Abstract
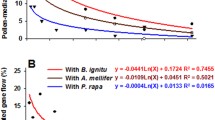
Pollen mediated gene flow is the most widely debated biosafety issue in case of genetically modified crop plants and is a primary determining factor for permitting their field release, particularly major food crops like rice. The alleged consequences of gene escape into wild/weedy relatives that coexist together with cultivated forms in rice fields in several countries is perceived to be a major concern. In an effort to estimate the gene flow in rice in a tropical environment, rice varieties stacked with three bacterial blight (BB) resistance alleles and a cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line were used as donors and receiver of pollen respectively and the pollen flow was tracked with molecular markers that are closely linked to BB resistance genes. The study could detect gene flow up to 20 m distance with environmental factors like temperature and humidity influencing it. The gene flow observed at longer distances than the 10 m distance suggested earlier advocate caution and suggests that all the relevant biosafety issues need to be addressed prior to release of GM rice in tropical countries where sympatric association of wild relatives with cultivated rice with frequent crop-weedy gene flow both ways is quite common.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B (1990) Inbreeding depression with heterozygote advantage and its effect on selection for modifiers changing the out crossing rate. Evolution 44:870–888
Dillon TL, Baldwin FL, Talbert RE, Estorninos LE, Gealy DR (2002) Gene flow from Clearfield rice to red rice. Weed Sci Soc Am 42:124, Abstracts
Directorate of Rice Research (2012) Draft Proceedings-47th Annual Rice Research Group Meetings AICRIP, DRR, Hyderabad, India pp. Xlvi (Appendix12) (http://www.drricar.org/AICRIP/Draft%Proceedings.pdf).
Eleftherohorinos IG, Dhima KV, Vasilakoglou IB (2002) Interference of red rice in rice grown in Greece. Weed Science 50:167–172
Ellstrand NC, Elam DR (1993) Population genetic consequences of small population-size-implications for plant conservation. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 24:217–242
Ellstrand NC, Schierenbeck KA (2000) Hybridization as a stimulus for the evolution of invasiveness in plants? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:7043–7050
Endo T, Sato H, Yamaguchi M, Kataoka T, Nakagomi K, Ito T, Mori K (2009) Estimate of out crossing rates in a rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) under field conditions using a purple grain rice cultivar, Okunomurasaki. Breed Sci 59:195–202
Gealy DR, Estorninos LE, Dillon TL, Baldwin FL, Te Beest DO, Tai TH (2002) Using micro satellite markers to confirm hybridization between rice and red rice. Weed Sci Soc Am 2002:42,139, Abstracts
Hoff BJ, De La Torre M (1981) Stigma exertion in rice and its effect on the seed set of male sterile plants pp 240–243 In 73rd annual progress report of the Rice Experiment Station. Crowley, Louisiana
International Rice Research Institute (2007) Crop Stat 7.2. http://www.irri.org
Jackson ST, Lyford ME (1999) Pollen dispersal models in quaternary plant ecology: assumptions, parameters, and prescriptions. Bot Rev 65:39–75
James C (2007) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops. ISAAA brief no. 37, International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-Biotech Applications, Ithaca NY, USA
Khush GS (1993) Floral structure, pollination biology, breeding behavior, transfer distance and isolation considerations. World Bank Technical Paper. Biotechnology Series No. 1. Rice Bio safety. The Rockefeller Foundation, USA
Kiang YT, Antonvics J, Wu L (1979) The extinction of wild rice (Oryza perennis formosa) in Taiwan. J Asian Ecol 1:1–9
Kwon SL, Smith RJ, Talbert RE (1991) Interference durations of red rice (Oryza sativa) in rice (Oryza sativa). Weed Sci 39:363–368
Langevin SA, Clay K, Grace JB (1990) The incidence and effects of hybridization between cultivated rice and its related weed red rice (O. sativa L.). Evolution 44:1000–1008
Majumder ND, Ram T, Sharma AC (1997) Cytological and morphological variation in hybrid swarms and introgressed population of interspecific hybrids (Oryza rufipogon Griff. X Oryza sativa L.) and its impact on evolution of intermediate types. Euphytica 94:295–302
Messeguer J, Fogher C, Guiderdoni E, Marfà V, Català MM, Baldi G, Melé E (2001) Field assessments of gene flow from transgenic to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a herbicide resistance gene as tracer marker. Theor Appl Genet 103:1151–1159
Mortimer M, Pandey S, Piggin C (2000) Weedy rice: approaches to ecological appraisal and implications for research priorities. In: Baki BB, Chin DV, Mortimer M (eds) Wild and weedy rice in rice ecosystems in Asia- a review. Limited proceedings no. 2, International Rice Research Institute, Philippines, pp 97–105
Murray MG, Thompson WK (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Oka HI (1988) Origin of cultivated rice. Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo
Oka HI, Morishima H (1967) Variations in the breeding system of wild rice Oryza perennis. Evolution 21:249–258
Osada A, Nara M, Chakrabandhu H, Rahong M, Gesprasert M (1973) Seasonal changes in growth pattern of tropical rice. II. Environmental factors affecting yield and its components. Proc Crop Sci Soc Jpn 42:351–361
Ronald PC, Albato B, Tabien R, Abenes MLP, Wu KS, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1992) Genetic and physical analysis of the rice bacterial blight disease resistance locus Xa 21. Mol Gen Genet 236:113–120
Rong J, Song Z, Su J, Xia H, Lu BR, Wang F (2005) Low frequency of transgene flow from Bt/CpTIrice to its non-transgenic counterparts planted at close spacing. New Phytol 168:559–566
Rong J, Lu BR, Song Z, Snow AA, Zhang X, Sun S, Chen R, Wang F (2006) Dramatic reduction of crop-to-crop gene flow within a short distance from transgenic rice fields. New Phytol 173:346–353
Sakai KI, Narise T (1959) Studies on the breeding behavior’ of a wild rice (Oryza rufipogon and Oryza perennis). Inst Genet Jpn 9:64–65
Sarkar HC, Miah NM (1983) Local indica rice varieties with desirable floral traits influencing out crossing. Int Rice Res Newsl 8(5):3
Shivrain VK, Burgos NR, Sales MA, Mauromoustakos A, Gealy DR, Smith KL, Black HL, Jia M (2009) Factors affecting the outcrossing rate between ClearfieldTM Rice and Red Rice (Oryza sativa). Weed Sci 57:394–403
Siddiq EA, Ilyas Ahmed M, Viraktamath BC, Rangaswamy M, Vijaya Kumar R, Vidyachandra B, Zaman FU, Chatterjee SD (1998) Hybrid rice technology in India: Current status and future outlook. In: Virmani SS, Siddiq EA, Muralidharan K (eds) Advances in hybrid rice technology. Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, 14–16 Nov 1996 Hyderabad. International Rice Research Institute, Philippines, pp 311–324
Singh AK et al (2011). Marker assisted selection: a paradigm shift in Basmati breeding. Indian J Genet Plant Breed, 71, Special Issue, 1–9
Song ZP, Lu BR, Chen JK (2001) A study of pollen viability and longevity in Oryza rufipogon, O.sativa and their hybrid. Int Rice Res Notes 26:31–2
Song ZP, Lu BR, Chen JK (2004) Pollen flow of cultivated rice measured under experimental conditions. Biodivers Conserv 13:579–590
Vaughan DA (1994) The wild relatives of rice: a genetic resources guide book. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
Walklate PJ, Hunt JCR, Higson HL, Sweet JB (2004) A model of pollen-mediated gene flow for oilseed rape. Proc R Soc London, Ser B 271:441–449
Yoshimura S, Yoshimura A, Iwata N, McCouch SR, Abenes ML, Baraoidan MR, Mew TW, Nelson RJ (1995) Tagging and combining bacterial blight resistance genes in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers. Mol Breed 1:375–387
Zhang G, Angeles ER, Abenes MLP, Huang N, Khush GS (1996) RAPD and RFLP mapping of the bacterial blight resistance gene xa-13 in rice. Theor Appl Genet 93:65–70
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly grateful to the Director, Central Rice Research Institute, Cuttack for providing all the necessary facilities. The authors also express their sincere thanks to Dr. R. Sridhar for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Graham Bonnett
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, G.J.N., Swain, D., Mishra, R. et al. Marker Based Estimation of Gene Flow in Tropical Rice Fields and Its Ecological Consequences. Tropical Plant Biol. 5, 277–285 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-012-9110-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-012-9110-0