Abstract
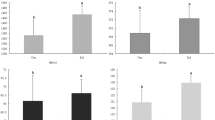
The preproinsulin gene encodes a precursor protein of insulin, which is the most important hormone for lowering blood glucose levels and promoting the synthesis of glycogen, fat and protein. To explore the correlation between polymorphisms in the preproinsulin gene and growth traits in grass carp, the preproinsulin gene sequence, measuring a total of 5708 bp, was identified in the grass carp genome. The sequence includes a promoter, two introns and three exons, and encodes a 108-aa protein. A total of three SNPs were identified, including SNP1 (g.-2661C > G) in the promoter and SNP2 (g.1305G > C) and SNP3 (g.1682G > A) in intron 2. The correlation between SNPs and growth traits in grass carp was analysed by a general linear model (GLM). The results indicated that no genotype in each single SNP, SNP1 with SNP2, or SNP1 with SNP3 was related to rapid growth and low fatness, respectively. While eight genotypes of SNP1, SNP2 and SNP3 were combined into six types of effective diplotypes, the H5 diplotype was significantly superior to the other diplotypes (P < 0.05) concerning body weight, body length, body height and body width, and its fatness was lower than those of the other diplotypes, except for H6 diplotype. This result indicated that the H5 diplotype of the preproinsulin gene in grass carp may be a candidate molecular marker for selecting fast-growing and low-fatness grass carp.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachl J., Olsson C., Chitkara N. and Wabl M. 1998 The Ig mutator is dependent on the presence, position, and orientation of the large intron enhancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2396–2399.
Caruso M. A. and Sheridan M. A. 2011 New insights into the signaling system and function of insulin in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocr. 173, 227–247.
Chang X., Joergensen A. M., Bardrum P. and Led J. J. 1997 Solution structures of the R6 human insulin hexamer. Biochemistry 36, 9409–9422.
Clarke W. L., Vance M. L. and Rogol A. D. 1993 Growth and the child with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 16, 101–106.
Conlon J. M., Fan H. and Fritzsch B. 1998 Purification and structural characterization of insulin and glucagon from the bichir polypterus senegalis (Actinopterygii: Polypteriformes). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 109, 86–93.
Darriba D., Taboada G. L., Doallo R. and Posada D. 2011 ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 27, 1164–1165.
De Pablo F. and De La Rosa E. J. 1995 The developing CNS: a scenario for the action of proinsulin, insulin and insulin-like growth factors. Trends. Neurosci. 18, 143–150.
Dong J., Chen Z., Sun C., Tian Y., Hu J., Lu M. et al. 2019 Cloning, SNP detection, and growth correlation analysis of the 5′ flanking regions of two myosin heavy chain-7 genes in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 228, 10–16.
Duan C. and Hirano T. 1992 Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin on the in-vitro uptake of sulphate by Eel Branchial Cartilage: evidence for the presence of independent hepatic and pancreatic sulphation factors. J. Endocrinol. 133, 211–219.
Enes P., Sanchez-Gurmaches J., Navarro I., Gutiérrez J. and Oliva-Teles A. 2010 Role of insulin and IGF-I on the regulation of glucose metabolism in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed with different dietary carbohydrate levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 157, 346–353.
Fishery Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture. 2020 China fishery statistics yearbook 2019, p. 25. China Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Hahn V., Winkler J., Rapoport T. A., Liebscher D. H., Coutelle C. and Rosenthal S. 1983 Carp preproinsulin cDNA sequence and evolution of insulin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 4541–4552.
Kim K. S., Larsen N., Short T., Plastow G. and Rothschild M. F. 2000 A missense variant of the porcine melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) gene is associated with fatness, growth, and feed intake traits. Mamm. Cenome. 11, 12–16.
Kong X. J., Liu X. L., Wu Y. and Wang J. 2008 Genetic variance of duck preproinsulin gene and its correlations to the traits of carcasses. Hereditas (Beijing) 30, 760–764 (in Chinese).
Li S. F. 1998 Genetic characterization of major freshwater culture fishes in China, pp. 91–96. Shanghai Scientifific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai (in Chinese).
Li X., Bai J., Hu Y., Ye X., Li S. and Yu L. 2012 Genotypes, haplotypes and diplotypes of IGF-II SNPs and their association with growth traits in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Mol. Biol. Rep. 39, 4359–4365.
Ma D. M., Han L. Q., Bai J. J., Li S. J., Fan J. J., Yu L. Y. et al. 2014 A 66-bp deletion in growth hormone releasing hormone gene 5´-flanking region with largemouth bass recessive embryonic lethal. Anim. Genet. 45, 421–426.
Montserrat N., Gabillard J. C., Capilla E., Navarro M. I. and Gutiérrez J. 2007 Role of insulin, insulin-like growth factors, and muscle regulatory factors in the compensatory growth of the trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Gen. Comp. Endocr. 150, 462–472.
Moon T. W. 2001 Glucose intolerance in teleost fish: fact or fiction? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 129, 243–249.
Nott A., Meislin S. H. and Moore M. J. 2003 A quantitative analysis of intron effects on mammalian gene expression. RNA 9, 607–617.
Oscarson M., Hidestrand M., Johansson I. and Ingelman-Sundberg M. 1997 A combination of mutations in the cyp2d6*17 (cyp2d6z) allele causes alterations in enzyme function. Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 1034–1040.
Pagani F. and Baralle F. E. 2004 Genomic variants in exons and introns: identifying the splicing spoilers. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 389–396.
Polakof S., Panserat S., Soengas J. L. and Moon T. W. 2012 Glucose metabolism in fish: a review. J. Comp. Physiol. B. 182, 1015–1045.
Shi M. and Feng Y. M. 1997 The growth promoting effects of insulin. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 24, 215–219.
Simon J., Laurent S., Grolleau G., Thoraval P., Soubieux D. and Rasschaert D. 2004 Evolution of preproinsulin gene in birds. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 30, 755–766.
Steiner D. F. 1977 Insulin today. Diabetes 26, 322–340.
Steiner D. F., Cunningham D., Spigelman L. and Aten B. 1967 Insulin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Science 157, 697–700.
Steiner D. F., Chan S. J., Welsh J. M. and Kwok S. C. M. 1985 Structure and evolution of the insulin gene. Ann. Rev. Genet. 19, 463–484.
Stephens M., Smith N. J. and Donnelly P. 2001 A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68, 978–989.
Støy J., Edghill E. L., Flanagan S. E., Ye H., Paz V. P., Pluzhnikov A. et al. 2007 Insulin gene mutations as a cause of permanent neonatal diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 15040–15044.
Støy J., Steiner D. F., Park S., Ye H., Philipson L. H. and Bell G. I. 2010 Clinical and molecular genetics of neonatal diabetes due to mutations in the insulin gene. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 11, 205–215.
Straus D. S. 1984 Growth-stimulatory actions of insulin in vitro and in vivo. Endocr. Rev. 5, 356–369.
Sun C. F., Sun H. L., Dong J. J., Tian Y. Y. and Ye X. 2019 Correlation analysis of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) growth hormone gene polymorphisms and growth traits. J. Genet. 98, 58.
Tamura K., Dudley J., Nei M. and Kumar S. 2007 MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599.
Thompson J. D., Gibson T. J., Plewniak F., Jeanmougin F. and Higgins D. G. 1997 The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4876–4882.
Tsai H. Y., Hamilton A., Guy D. R. and Houston R. D. 2014 Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) gene are associated with growth-related traits in farmed Atlantic salmon. Anim. Genet. 45, 709–715.
Wang Y., Lu Y., Zhang Y., Ning Z., Li Y., Zhao Q. et al. 2015 The draft genome of the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) provides insights into its evolution and vegetarian adaptation. Nat. Genet. 47, 625–631.
Wilson R. P. 1994 Utilization of dietary carbohydrate by fish. Aquaculture 124, 67–80.
Xu Y., Peng G., Sun M., Li J., Yan W., Tang J. et al. 2019 Genomic organization of the molt-inhibiting hormone gene in the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii and characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with growth. Comput. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 237, 1–8.
Yu L. Y., Bai J. J., Fan J. J., Ma D. M., Quan Y. C. and Jiang P. 2015 Transcriptome analysis of the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) using 454 pyrosequencing methodology for gene and marker discovery. Genet. Mol. Res. 14, 19249–19263.
Zhou S. X., Xie J. M., Sun X. and Lu Z. H. 2003 Comparison and analysis of insulin sequences and their coded mRNA and DNA among different species. J. Southeast Univ. 33, 292–295 (in Chinese).
Zhu W. Q., Chen W. F., Song W. T., Song C., Hu Y., Li H. F. et al. 2014 Study on single nucleotide polymorphism of preproinsulin gene in duck. Anim. Hus. Vet. Med. 46, 40–42 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31902365). We thank the Foshan Sanshui Baijin Aquatic Varieties Limited Company in Guangdong Province of China for assistance with grass carp sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Punyasloke Bhadury
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, J., Ma, D., Zhu, H. et al. Gene structure, SNP screening and growth correlation analysis of the preproinsulin gene in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). J Genet 100, 48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01289-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01289-z