Abstract
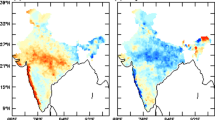
India experienced two extreme summer monsoons, 2007 (active monsoon) and 2009 (weak monsoon) in the recent past decade. The characteristic features of these two contrasting Indian summer monsoons have been presented. The country received 11.8% excess and 17.1% deficit rainfall during 2007 and 2009 monsoon seasons, respectively. These large deviations in rainfall encourage us to study the influence of meteorological factors on rainfall activity. The distributions of rainfall over India, latent heat flux, wind, Vertically Integrated Moisture Transport (VIMT), and Vertically Integrated Moisture Divergence (VIMD) values in the layer 1000–300 hPa for the domain, 0°–40°N, 40°–120°E in the two contrasting monsoon seasons are evaluated. In active monsoon, (i) predominant low level southwesterly flow over the Arabian sea and deflection of winds over the Bay of Bengal, strengthening of the tropical easterly jet stream, wide area extent of easterlies in the upper troposphere, the maximum strength of easterlies in the upper troposphere (150 hPa) is observed over the area around 10°–15°N and 70°–75°E; (ii) position of subtropical ridge is more northward, i.e., 32°N; (iii) a predominant moisture transport in the layer 1000–300 hPa from Southern Hemisphere, Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal to the Indian mainland, westward/northward transport of moisture and area coverage of larger quantum of moisture flux is seen; and (iv) India experienced more number of mesoscale systems. The reverse is true for weak monsoon. Positive (neutral) Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and La-Nina (El-Nino) conditions lead to active (poor) summer monsoon conditions over India in 2007 (2009) year.
Highlights
-
The inter-annual variations in summer monsoon rainfall over India exhibited two extreme summer monsoons 2007 (active) and 2009 (weak) during recent past decade, 2001–2010.
-
Dominant lower and upper tropospheric circulations over monsoon region are evident in the active monsoon.
-
The incursion of subtropical westerlies in the mid as well as upper troposphere inhibits the rainfall activity over India in the weak monsoon season.
-
A predominant moisture transport from the surrounding oceanic area as well as Southern Hemisphere to Indian mainland is seen in the active monsoon.
-
The moisture divergence over the surrounding oceanic area is high in active monsoon.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrol Y P and Gadgil S (eds) 1999 Rice- in a Variable Climate, APC Publications Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, 243p.
Alexander G, Keshavamurty R, De U, Chellapa R, Das S and Pillai P 1978 Fluctuations of monsoon activity; J. Meteorol. Hydrol. Geophys. 29 76–87.
Annamalai H and Liu P 2005 Response of the Asian summer monsoon to changes in El Niño properties; Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc.: J. Atmos. Sci. Appl. Meteorol. Phys. Oceanogr. 131(607) 805–831.
Ashok K and Zhaoyong G 2004 Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean dipole on the Indian summer monsoon; J. Clim. 17 3141–3155.
Ashok K, Behera S K, Rao S A, Weng H and Yamagata T 2007 El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection; J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 112(C11) 69.
Ashok K, Guan Z and Yamagata T 2001 Impact of the Indian Ocean Dipole on the relationship between the Indian Monsoon rainfall and ENSO; Geophys. Res. Lett. 26 4499–4502.
Ashok K, Guan Z, Saji N H and Yamagata T 2004 Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Indian Summer Monsoon; Geophys. Res. Lett. 26 4499–4502.
Behera S K and Ratnam J V 2018 Quasi-asymmetric response of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall to opposite phases of the IOD; Sci. Rep. 8 123, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18396-6.
Bhatla R, Singh A K, Mandal B, Ghosh S, Pandey S N and Sarkar A 2016 Influence of North Atlantic oscillation on Indian summer monsoon rainfall in relation to quasi-binneal oscillation; Pure Appl. Geophys. 173 2959–2970.
Bjerknes J 1969 Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial pacific; J. Phys. Oceanogr. 97(3) 163–172.
Cadet D and Reverdin G 1981 Water vapour transport over the Indian Ocean during summer 1975; Tellus 33 476–487.
Chakravorty S, Chowdary J S and Gnanaseelan C 2014 Epochal changes in the seasonal evolution of tropical Indian Ocean warming associated with El Niño; Clim. Dynam. 42(3–4) 805–822.
Chakravorty S, Gnanaseelan C and Pillai P A 2016 Combined influence of remote and local SST forcing on Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall variability; Clim. Dynam. 47(9–10) 2817–2831.
Charlotte B V, Dhanya and Basil Mathew 2012 EQUINOO: The entity and validity of this oscillation to Indian monsoon: Research inventy; Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1(11) 45–54, ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, www.researchinventy.com.
Chowdary J S and Gnanaseelan C 2007 Basin-wide warming of the Indian Ocean during El Niño and Indian Ocean dipole years; Int. J. Climatol. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 27(11) 1421–1438.
Chowdary J S, Gnanaseelan C and Chakravorty S 2013 Impact of northwest Pacific anticyclone on the Indian summer monsoon region; Theor. Appl. Climatol. 113(1–2) 329–336.
Fasullo J and Webster P J 2003 A hydrological definition of the Indian summer monsoon onset and withdrawal; J. Climate 16(19) 3200–3211.
Gadgil S 2003 The Indian monsoon and its variability; Annu Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 31 429–467.
Gadgil S, Vinayachandran P N, Francis P A and Gadgil S 2004 Extremes of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall: ENSO and equatorial Indian Ocean Oscillation; Geophys. Res. Lett. 31 L12213, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GLO19733.
Gadgil S and Francis 2010 Towards understanding the unusual Indian monsoon in 2009; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 119(4) 397–415.
Holt T and Raman S A 1987 Study of mean boundary layer structures over the Arabian sea and Bay of Bengal during active and break monsoon periods; Bound. Layer Meteorol. 38 73–94.
Izumo T, Montégut C B, Luo J J, Behera S K, Masson S and Yamagata T 2008 The role of the western Arabian Sea upwelling in Indian monsoon rainfall variability; J. Climate 21(21) 5603–5623.
Jin-Yi Yu and Seon Tae Kim 2013 Identifying the types of major El Niño events since 1870; Int. J. Climatol. 33 2105–2112.
Kakade S and Kulkarni A 2017 Association between Arctic circulation and Indian summer monsoon rainfall; J. Climatol. Wea. Forecast. 5 207, https://doi.org/10.4172/2332-2594.1000208.
Kalnay E et al. 1996 The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project; Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 77 437–471.
Kinter J L III, Miyakoda K and Yang S 2002 Recent change in the connection from the Asian monsoon to ENSO; J. Climate 15(10) 1203–1215.
Klein S A, Soden B J and Lau N C 1999 Remote sea surface temperature variations during ENSO: Evidence for a tropical atmospheric bridge; J. Climate 12(4) 917–932.
Kripalani R H and Pankajkumar 2004 Northeast monsoon rainfall variability over south-peninsular India vis‐à‐vis the Indian ocean dipole mode; Int. J. Climatol. 24 1267–1282.
Krishna Kumar K, Rajagopalan B, Hoerling M, Bates G and Cane M 2006 Unraveling the mystery of Indian monsoon failure during El Nino; Science 314 115–119.
Krishnamurthy V and Goswami B N 2000 Indian monsoon–ENSO relationship on interdecadal time scale; J. Climate 13 579–595.
Krishnamurti T N and Bhalme H N 1976 Oscillations of monsoon system. Part I: observational aspects; J. Atmos. Sci. 45 1937–1954.
Kumar K K, Rajagopalan B and Cane M A 1999 On the weakening relationship between the Indian monsoon and ENSO; Science 284(5423) 2156–2159.
Mooley D A and Shukla J 1987 Variability and forecasting of the summer monsoon rainfall over India; In: Monsoon Meteorology (eds) Chang C P and Krishnamurti T N, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 26–59.
Murtugudde R, McCreary J P Jr and Busalacchi A J 2000 Oceanic processes associated with anomalous events in the Indian Ocean with relevance to 1997–1998; J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 105(C2) 3295–3306.
Naidu C V, Muni Krishna K, Ramalingeswara Rao S, Bhanu Kumar O S R U, Durgalakshmi K and Ramakrishna S S V S 2011 Variations of Indian summer monsoon rainfall induce the weakening of easterly jet stream in the warming environment? Glob. Planet. Chang. 75 21–30.
Nitta T and Yamada S 1989 Recent warming of tropical sea surface temperature and its relationship to the Northern Hemisphere circulation; J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 67(3) 375–383.
Parthasarathy B A and Mooley D A 1978 Some features of a long homogeneous series of Indian summer monsoon rainfall; Monthly Wea. Rev. 106(6) 771, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1978)106-0771.
Parthasarathy B A, Munot A A and Kothawale D R 1988 Regression model for estimation of Indian food grain production from Indian summer rainfall; Agric. For. Meteorol. 42(2–3) 167–182, https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1923(88)90075-5.
Qiu Y, Wenju C, Xiaogang G and Benjamin Ng 2014 The asymmetric influence of the positive and negative IOD events on China’s rainfall; Sci. Rep. 4 4943, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04943.
Raghavan K 1973 Break monsoon over India; Mon. Weather Rev. 101 33–43.
Ramage C S 1971 Monsoon meteorology; Int. Geophys. Ser., Academic Press 15 296.
Ramamurthy K 1969 Monsoon of India: Some aspects of the ‘break’ in the Indian southwest monsoon during July and August; India Meteorol. Dept., Poona India; Forecast. Man. 183(4) 1–57.
Ramanadham R, Samanadham S V S and Rao R R 1981 Heat budget of the northern Indian Oceanic surface during monsoon-77; In: Dynamics Monsoon (eds) Lighthill and Pearce; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 1–735.
Rao Y P 1976 Southwest monsoon, India Meteorological Department, New Delhi, Meteorological Monograph, 366p.
Rasmusson E M and Carpenter T H 1983 The relationship between eastern equatorial Pacific sea surface temperatures and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka; Mon. Wea. Rev. 111 517–528.
Saji N H, Goswami B N, Vinayachandran P N and Yamagata T 1999 A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean; Nature 401(6751) 360–363, https://doi.org/10.1038/43854,PMID16862108,S2CID4427627.
Shukla J 1975 Effect of Arabian sea–surface temperature anomaly on Indian summer monsoon: A numerical experiment with the GFDL model; J. Atmos. Sci. 32(3) 503–511.
Sikka D R 1980 Some aspects of large-scale fluctuations of summer monsoon rainfall over India in relation to fluctuations in planetary and regional scale circulation parameters; Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) 89 179–195.
Simon B and Desai P S 1986 Equatorial Indian Ocean evaporation estimates from operational meteorological satellites and some inferences in the context of monsoon onset and activity; Bound.-Lay. Meteorol. 37 37–52.
Swapna P and Ramesh Kumar M R 2002 Role of low-level flow on the summer monsoon rainfall over the Indian subcontinent during two contrasting monsoon years; J. Indian Geophys. Union 6 123–137.
Trenberth K E and Guillemot C J 1998 Evaluation of the atmospheric moisture and hydrological cycle in the NCEP/NCAR reanalyses; Clim. Dyn. 14(3) 213–231, https://doi.org/10.1007/s003820050219.
Trenberth K E and Hurrell J W 1994 Decadal atmosphere–ocean variations in the Pacific; Clim. Dynam. 9(6) 303–319.
Vinay K P, Naidu C V and Prasanna K 2019 Inconsistency in the frequency of rainfall events in the Indian summer monsoon season; Int. J. Climatol. 5 10, https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6113.
Vinay Kumar P, Naidu C V and Prasanna K 2020 Recent unprecedented weakening of Indian summer monsoon in warming environment; Theor. Appl. Climatol. 140 467–486.
Vishnu S, Francis P A, Shenoi S S C and Ramakrishna S S V S 2016 On the decreasing trend of the number of monsoon depressions in the Bay of Bengal; Environ. Res. Lett., https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/1/014011.
Wang B 1995 Interdecadal changes in El Nino onset in the last four decades; J. Climate 8(2) 267–285.
Webster P J, Magaña V, Palmer T N, Shukla J, Tomas R A, Yanai M and Yasunari T 1998 Monsoons: processes, predictability and prospects for prediction; J. Geophys. Res. 103 14,451–14,510.
Webster P J, Moore A M, Loschnigg J P and Leben R R 1999 Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98; Nature 401(6751) 356–360.
Wu R, Kirtman B P and Krishnamurthy V 2008 An asymmetric mode of tropical Indian Ocean rainfall variability in boreal spring; J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 113(D5) 5.
Wyrtki K 1975 El Niño-the dynamic response of the equatorial Pacific Ocean to atmospheric forcing; J. Phys. Oceanogr. 5 572–583.
Xie S P, Du Y, Huang G, Zheng X T, Tokinaga H, Hu K and Liu Q 2010 Decadal shift in El Niño influences on Indo-western Pacific and East Asian climate in the 1970s; J. Climate 23(12) 3352–3368.
Yang J, Liu Q, Xie S P, Liu Z and Wu L 2007 Impact of the Indian Ocean SST basin mode on the Asian summer monsoon; Geophys. Res. Lett. 34(2) 97.
Yeh S W, Kug J S, Dewitte B, Kwon M H, Kirtman B P and Jin F F 2009 El Niño in a changing climate; Nature 461(7263) 511–514.
Zhu Y 2012 Variations of the summer Somali and Australia cross-equatorial flows and the implications for the Asian summer monsoon; Adv. Atmos. Sci. 29 509–518.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the DGM, IMD for his encouragement. The authors are also grateful to the NCEP-NCAR for providing data resources. Thanks are also due to anonymous reviewers without whose probing queries this work would not have been more refined and boiled to the crux.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD: Proposed and mooted the central idea and did statistical work. CVN: Supervised the overall progress, made suitable suggestions and completed the final manuscript. RK: Data collection, visualizations and necessary inputs for graphics. SV: Analyzed the data, interpreted and drafted the manuscript. Also, carried out the standardization of the data of rainfall time series and prepared the visualizations. KN: Guided the preliminary work and helped in providing data, and in the analysis of oceanic and circulation patterns observed in the study.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C Gnanaseelan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raju, A.D., Naidu, C.V., Karumuri, R.K. et al. Two contrasting summer monsoon seasons in the recent past decade: An observational study. J Earth Syst Sci 130, 66 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01559-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01559-5