Abstract
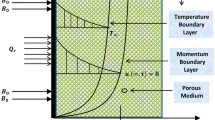
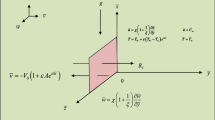
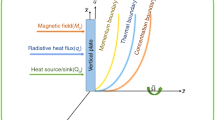
In the present era of research, entropy generation is one of the most important topics, which is used to control the irreversibility phenomena during heat transfer. Due to the important application in engineering, atomic reactors and cooling process in different fields, this work aims to study the second law analysis of Casson fluid. Vertical plate geometry was considered, where the plate at the boundary exhibits arbitrary wall shear stress and the fluid lies above the plate. Exponential type heating was produced at the bounding plate whereas natural convection is caused because of buoyancy force. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) analysis was also considered perpendicular to the plate. The usual Darcy’s law of Newtonian fluid was modified to Darcy’s law for Casson fluid. The exact analysis was performed using the Laplace transform technique to establish exact solutions for the velocity field and temperature distribution. Results are interpreted physically using various plots and discussed in detail.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Saqib, I Khan and S Shafie, J. Magn. Magn. 484, 490 (2019)
K Bashirnezhad et al, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 73, 114 (2016)
K A Abro, A D Chandio, I A Abro and I Khan, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135(4), 2197 (2019)
V Rajesh, Ann. Fac. Eng. Hunedoara – Int. J. Eng. 8, 426 (2010)
W R Schowalter, AIChE J. 6(1), 24 (1960)
M A Imran, S Sarwar and M Imran, Bound. Value Probl. 2016(1), 1 (2016)
Y Li, S Tung, E Schneider and S Xi, Powder Technol. 196(2), 89 (2009)
J H Lee, S H Lee, C Choi, S Jang and S Choi, Int. J. Micro-nano Scale Tran. 1, (2011)
A Ghadimi, R Saidur and H S C Metselaar, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54, 4051 (2011)
G Ramesh and N K Prabhu, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6(1), 334 (2011)
K Khanafer and K Vafai, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54(19), 4410 (2011)
J Fan and L Wang, J. Heat Transf. 133(4), (2011)
R S Vajjha and D K Das, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55(15), 4063 (2012)
M Sheikholeslami and R Ellahi, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 89, 799 (2015)
W A Khan and I Pop, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53(11–12), 2477 (2010)
F Mebarek-Oudina, Heat Transf. Asian Res. 48(1), 135 (2019)
J Raza, F Mebarek-Oudina and A J Chamkha, Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 15, 737 (2019)
S Pramanik, Ain Shams Eng. J. 5(1), 205 (2014)
N A Sheikh, D L C Ching, I Khan, D Kumar and K S Nisar, AEJ 59(5), 2865 (2020)
S Aman, I Khan, Z Ismail, M Z Salleh and I Tlili, Results Phys. 9, 1352 (2018)
A Bejan, Entropy generation minimization: the method of thermodynamic optimization of finite-size systems and finite-time processes (CRC Press, 2013)
A Bejan, Int. J. Energy Res. 26(7), 545 (2002)
A S Butt and A Ali, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 128(5), 51 (2013)
A Khan, F UlKarim, I Khan, F Ali and D Khan, Results Phys. 8, 1283 (2018)
N S Gibanov, M A Sheremet, H F Oztop and K Al-Salem, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 193 (2018)
M Saqib, F Ali, I Khan, N A Sheikh and A Khan, Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(1), 531 (2019)
R Ellahi, S Z Alamri, A Basit and A Majeed, J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 12(4), 476 (2018)
M Maskaniyan, M Nazari, S Rashidi and O Mahian, Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 6, 186 (2018)
M I Afridi, M Qasim and O D Makinde, J. Heat Transf. 141(2), 1 (2019)
W A Azhar, D Vieru and C Fetecau, Heat Transf. Res. 49(15), 1507 (2018)
A Z Şahin, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 19(3), 349 (1992)
A L Lare, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2(2), 63 (2015)
Y T Zuo, Therm. Sci. 25, 2405 (2021)
Y-T Zuo and H-J Liu, Facta. Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 19, 271 (2021)
Y Mei, Y Q Liu and J H He, Therm. Sci. 25, 4817 (2021)
J H He, G M Moatimid and D R Mostapha, J. Electroanal. Chem. 895, 115 (2021)
J H Tian and K Jiang, Numer. Heat Transf. A 72(2), 141 (2017)
A Kumar, J V Ramana Reddy, V Sugunamma and N Sandeep, Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 14, 999 (2018)
B Mahanthesh, N S Shashikumar, B J Gireesha and I L Animasaun, J. Comput. Des. Eng. 6(4), 551 (2019)
M Saqib, I Khan, Y M Chu, A Qushairi, S Shafie and K S Nisar, Appl. Sci. 10(11), 3886 (2020)
M Saqib, A R M Kasim, N F Mohammad, D L C Ching and S Shafie, Symmetry 12(5), 768 (2020)
M Saqib, H Hanif, T Abdeljawad, I Khan, S Shafie and K S Nisar, Comput. Mater. Contin, 65(3), 1959 (2020)
M Saqib, I Khan and S Shafie, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 484, 490 (2019)
M Saqib, S Shafie, I Khan, Y M Chu and K S Nisar, Symmetry 12(4), 663 (2020)
A M Megahed, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130(4), 1 (2015)
M Atlas, S Hussain and M Sagheer, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134(1), 33 (2019)
E K Ghiasi and R Saleh, Pramana – J. Phys. 92, 12 (2019)
A Hiremath, H Basha, B Kethireddy, G J Reddy and N V Narayanan, Pramana – J. Phys. 93, 20 (2019)
M Qasim and S Noreen, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129(1), 1 (2014)
M Saleem, M N Tufail and Q A Chaudhry, Pramana – J. Phys. 95, 28 (2021)
A Hussanan, M Z Salleh, I Khan and R M Tahar, J. Nanofluids 6(4), 784 (2017)
J H Merkin, J. Eng. Math. 19(3), 189 (1985)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Center of Excellence in Theoretical and Computational Science (TaCS-CoE), KMUTT. This research project is supported by Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI) Basic Research Fund: Fiscal year 2022 under project number FRB650048/0164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, D., Kumam, P., Watthayu, W. et al. Mathematical analysis of second law on Casson fluid through a vertical plate with arbitrary shear stress and exponential heating. Pramana - J Phys 96, 106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-022-02343-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-022-02343-w
Keywords
- Entropy generation
- Bejan number
- Casson fluid
- shear stress
- magnetohydrodynamics
- Darcy’s resistance
- heat transfer