Abstract
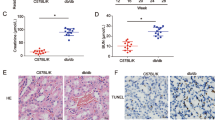
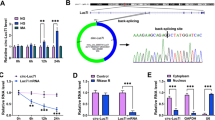
Diabetic nephropathy (DN), a common cause of chronic renal failure and end-stage renal disease, leads to a high mortality. However, the role of TTN-AS1 in extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation during DN remains unclear. In our study, TTN-AS1 exhibited high expression in high glucose-treated mesangial cells, and TTN-AS1 silencing alleviated high glucose-induced ECM accumulation in mesangial cells. Additionally, animal study revealed that TTN-AS1 was upregulated in renal tissues of DN rats, and TTN-AS1 knockdown mitigated renal injury of DN rats. Mechanistically, TTN-AS1 was validated to bind to miR-493-3p, and miR-493-3p targeted forkhead box P2 (FOXP2) 3′untranslated region in mesangial cells. TTN-AS1 interacted with miR-493-3p to upregulate FOXP2 in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, FOXP2 overexpression counteracted the effects of TTN-AS1 silencing on the ECM accumulation. In conclusion, TTN-AS1 exacerbated ECM accumulation via the miR‐493-3p/FOXP2 axis during DN development. This research may provide a potential new direction for DN treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams B. D., Parsons C., Walker L., Zhang W. C. and Slack F. J. 2017 Targeting noncoding RNAs in disease. J Clin Invest. 127, 761–771.
Alvarez M. L. and Distefano J. K. 2013 The role of non-coding RNAs in diabetic nephropathy: potential applications as biomarkers for disease development and progression. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 99, 1–11.
Boon R. A., Jaé N., Holdt L. and Dimmeler S. 2016 Long noncoding RNAs: from clinical genetics to therapeutic targets? J Am Coll Cardiol. 67, 1214–1226.
Choudhury D., Tuncel M. and Levi M. 2010 Diabetic nephropathy: a multifaceted target of new therapies. Discov Med. 10, 406–415.
Dashti S., Taherian-Esfahani Z., Kholghi-Oskooei V., Noroozi R., Arsang-Jang S., Ghafouri-Fard S. et al. 2020 In silico identification of MAPK14-related lncRNAs and assessment of their expression in breast cancer samples. Sci Rep. 10, 8316.
Duan L. J., Ding M., Hou L. J., Cui Y. T., Li C. J. and Yu D. M. 2017 Long noncoding RNA TUG1 alleviates extracellular matrix accumulation via mediating microRNA-377 targeting of PPARγ in diabetic nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 484, 598–604.
Gao B. H., Wu H., Wang X., Ji L. L. and Chen C. 2020 MiR-30c-5p inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by down-regulation of JAK1 in diabetic nephropathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24, 1338–1349.
Gu Z. F., Zhang Z. T., Wang J. Y. and Xu B. B. 2017 Icariin exerts inhibitory effects on the growth and metastasis of KYSE70 human esophageal carcinoma cells via PI3K/AKT and STAT3 pathways. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 54, 7–13.
Huang H., Ni H., Ma K. and Zou J. 2019 ANGPTL2 regulates autophagy through the MEK/ERK/Nrf-1 pathway and affects the progression of renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Transl Res. 11, 5472–5486.
Ji T. T., Wang Y. K., Zhu Y. C., Gao C. P., Li X. Y., Li J. et al. 2019 Long noncoding RNA Gm6135 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate toll-like receptor 4 expression by sponging miR-203-3p in diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Physiol. 234, 6633–6641.
Jia L., Chopp M., Wang L., Lu X., Zhang Y., Szalad A. et al. 2018 MiR-34a regulates axonal growth of dorsal root ganglia neurons by targeting FOXP2 and VAT1 in postnatal and adult mouse. Mol Neurobiol. 55, 9089–9099.
Katoh M. and Katoh M. 2004 Human FOX gene family (Review). Int J Oncol. 25, 1495–1500.
Kopp F. and Mendell J. T. 2018 Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 172, 393–407.
Liu Y., Sun J., Ma X., Li S., Ai M., Xu F. et al. 2020 Vaccarin Regulates Diabetic Chronic Wound Healing through FOXP2/AGGF1 Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21.
Livak K. J. and Schmittgen T. D. 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25, 402–408.
Loganathan T. S., Sulaiman S. A., Abdul Murad N. A., Shah S. A., Abdul Gafor A. H., Jamal R. et al. 2020 Interactions among non-coding RNAs in diabetic nephropathy. Front Pharmacol. 11,191.
Lucas T., Bonauer A. and Dimmeler S. 2018 RNA therapeutics in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 123, 205–220.
Matboli M., Kamel M. M., Essawy N., Bekhit M. M., Abdulrahman B., Mohamed G. F. et al. 2021 Identification of novel insulin resistance related ceRNA network in T2DM and its potential editing by CRISPR/Cas9. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22.
Miyashita A., Kobayashi M., Ishibashi S., Nagata T., Chandrasekhar A., Zochodne D. W. et al. 2022 The role of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in diabetic polyneuropathy and the impact of its silencing in the dorsal root ganglion by a DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide. Diabetes. 71, 1299–1312.
Oh H. J., Kato M., Deshpande S., Zhang E., Das S., Lanting L. et al. 2016 Inhibition of the processing of miR-25 by HIPK2-phosphorylated-MeCP2 induces NOX4 in early diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep. 6, 38789.
Pan Y., Wu Y., Hu J., Shan Y., Ma J., Ma H. et al. 2018 Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes renal cell carcinoma malignancy through alpha-2, 8-sialyltransferase 4 by sponging microRNA-124. Cell Prolif. 51, e12507.
Pasupulati A. K. and Paturi A. S. V. 2022 The sponging effect of a lncRNA on a miRNA contributes to diabetic nephropathy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 28, 259–260.
Putta S., Lanting L., Sun G., Lawson G., Kato M. and Natarajan R. 2012 Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23, 458–469.
Rivera-Barahona A., Pérez B., Richard E. and Desviat L. R. 2017 Role of miRNAs in human disease and inborn errors of metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 40, 471–480.
Roux M., Perret C., Feigerlova E., Mohand Oumoussa B., Saulnier P. J., Proust C. et al. 2018 Plasma levels of hsa-miR-152-3p are associated with diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 33, 2201–2207.
Rupaimoole R. and Slack F. J. 2017 MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16, 203–222.
Sadeghi M., Bahrami A., Hasankhani A., Kioumarsi H., Nouralizadeh R., Abdulkareem S. A. et al. 2022 lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network involved in sheep prolificacy: an integrated approach. Genes (Basel). 13.
Sehgal P., Mathew S., Sivadas A., Ray A., Tanwar J., Vishwakarma S. et al. 2021 LncRNA VEAL2 regulates PRKCB2 to modulate endothelial permeability in diabetic retinopathy. Embo J. 40, e107134.
Shen J., Zhang J., Jiang X., Wang H. and Pan G. 2018 LncRNA HOX transcript antisense RNA accelerated kidney injury induced by urine-derived sepsis through the miR-22/high mobility group box 1 pathway. Life Sci. 210, 185–191.
Srivastava S. P., Goodwin J. E., Tripathi P., Kanasaki K. and Koya D. 2021 Interactions among long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs influence disease phenotype in diabetes and diabetic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22.
Su K., Yi B., Yao B. Q., Xia T., Yang Y. F., Zhang Z. H. et al. 2020 Liraglutide attenuates renal tubular ectopic lipid deposition in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting lipid synthesis and promoting lipolysis. Pharmacol Res. 156, 104778.
Sutariya B., Jhonsa D. and Saraf M. N. 2016 TGF-β: the connecting link between nephropathy and fibrosis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 38, 39–49.
Tian C., Yang Y., Ke Y., Yang L., Zhong L., Wang Z. et al. 2021 Integrative analyses of genes associated with right ventricular cardiomyopathy induced by tricuspid regurgitation. Front Genet. 12, 708275.
Tian Y., Lv G., Yang Y., Zhang Y., Yu R., Zhu J. et al. 2014 Effects of vitamin D on renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy model rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7, 3028–3037.
Tsai S. F., Hsieh C. C., Wu M. J., Chen C. H., Lin T. H. and Hsieh M. 2016 Novel findings of secreted cyclophilin A in diabetic nephropathy and its association with renal protection of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor. Clin Chim Acta. 463, 181–192.
Visavadiya N. P., Li Y. and Wang S. 2011 High glucose upregulates upstream stimulatory factor 2 in human renal proximal tubular cells through angiotensin II-dependent activation of CREB. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 117, e62-70.
Wang X., Xu Y., Zhu Y. C., Wang Y. K., Li J., Li X. Y. et al. 2019 LncRNA NEAT1 promotes extracellular matrix accumulation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-27b-3p and ZEB1 in diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Physiol. 234, 12926–12933.
Wu X. Y., Yu J. and Tian H. M. 2019 Effect of SOCS1 on diabetic renal injury through regulating TLR signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23, 8068–8074.
Yang J., Shen Y., Yang X., Long Y., Chen S., Lin X. et al. 2019 Silencing of long noncoding RNA XIST protects against renal interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via microRNA-93-5p-mediated inhibition of CDKN1A. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 317, F1350-f1358.
Yu Y., Jia Y. Y., Wang M., Mu L. and Li H. J. 2021 PTGER3 and MMP-2 play potential roles in diabetic nephropathy via competing endogenous RNA mechanisms. BMC Nephrol. 22, 27.
Zha F., Qu X., Tang B., Li J., Wang Y., Zheng P. et al. 2019 Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes fibrosis and inflammatory response in diabetic nephropathy via miR-181a/Egr-1/TLR4 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 11, 3716–3730.
Zhou H., Qiu Z. Z., Yu Z. H., Gao L., He J. M., Zhang Z. W. et al. 2019 Paeonol reverses promoting effect of the HOTAIR/miR-124/Notch1 axis on renal interstitial fibrosis in a rat model. J Cell Physiol. 234, 14351–14363.
Zhou X., Zhang W., Jin M., Chen J., Xu W. and Kong X. 2017 lncRNA MIAT functions as a competing endogenous RNA to upregulate DAPK2 by sponging miR-22-3p in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 8, e2929.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Upendra Nongthomba
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, L., Wang, W., Liu, H. et al. LncRNA TTN-AS1 exacerbates extracellular matrix accumulation via miR-493-3p/FOXP2 axis in diabetic nephropathy. J Genet 102, 11 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-022-01397-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-022-01397-4