Abstract
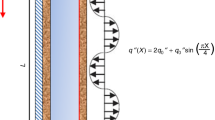
Heat transfer that occurs in micro scale devices has a very important place among the engineering applications that cooling or heating. This heat transfer mechanism in devices having dimensions at micron level is a completely different problem in the macro level analysis. Therefore, in the calculations made, the flow events and heat transfer in micron scale pipes are calculated by using more realistic expressions. For this reason, in this study heat transfer in a circular micro pipe with wall and fluid conjugation for laminar rarefied gas flow in transient regime is investigated under the second order slip boundary conditions at the interface. Patankar’s control volume method is used here to solve the problem numerically. This analysis includes of axial conduction, viscous dissipation and rarefaction effects which are indispensable in micro-flow structure. From the results, it is seen that the values that are indicating heat transfer are excessively affected by wall thickness, viscous heating and gas rarefaction especially in transient regime.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \( a \) :
-
discretization constants
- \( b \) :
-
residual term
- \( Br \) :
-
Brinkman number [\( = \frac{{\mu_{f} u_{m}^{2} }}{{k\left( {T_{1} - T_{0} } \right)}} \)]
- \( c_{p} \) :
-
specific heat [J/kgK]
- \( d \) :
-
wall thickness [m]
- \( D \) :
-
hydraulic diameter [m]
- \( k \) :
-
thermal conductivity [W/mK]
- \( Kn \) :
-
Knudsen number [=λ/D]
- \( Nu \) :
-
Nusselt Number [\( = \frac{hD}{k} \)]
- \( Pe \) :
-
Peclet number [=\( \text{Re} \Pr = \tfrac{{2r_{wi} u_{m} \rho_{f} c_{pf} }}{{k_{f} }} \)]
- \( Pr \) :
-
Prandtl number [=µcp/k]
- \( Po \) :
-
Poiseuille number
- \( q \) :
-
heat flux [W/m2]
- R :
-
radial coordinate [m]
- Re :
-
Reynolds number [=umD/ν]
- \( t \) :
-
time [s]
- \( T \) :
-
temperature [K]
- \( T_{s} \) :
-
slip fluid temperature [K]
- \( u \) :
-
axial velocity [m/s]
- \( u_{s} \) :
-
slip velocity [m/s]
- \( v \) :
-
radial velocity [m/s]
- \( x \) :
-
axial coordinate [m]
- \( \alpha \) :
-
thermal diffusivity [m2/s]
- γ :
-
specific heat ratio
- λ :
-
molecular mean free path [m]
- \( \delta r \) :
-
radial grid difference [m]
- \( \delta x \) :
-
axial grid difference [m]
- \( \kappa \) :
-
kappa [\( = \tfrac{2\gamma }{\gamma + 1}\frac{1}{\Pr } \)]
- \( \Delta r \) :
-
radial step [m]
- \( \Delta t \) :
-
time step [s]
- \( \Delta x \) :
-
axial step [m]
- \( \rho \) :
-
density [kg/m3]
- σm :
-
tangential momentum accommodation coefficient
- σT :
-
thermal accommodation coefficient
- \( \mu \) :
-
dynamic viscosity [Pa.s]
- \( b \) :
-
bulk
- \( f \) :
-
fluid
- \( i \) :
-
inner
- \( i,j \) :
-
at nodal point i, j
- \( m \) :
-
mean
- \( w \) :
-
wall
- \( ' \) :
-
dimensionless quantity
- 0 :
-
at previous time step
References
Patankar S 1980 Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kandlikar S G, Garimella S Li D, Colin S and King M R 2006 Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow in Minichannels and Microchannels. Oxford: Elsevier
Jeong H E and Jeong J T 2006 Extended graetz problem including streamwise conduction and viscous dissipation in microchannel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49(13): 2151–2157
Barletta A and Di Schio E R 2000 Periodic forced convection with axial heat conduction in a circular duct. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 43(16): 2949–2960
Çetin B, Yazicioglu A G and Kakac S 2008 Fluid flow in microtubes with axial conduction including rarefaction and viscous dissipation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 35(5): 535–544
Rosa P, Karayiannis T G and Collins M W 2009 Single-phase heat transfer in microchannels: the importance of scaling effects. Appl. Therm. Eng. 29: 3447–3468
Zhu X and Liao Q 2006 Heat transfer for laminar slip flow in a microchannel of arbitrary cross section with complex thermal boundary conditions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 26: 1246–1256
Hong C and Asako Y 2008 Heat transfer characteristics of gaseous flows in microtube with constant heat flux. Appl. Therm. Eng. 28: 1375–1385
Nam T P and Le Roohi E 2015 A new form of the second-order temperature jump boundary condition for the low-speed nanoscale and hypersonic rarefied gas flow simulations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 98: 51–59
Kushwaha H M and Sahu S K 2014 Analysis of gaseous flow in a micro pipe with second order velocity slip and temperature jump boundary conditions. Heat Mass Transfer 50: 1649–1659
Dongari N and Agrawal A 2007 Analytical solution of gaseous slip in long microchannels. Heat Mass Transfer 50: 3411–3421
Xiao N, Elsnab J and Ameel T 2009 Microtube gas flows with second order slip flow and temperature jump boundary conditions. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48: 243–251
Aubert C and Colin S 2001 High order boundary conditions for gaseous flows in rectangular microducts. Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 5: 41–54
Cercignani C and Lorenzani S 2010 Variational derivation of second order coefficients on the basis of the Boltzmann equation for hard-sphere molecules. Phys. Fluids 22: 062004
Duan Z 2012 Second-order gaseous slip flow models in long circular and noncircular microchannels and nanochannels. Micro Nanofluidics 12: 805–820
Lelea D and Cioabla A E 2010 The viscous dissipation effect on heat transfer and fluid flow in micro-tubes. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37(9): 1208–1214
Rahimi M and Mehryar R 2012 Numerical study of axial heat conduction effects on the local Nusselt number at the entrance and ending regions of a circular microchannel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 59: 87–94
Aziz A and Niedbalski N 2011 Thermally developing microtube gas flow with axial conduction and viscous dissipation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50(3): 332–340
Barron R F, Wang X, Warrington R O and Ameel T 1996 Evaluation of the eigenvalues for the Graetz problem in slip-flow. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 23(4): 563–574
Barron R F, Wang X, Ameel T A and Warrington RO 1997 The Graetz problem extended to slip-flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 40(8): 1817–1823
Kabar Y, Bessaïh R and Rebay M 2013 Conjugate heat transfer with rarefaction in parallel plates microchannel. Superlattices Microstruct. 60: 370–388
Bilir Ş 1995 Laminar flow heat transfer in pipes including two-dimensional wall and fluid axial conduction. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38(9): 1619–1625
Bilir Ş 2002 Transient conjugated heat transfer in pipes involving two-dimensional wall and axial fluid conduction. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45(8): 1781–1788
Bilir Ş and Ateş A 2003 Transient conjugated heat transfer in thick walled pipes with convective boundary conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46(14): 2701–2709
Altun A H, Bilir Ş Ateş A 2016 Transient conjugated heat transfer in thermally developing laminar flow in thick walled pipes and minipipes with time periodically varying wall temperature boundary condition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 92: 643–657
Wei-Mon Y 1993 Transient conjugated heat transfer in channel flows with convection from yhe ambient. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 36(5): 1295–1301
Lın T F and Kuo J C 1988 Transient conjugated heat transfer in fully developed laminar pipe flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 31(5): 1093–1102
Knupp D C, Naveira-Cotta C P and Cotta R M 2012 Theoretical analysis of conjugated heat transfer with a single domain formulation and integral transforms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 39: 355–362
Knupp D C, Cotta R M, Naveira-Cotta C P and Kakaç S 2015 Transient conjugated heat transfer in microchannels: Integral transforms with single domain formulation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 88:248–257
Lelea D 2007 The conjugate heat transfer of the partially heated microchannels. Heat Mass Trans. Heat Mass Transf. 44: 33–41
Şen S and Darici S 2017 Transient conjugate heat transfer in a circular microchannel involving rarefaction, viscous dissipation and axial conduction effects. App. Therm. Eng. 111:855–862
Yener Y, Kakac S, Avelino M and Okutucu T 2005 Single phase forced convection in microchannels-state-of-the-art-review. Microscale Heat Transfer-Fundamentals and Applications. The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers 1–24
Rebay M, Kakaç S and Cotta R M 2016 Microscale and Nanoscale Heat Transfer: Analysis, Design and Application. CRC Press, Boca Rataon 391–405
Karniadakis G, Beskok A and Aluru N 2006 Microflows and Nanoflows: Fundamentals and Simulation. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Bilir Ş 1992 Numerical solution of Graetz problem with axial conduction. Num. Heat Transf. 21(4): 493–500
Faghri M and Sparrow E 1980 Simultaneous wall and fluid axial conduction in laminar pipe-flow heat transfer. J. Heat Transf. 102(1): 58–63
Acknowledgements
The Authour is thankful to Selçuk University for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şen, S. Numerical investigation of the effect of second order slip flow conditions on interfacial heat transfer in micro pipes. Sādhanā 44, 159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-019-1137-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-019-1137-6