Abstract
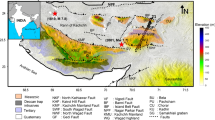
The East–West oriented Kachchh Mainland Fault (KMF) is a major primary fault in an active Kachchh rift basin in the western part of India. In the present work, we made an attempt to understand the tectonic features of the KMF system and the hydrological characteristics of the fault zone using a time domain electromagnetic (TDEM) survey. The TDEM investigations are carried out at 52 sites, distributed along six profiles, three across the fault and three along the fault zone, to study the hydrological phenomenon. The resistivity sections of these six profiles are correlated with well log and lithology data provided information up to a depth of around 250 m and suggest a multilayer aquifer system. The resistivity sections also show KMF as a sharp contact between the Mesozoic rocks and the Quaternary alluvium overlain on Tertiary rocks. Most of the groundwater potential aquifer zones are towards the South and very few groundwater potential aquifer zones are found in the North. In this region, streams are flowing towards Rann of Kachchh. We infer that the KMF zone is impervious that possibly bisects the aquifer zones and acts as a barrier for the groundwater flow in the North–South direction and conduit for the parallel flow in the East–West direction. The study highlights the significant tectonic controls of the groundwater flow in the Kachchh rift.
Research highlights
-
The study provides the hydrological characteristics of Kachchh Mainland Fault zone.
-
Time domain electromagnetic investigations for Fault zone hydrology and tectonic controls of the groundwater flow in the Kachchh rift.
-
Delineation of groundwater potential zones around Fault zone.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bense V F, Gleeson T, Loveless S E, Bour O and Scibek J 2013 Fault zone hydrogeology; Earth-Sci. Rev. 127 171–192.
Biswas S K 1971 The miliolite rocks of Kutch and Kathiawar; Sediment. Geol. 5 147–164.
Biswas S K 1977 Mesozoic rock-stratigraphy of Kutch; Quart. J. Geol. Min. Met. Soc. Ind. 49(3 and 4) 1–52.
Biswas S K 2005 A review of structure and Tectonics of Kutch Basin, Western India, with special reference to earthquakes; Curr. Sci. 88(10) 1592–1600.
Biswas S K 2016 Tectonic framework, structure and tectonic evolution of Kutch Basin, Western India; Spec. Publ. Geol. Soc. India 6 129–150.
CGWB 2013 Groundwater Brochure, Kachchh District. Central Ground Water Board, Government of India, West Central Region, Ahmedabad, http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Gujarat/Kachchh.pdf.
Chandra S, Dewandel B, Dutta S and Ahemed S 2010 Geophysical model of geological discontinuities in a granitic aquifer: Analysing small scale variability of electrical resistivity for groundwater occurrences; J. Appl. Geophys. 71 137–148.
Chowksey V, Maurya D M, Joshi J, Khonde N, Das A and Chamyal L S 2011 Lithostratigraphic development and neotectonic significance of the Quaternary sediments along the Kachchh Mainland Fault (KMF) zone, Western India; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 120(6) 979–999.
Dipankar Saha and Naresh Gor 2020 A prolific aquifer system in arid Kachchh region of India; Groundw. Sustain. Dev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100394.
Goldman M and Neubauer F 1994 Groundwater exploration using integrated geophysical techniques; Surv. Geophys. 15 331–361.
Goldman M, Gilad D, Rouen A and Melloul A 1991 Mapping of seawater intrusion into the coastal aquifer of Israel by the time domain electromagnetic method; Geoexploration 28 153–174.
Himansu K K and Thakkar M G 2011 Elemental concentration of U, Th, and K in tectonically active regions of Khari river basin, Kachchh, western India; J. Radioanalyt. Nucl. Chem. 290(1) 191–196.
Kandregula R S, Kothyari G C, Chauhan G, Pancholi V, Swamy K V, Abhishek L, Sneha M and Thakkar M G 2020 Evaluating the seismic hazard in the Kachchh region, western India using river gradient length anomaly technique; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 129 193.
MacInnes S and Raymond M 2001 STEMINV documentation – Smooth Model TEM Inversion, v3, Zonge Engineering and Research Org, Tucson, AZ.
Mandal P and Pujol J 2006 Seismic imaging of the aftershock zone of the 2001 Mw 7.7 Bhuj earthquake, India; Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 L05309.
Manglik A, Verma S K, Muralidharan D and Sasmal R P 2011 Electrical and electromagnetic investigations for HVDC ground electrode sites in India; J. Phys. Chem. Earth 36 1405–1411.
McNeill J D 1994 Principles and application of time domain electromagnetic techniques for resistivity sounding; Geonics Technical Note TN-27, Mississauga, Ontario 1–15.
Mehul Nagar, Pavankumar G, Mahesh P, Rakesh N, Chouhan A K, Nagarjuna D, Sumer Chopra and Ravi Kumar M 2021 Magnetotelluric evidence for trapped fluids beneath the seismogenic zone of the Mw 6.0 Anjar earthquake, Kachchh intraplate region, Northwest India; Tectonophys. 814(8) 228969, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2021.228969.
Mills T, Hoekstra P, Blohm M and Evans L 1988 Time domain electromagnetic soundings for mapping sea-water intrusion in Monterey County, California; Ground Water 26 771–782.
Mohan K, Chaudhary P, Patel P, Chaudhary B S and Chopra S 2018 Magnetotelluric study to characterize Kachchh Mainland Fault (KMF) and Katrol Hill Fault (KHF) in the western part of Kachchh region of Gujarat, India; Tectonophys. 726 43–61.
Nabighian M N and Macnae J C 1991 Time domain electromagnetic prospecting methods; In: Electromagnetic methods in applied geophysics (ed.) Nabighian M N, Soc. Explor. Geophysicists 02 427–520.
Pavan Kumar G, Mahender E, Singh Y K, Mahesh P and Mohan Kapil 2016 Delineation of aquifer layer along Anjar-Rapar Corridor, eastern Kachchh basin, Gujarat using electromagnetic investigations; J. Indian. Geophys. Union 20(2) 201–208.
Pavan Kumar, Virender Kumar Choudhary, Mehul Nagar, Mahendhar E, Dilip Singh, Patel P and Mahesh P 2017 Magntotelluric impedance tensor analysis for identification of transverse tectonic feature in the Wagad uplift, Kachchh, northwest India; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 126 68, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0851-x.
Pavan Kumar, Indu Chaudhary, Mehul Nagar, Avinash Chauhan, Prizomwala S P, Mahesh P and Sumer Chopra 2018 Transient electromagnetic investigations in a tectonic domain of the Kachchh Intraplate Region, Western India: A morphotectonic study of the Kachchh Mainland Fault; Tectonics 37, https://doi.org/10.1029/2017TC004884.
Prizomwala S P, Solanki T, Chuhan G, Das A, Bhatt N, Thakkar M G and Rastogi B K 2016 Spatial variations in tectonic activity along the Kachchh Mainland Fault, Kachchh, Western India: Implications in seismic hazard assessment; Nat. Hazards 82(2) 947–961, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2228-x.
Rai S N, Thiagarajan S, Ratna Kumari Y, Anand Rao V and Manglik A 2013 Delineation of aquifers in basaltic hard rock terrain using vertical electrical soundings data; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 122 29–41.
Rajendran K, Rajendran C P, Thakkar M and Tuttle M P 2001 The 2001 Kutch (Bhuj) earthquake: Coseismic surface features and their significance; Curr. Sci. 80(11) 1397–1405.
Sinha R, Yadav G S, Gupta S, Singh A and Lahiri S K 2013 Geo-electric resistivity evidence for subsurface paleochannel systems adjacent to Harappan sites in northwest India; Quat. Int. 308–309 66–75.
Spies B R 1989 Depth of investigation in electromagnetic sounding methods; Geophysics 54(7) 872–888, https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1442716.
Taylor K, Widmer M and Chesley M 1992 Use of transient electromagnetics to define local hydrogeology in an arid alluvial environment; Geophysics 57(2) 343–352.
Villani F, Tulliani V, Sapia V, Fierro E, Civico R and Pantosti D 2015 Shallow subsurface imaging of Piano di Pezza active normal fault (Central Italy) by high resolution refraction and electrical resistivity tomography coupled with time domain electromagnetic data; Geophys. J. Int. 203 1482–1494.
Zonge 2002 Zonge international, USA, GDP32–24 manual, section 15, Useful TEM Equations.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Director General of ISR for his kind permission to publish the present work. We also thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of Gujarat for sponsoring this work. We are also thankful to WCR, Central Groundwater Board, Central Govt. of India for the borehole data and groundwater data. The study forms part of the doctoral thesis of Rakesh Nikam. We sincerely thank the Editor and an anonymous reviewer for their constructive comments for improving the MS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rakesh Nikam collected and analysed the data, performed modelling and manuscript writing. Sumer Chopra and G Pavan Kumar conceived the idea, overviewed the MS writing and supervised the work. Indu Chaudhary, Mehul Nagar, Himanshu Chaube, Dinesh Singh and Durga Prasad collected the data and analysed datasets. Nagarjuna assisted in results interpretation and MS writing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Arkoprovo Biswas
Supplementary material pertaining to this article is available on the Journal of Earth System Science website (http://www.ias.ac.in/Journals/Journal_of_Earth_System_Science)
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikam, R., Chopra, S., Kumar, G.P. et al. Investigation of hydrological characteristics of the Kachchh Mainland Fault (KMF) Zone, Gujarat, Western India using time domain electromagnetic study. J Earth Syst Sci 131, 248 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-02004-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-02004-x