Abstract
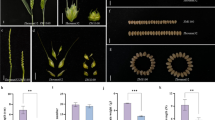
The multifoliate pinna (mfp) mutation alters the leaf-blade architecture of pea, such that simple tendril pinnae of distal domain are replaced by compound pinna blades of tendrilled leaflets in mfp homozygotes. The MFP locus was mapped with reference to DNA markers using F2 and F2:5 RIL as mapping populations. Among 205 RAPD, 27 ISSR and 35 SSR markers that demonstrated polymorphism between the parents of mapping populations, three RAPD markers were found linked to the MFP locus by bulk segregant analyses on mfp/mfp and MFP/MFP bulks assembled from the F2:5 population. The segregational analysis of mfp and 267 DNA markers on 96 F2 plants allowed placement of 26 DNA markers with reference to MFP on a linkage group. The existence of common markers on reference genetic maps and MFP linkage group developed here showed that MFP is located on linkage group IV of the consensus genetic map of pea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubert G., Morin J., Jacquin F., Loridon K., Quillet M. C., Petit A. et al. 2006 Functional mapping in pea, as an aid to the candidate gene selection and for investigating synteny with the model legume Medicago truncatula. Theor. Appl. Genet. 112, 1024–1041.
Blixt S. 1972 Mutation genetics in Pisum. Agri. Hort. Genet. 30, 1–293.
Champagne C. E. M., Goliber T. E., Wojciechowski M. F., Mei R. W., Townsley B. T., Wang K. et al. 2007 Compound leaf development and evolution in the legumes. Plant Cell 19, 3369–3378.
de Vilmorin P. and Bateson W. 1911 A case of gametic coupling in Pisum. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B. 84, 9–11.
Dirlewanger F., Issac P. G., Ranade S., Belajouza M., Cousin R. D. E. and Vienne D. 1994 Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of loci associated with disease resistance genes and developmental traits in Pisum sativum L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 88, 17–27.
Doyle J. J. and Doyle J. L. 1990 Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12, 13–15.
Ellis T. H. N. and Poyser S. J. 2002 An integrated and comparative view of pea genetic and cytogenetic maps. New Phytol. 153, 17–25.
Ellis T. H. N., Turner L., Helleus R. P., Lee D., Harker C. L., Enard C. et al. 1992 Linkage maps in pea. Genetics 130, 649–663.
Eujayl I., Sledge M. K., Wang L., May G. D., Chekhoyskiy K., Zwonitzer J. C. and Mian M. A. R. 2004 Medicago truncatula EST-SSRs reveal cross-species genetic markers for Medicago spp. Theor. Appl. Genet. 108, 414–422.
Gilpin B. J., Mccallum J. A., Frew T. J. and Timmerman-Vaughn G. M. 1997 A linkage map of pea (Pisum sativum L.) genome containing cloned sequences of known function and expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Theor. Appl. Genet. 95, 1289–1299.
Goldenberg J. B. 1965 afila, a new mutation in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Bol. Genet. 1, 27–31.
Gourlay C. W., Hofer J. M. I. and Ellis T. H. N. 2000 Pea compound leaf architecture is regulated by interactions among the genes UNIFOLIATA, COCHLEATA, AFILA and TENDRILLESS. Plant Cell 12, 1279–1294.
Gutierrez M. U., Vazpatto M. C., Huguet T., Cubero J. J., Moreno M. T. and Torres A.M. 2005 Cross-species amplification of Medicago truncatula microsatellites across three major pulse crops. Theor. Appl. Genet. 110, 1210–1217.
Hake S., Smith H. M. S., Holtan H., Magnani E., Mele G. and Ramirez J. 2004 The role of KNOX genes in plant development. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20 125–151.
Hofer J., Turner I., Hellens R., Ambrose M., Mathews P., Michael A. and Ellis N. 1997 UNIFOLIATA regulates leaf and flower morphogenesis in pea. Curr. Biol. 7, 581–587.
Hofer J., Gourlay C., Michael A. and Ellis T. H. N. 2001 Expression of a class I knotted-1 like homeobox gene is down-regulated in pea compound leaf primordia. Plant Mol. Biol. 45, 387–391.
Irzykowska L. and Wolko B. 2004 Interval mapping of QTLs controlling yield-related traits and seed protein content in Pisum sativum. J. Appl. Genet. 45, 297–306.
Irzykowska L., Wolko B. and Swiecicki W. K. 2001 The genetic linkage map of pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on molecular, biochemical and morphological markers. Pisum Genet. 33, 13–18.
Kosambi D. D. 1944 The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann. Eugen. 12, 172–175.
Kujala V. 1953 Felderbse bie welcher die ganze blattspreite in ranken umgewandelt ist. Arch. Soc. Zoo. Bot. Fenn. Vanamo 8, 44–45.
Kumar S., Rai S. K., Pandey-Rai S., Srivastava S. and Singh D. 2004 Regulation of unipinnate character in the distal tendrilled domain of compound leaf-blade by the gene MULTIFOLIATE PINNA (MFP) in pea Pisum sativum. Plant Sci. 166, 929–940.
Lamprecht H. 1933 Ein unifoliata — Typus von Pisum mit gleichzeitiger Pistilloidie. Hereditas 18, 56–64.
Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barolw A., Daly M., Lincoln S. and Newberg L. 1987 MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1, 174–181.
Laucou V., Haurogne K., Ellis N. and Rameau C. 1998 Genetic mapping in pea.1. RAPD-based genetic linkage map of Pisum sativum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97, 905–915.
Lincoln S., Daly M. and Lander E. S. 1992 Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0 Whitehead Institute Technical Report, 3rd edition. Whitehouse Technical Institute, Cambridge, USA.
Loridon K., Mcphee K., Morin J., Dubreuil P., Pilet-Nayel M. L., Aubert G. et al. 2005 Microsatellite marker polymorphism and mapping in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 111, 1022–1031.
Michelmore R.W., Paran J. and Kisseli R. V. 1991 Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions using segregating populations. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 9828–9832.
Pellew C. and Sverdrup A. 1923 New observations on the genetics of peas (Pisum sativum). J. Genet. 13, 125–131.
Prajapati S. and Kumar S. 2001 Role of LLD, a new locus for leaflet/pinna morphogenesis in Pisum sativum. J. Biosci. 26, 607–625.
Prajapati S. and Kumar S. 2002 Interaction of the UNIFOLIATATENDRILLED ACACIA gene with AFILA and TENDRIL-LESS genes in the determination of leaf-blade growth and morphology in pea Pisum sativum. Plant Sci. 162, 713–721.
Remeau C., Denoue D., Fravel F., Haurogne K., Josserand J., Laucou V. et al. 1998 Genetic mapping of pea 2. Identification of RAPD and SCAR markers linked to genes affecting plant architecture. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97, 916–928.
Tattersall A. D., Turner L., Knox M. R., Ambrose M. J., Ellis T. H. N. and Hofer J. M. I. 2005 The mutant crispa reveals multiple roles for PHANTASTICA in pea compound leaf development. Plant Cell 17, 1046–1060.
Taylor S., Hofer J. and Murfet I. 2001 Stamina pistilloida, the pea ortholog of Fim and UFO, is required for normal development of flowers, inflorescences and leaves. Plant Cell 13, 31–46.
Wang Z., Luo Y., Li X., Wang L., Xu S., Yang J. et al. 2008 Genetic control of floral zygomorphy in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 10414–10419.
Weeden N. F. and Marx G. A. 1987 Further genetic analysis and linkage relationships of isozyme loci in the pea. J. Hered. 78, 153–159.
Weeden N. F., Ellis T. H. N., Timmerman-Vaughan G. M., Swiecicki W. K., Rozov S. M. and Berdnikov V. A. 1998 A consensus linkage map of Pisum sativum. Pisum Genet. 30, 1–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, R.K., Kumar, A., Chaudhary, S. et al. Mapping of the multifoliate pinna (mfp) leaf-blade morphology mutation in grain pea Pisum sativum . J Genet 88, 227–232 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-009-0031-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-009-0031-0