behind the hump? Rev Econ Stat 93(2):590–605
Cadot O, Carrère C, Strauss-Kahn V (2014) OECD imports: diversification of suppliers and quality search. Rev World Econ 150(1):1–24
Can M, Gozgor G (2017) The impact of economic complexity on carbon emissions: evidence from France. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(19):16364–16370
Can M, Dogan B, Saboori B (2020) Does trade matter for environmental degradation in developing countries? New evidence in the context of export product diversification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:14702–14710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08000-2
Charfeddine L, Kahia M (2019) Impact of renewable energy consumption and financial development on CO 2 emissions and economic growth in the MENA region: a panel vector autoregressive (PVAR) analysis. Renew Energy 139:198–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.010
Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhong Z (2019) CO2 emissions, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy production and foreign trade in China. Renew Energy 131:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.07.047
Doğan B, et al. (2020) The mitigating effects of economic complexity and renewable energy on carbon emissions in developed countries. Sustain Dev (September). https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2125
Dogan B, Madaleno M, Tiwari AK, Hammoudeh S (2020) Impacts of export quality on environmental degradation: does income matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13735–13772
Duro JA, Alcántara V, Padilla E (2010) International inequality in energy intensity levels and the role of product composition and energy efficiency: an analysis of OECD countries. Ecol Econ 69(12):2468–2474
Etokakpan MU et al (2020) Does globalization in Turkey induce increased energy consumption: insights into its environmental pros and cons. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(21):26125–26140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08714-3
Fang J, Gozgor G, Lu Z, Wu W (2019) Effects of the export product quality on carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from developing economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):12181–12193
Farooq TH, Xincheng X, Shakoor A, Rashid MHU, Bashir MF, Nawaz MF, Yan W (2022a) Spatial distribution of carbon dynamics and nutrient enrichment capacity in different layers and tree tissues of Castanopsis eyeri natural forest ecosystem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):10250–10262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16400-1
Farooq U, Nasir A, Bilal, Bashir MF (2022b) The COVID-19 pandemic and stock market performance of transportation and travel services firms: a cross-country study. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2022.2053784
Gök A (2020) The role of financial development on carbon emissions: a meta regression analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(11):11618–11636
Gozgor G, Can M (2016) Export product diversification and the environmental Kuznets curve: evidence from Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:21594–21603
Haddad M, Lim JJ, Pancaro C, Saborowski C (2013) Trade openness reduces growth volatility when countries are well diversified. Canadian J Econ/revue Canadienne D’économique 46(2):765–790
Hansen B & Østerhus S (2000) North atlantic–nordic seas exchanges. Prog Oceanogr 45(2):109–208
Hu G, Can M, Paramati SR, Doğan B, Fang J (2020) The effect of import product diversification on carbon emissions: new evidence for sustainable economic policies. Econ Anal Policy 65:198–210
Hussain M, Bashir MF, Shahzad U (2021) Do foreign direct investments help to bolster economic growth? New insights from Asian and Middle East economies. World J Entrep Manag Sustain Dev 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1108/WJEMSD-10-2019-0085
Ibrahim MH, Law SH (2016) Institutional quality and CO2 emission–trade relations: evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa. South African J Econ 84(2):323–340
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econom 115(1):53–74
Imbs J, Wacziarg R (2003) Stages of diversification. Am Econ Rev 93(1):63–86
Jian M, He H, Ma C et al (2019) Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: a duopoly market pricing competition and cooperation under the carbon emissions cap. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16847–16854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8767-1
Khan MK, Teng JZ, Khan MI (2019) Effect of energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan with dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):23480–23490
Khan Z, Ali M, Kirikkaleli D, Wahab S, Jiao Z (2020) The impact of technological innovation and public‐private partnership investment on sustainable environment in China: consumption‐based carbon emissions analysis. Sustain Devt 28(5):1317–1330
Kihombo S, Ahmed Z Chen S, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: what is the role of technological innovation? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(43):61235–61245
Kripfganz S, Schwarz C (2019) Estimation of linear dynamic panel data models with time-invariant regressors. J Appl Economet 34(4):526–546
Le TH, Nguyen CP, Su TD, Tran-Nam B (2020) The Kuznets curve for export diversification and income inequality: evidence from a global sample. Econ Anal Policy 65:21–39
Lei J, Lin S, Khan MR, Xie S, Sadiq M, Ali R, Bashir MF, Shahzad L, Eldin S, Amin AH (2022) Research trends of board characteristics and firms’ environmental performance: research directions and agenda. Sustainability 14(21):14296. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114296
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CSJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econom 108(1):1–24
Liu H et al (2018a) Export diversification and ecological footprint: a comparative study on EKC theory among Korea, Japan, and China. Sustainability (Switzerland), 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103657
Liu B, Ma B, Bashir MF (2018b) Mechanism design of multi-attribute reverse auction on margin bid. In 2018 4th International Conference on Education Technology, Management and Humanities Science, pp 515–520
Lorente DB, Álvarez-Herranz A (2016) Economic growth and energy regulation in the environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16478–16494
Machado G, Schaeffer R, Worrell E (2001) Energy and carbon embodied in the international trade of Brazil: an input–output approach. Ecol Econ 39(3):409–424
Mania E, Rieber A (2019) Product export diversification and sustainable economic growth in developing countries. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 51:138–151
Mao Y (2018) Does democratic transition reduce carbon intensity? Evidence from Indonesia using the synthetic control method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(20):19908–19917
Ma BJ, Ye JY, Huang YJ, Bashir MF (2020a) Research of two‐period insurance contract model with a low compensation period under adverse selection. Manag Decis Econ 41(3):293–307
Ma B, Zhou Z, Bashir MF, Huang Y (2020b) A multi-attribute reverse auction model on margin bidding. Asia-Pac J Oper Res 37(06):2050032
Ma B, Zhang Y, Qin Y, Bashir MF (2021a) Optimal insurance contract design with no-claim bonus and coverage upper bound under moral hazard. Expert Syst Appl 178:115050
Ma B, Tang Q, Qin Y, Bashir MF (2021b) Policyholder cluster divergence based differential premium in diabetes insurance. Manag Decis Econ 42(7):1793–1807
Ma B, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Lai Y, Zhou Z, Bashir MF (2022) Can controlling family involvement promote firms to fulfill environmental responsibilities?—Evidence from China. Manag Decis Econ 43(2):569–592
Mavi NK, Mavi RK (2019) Energy and environmental efficiency of OECD countries in the context of the circular economy: common weight analysis for Malmquist productivity index. J Environ Manage 247:651–661
Murshed M Dao NTT (2020) Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: the role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal (August). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9
Nasir A, Farooq U, & Bashir MF (2022). Stock returns, government response strategies, and daily new case bursts during COVID‐19: a cross‐country perspective. Int J Financ Econ 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijfe.2694
Neagu O, Teodoru MC (2019) The relationship between economic complexity, energy consumption structure, and greenhouse gas emission: heterogeneous panel evidence from the EU countries. Sustainability 11(2):497
Okoro AS, Ujunwa A, Umar F, Ukemenam A (2020) Does regional trade promote economic growth? Evidence from Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). J Econ Devt 22(1):131–147
Olander P (2019) Economic diversification and institutional quality—issues of concentrated interests. Stud Comp Int Dev 54(3):346–364
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2013) The long-run and causal analysis of energy, growth, openness and financial development on carbon emissions in Turkey. Energy Econ 36:262–267
Paramati SR et al (2018) Determinants of energy demand in African frontier market economies: an empirical investigation. Energy 148:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.146
Parteka A, Tamberi M (2013) Product diversification, relative specialisation and economic development: Import–export analysis. J Macroecon 38:121–135
Rauf A et al (2018) Structural changes, energy consumption and carbon emissions in China: empirical evidence from ARDL bound testing model. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 47:194–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2018.08.010
Sadiq M, Wen F, Bashir MF, Amin A (2022) Does nuclear energy consumption contribute to human development? Modeling the effects of public debt and trade globalization in an OECD heterogeneous panel. J Clean Prod 375:133965
Salim RA, Shafiei S (2014) Urbanization and renewable and non-renewable energy consumption in OECD countries: an empirical analysis. Econ Model 38:581–591
Sarkodie SA, Adams S (2018) Renewable energy, nuclear energy, and environmental pollution: accounting for political institutional quality in South Africa. Sci Total Environ 643:1590–1601
Shahbaz M, Gozgor G, Hammoudeh S (2019a) Human capital and export diversification as new determinants of energy demand in the United States. Energy Econ 78:335–349
Shahbaz M, Gozgor G, Adom PK, Hammoudeh S (2019b) The technical decomposition of carbon emissions and the concerns about FDI and trade openness effects in the United States. Int Econ 159:56–73
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Sadorsky P (2016) The role of globalization on the recent evolution of energy demand in India: implications for sustainable development. Energy Econ 55:52–68
Shahbaz M, Nasreen S, Ahmed K, Hammoudeh S (2017) Trade openness–carbon emissions nexus: the importance of turning points of trade openness for country panels. Energy Econ 61:221–232
Shahzad SJH, Kumar RR, Zakaria M, Hurr M (2017) Carbon emission, energy consumption, trade openness and financial development in Pakistan: a revisit. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:185–192
Shahbaz M, Bashir MF, Bashir MA, Shahzad L (2021) A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review of tourism-environmental degradation nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(41):58241–58257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14798-2
Shahzad U, Ferraz D, Doğan B, do NascimentoRebelatto DA (2020) Export product diversification and CO2 emissions: contextual evidences from developing and developed economies. J Clean Prod 276:124146
Sharma R, Shahbaz M, Kautish P, Vo XV (2021) Analyzing the impact of export diversification and technological innovation on renewable energy consumption: evidences from BRICS nations. Renew Energy 178:1034–1045
Shi X, Liu H, Riti JS (2019) The role of energy mix and financial development in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions’ reduction: evidence from ten leading CO 2 emitting countries. Economia Politica 36(3):695–729
Singhania M, Saini N (2021) Demystifying pollution haven hypothesis: role of FDI. J Bus Res 123:516–528
Steinbuks J, Neuhoff K (2014) Assessing energy price induced improvements in efficiency of capital in OECD manufacturing industries. J Environ Econ Manag 68(2):340–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2014.07.003
Sultan N, Mohamed N, Bashir MA, Bashir MF (2021) The anti‐money laundering and counter financing of terrorism policy in Pakistan: is it truly combating or just a high‐level desk work bureaucracy?. J Public Aff e2731
Talbi B, Jebli MB, Bashir MF, Shahzad U (2022) Does economic progress and electricity price induce electricity demand: a new appraisal in context of Tunisia. J Public Aff 22(1):e2379. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2379
Teng JZ, Khan MK, Khan MI, Chishti MZ, Khan MO (2021) Effect of foreign direct investment on CO2 emission with the role of globalization, institutional quality with pooled mean group panel ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5271–5282
Wang L, Chang HL, Rizvi SKA, Sari A (2020) Are eco-innovation and export diversification mutually exclusive to control carbon emissions in G-7 countries? J Environ Manage 270:110829
Wang Y, Su X, Qi L et al (2019) Feasibility of peaking carbon emissions of the power sector in China’s eight regions: decomposition, decoupling, and prediction analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:29212–29233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05909-1
Wawrzyniak D, Doryń W (2020) Does the quality of institutions modify the economic growth-carbon dioxide emissions nexus? Evidence from a group of emerging and developing countries. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja 33(1):124–144
Xia W, Apergis N, Bashir MF, Ghosh S, Doğan B, Shahzad U (2022) Investigating the role of globalization, and energy consumption for environmental externalities: empirical evidence from developed and developing economies. Renew Energy 183:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.084
Zhang YJ (2011) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: an empirical analysis in China. Energy Policy 39(4):2197–2203
Zhou W, Zhu B, Chen D, Griffy-Brown C, Ma Y, Fei W (2012) Energy consumption patterns in the process of China’s urbanization. Popul Environ 33(2–3):202–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Adnan Bashir: original draft writing.
Zhao Dengfeng: research directions and methodology.
Muhammad Farhan Bashir: analysis.
Syed Rahim: data collection.
Zhang Xi: proofreading.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This is not applicable.
Consent to participate
This is not applicable.
Consent to publish
This is not applicable.
Competing interests
We have no competing interest with any person or organization.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, M.A., Dengfeng, Z., Bashir, M.F. et al. Exploring the role of economic and institutional indicators for carbon and GHG emissions: policy-based analysis for OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 32722–32736 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24332-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24332-7