Abstract
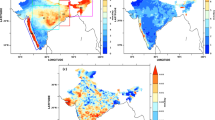
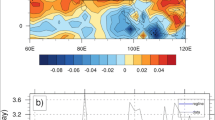
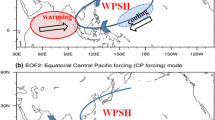
The combined influence of tropical Indian Ocean (TIO) and Pacific Ocean (TPO) sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies on Indian summer monsoon rainfall (ISMR) variability is studied in the context of mid-1970s regime shift. The rainfall pattern on the various stages of monsoon during the developing and decaying summer of El Niño is emphasized. Analysis reveals that ISMR anomalies during El Niño developing summer in epoch-1 (1950–1979) are mainly driven by El Niño forcing throughout the season, whereas TIO SST exhibits only a passive influence. On the other hand in epoch-2 (1980–2009) ISMR does not show any significant relation with Pacific during the onset phase of monsoon whereas withdrawal phase is strongly influenced by El Niño. Again the eastern Indian Ocean cooling and westward shift in northwest Pacific (NWP) cyclonic circulation during epoch-2 have strong positive influence on the rainfall over the central and eastern India during the matured phase of monsoon. ISMR in the El Niño decaying summer does not show any significant anomalies in epoch-1 as both Pacific and Indian Ocean warming dissipate by the summer. On the other hand in epoch-2 ISMR anomalies are significant and display strong variability throughout the season. In the onset phase of monsoon, central and east India experience strong negative precipitation anomalies due to westward extension of persistent NWP anticyclone (forced by persisting Indian Ocean warming). The persistent TIO warming induces positive precipitation anomalies in the withdrawal phase of monsoon by changing the atmospheric circulation and modulating the water vapour flux. Moisture budget analysis unravels the dominant processes responsible for the differences between the two epochs. The moisture convergence and moisture advection are very weak (strong) over Indian land mass during epoch-1 (epoch-2) in El Niño decaying summer. The changing moisture availability and convergence play important role in explaining the weakening of ENSO monsoon relation in the recent years. The local TIO SST forcing and NWP circulation are prominent forcing factors for the interannual variability of ISMR during epoch-2.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai H, Liu P, Xie SP (2005) Southwest Indian Ocean SST variability: its local effect and remote influence on Asian monsoons. J Clim 18:4150–4167
Ashok K, Behera SK, Rao SA, Weng H, Yamagata T (2007) El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2006JC003798
Boschat Ghyslaine, Terray Pascal, Masson Sébastien (2012) Robustness of SST teleconnections and precursory patterns associated with the Indian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 38(11–12):2143–2165
Chakravorty S, Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C (2013) Spring asymmetric mode in the tropical Indian Ocean: role of El Niño and IOD. Clim Dyn 40:1467–1481. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1340-1
Chakravorty S, Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C (2014a) Epochal changes in the seasonal evolution of tropical Indian Ocean warming associated with El Niño. Clim Dyn 42:805–822. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-1666-3
Chakravorty S, Gnanaseelan C, Chowdary JS (2014b) Relative role of El Nino and IOD forcing on the southern tropical Indian Ocean Rossby waves. J Geophys Res 119:5105–5122. doi:10.1002/2013JC009713
Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C (2007) Basin-wide warming of the Indian Ocean during El Niño and Indian Ocean dipole years. Int J Climatol 27(11):1421–1428. doi:10.1002/joc.1482
Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C, Vaid BH, Salvekar PS (2006) Changing trends in the tropical Indian Ocean SST during the La Niña years. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2006GL026707
Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C, Chakravorty S (2013) Impact of northwest Pacific anticyclone on the Indian summer monsoon region. Theor Appl Climatol 113:329–336. doi:10.1007/s00704-012-0785-9
Chowdary JS, Bandgar A, Gnanaseelan C, Luo JJ (2015) Role of tropical Indian Ocean air–sea interactions in modulating Indian summer monsoon in a coupled model. Atmos Sci Lett 16:170–176. doi:10.1002/asl2.561
Gadgil S, Vinayachandran PN, Francis PA, Gadgil S (2004) Extremes of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall, ENSO and equatorial Indian Ocean oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 31:L12213. doi:10.1029/2004GL019733
Gill AE (1980) Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q J R Meteorol Soc 106:447–462
Goswami BN, Xavier PK (2005) Dynamics of “internal” interannual variability of the Indian summer monsoon in a GCM. J Geophys Res 110:D24104. doi:10.1029/2005JD006042
Izumo T, Montégut CB, Luo JJ, Behera SK, Masson S, Yamagata T (2008) The role of the western Arabian Sea upwelling in Indian monsoon rainfall variability. J Clim 21:5603–5623
Kalnay E et al (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471
Kinter JL III, Miyakoda K, Yang S (2002) Recent change in the connection from the Asian monsoon to ENSO. J Clim 15:1203–1215
Klein SA, Soden BJ, Lau NC (1999) Remote sea surface temperature variations during ENSO: evidence for a tropical atmospheric bridge. J Clim 12:917–932
Kripalani RH, Kumar P (2004) Northeast monsoon rainfall variability over south peninsular India vis-à-vis the Indian Ocean dipole mode. Int J Climatol 24:1267–1282
Krishnamurthy V, Goswami BN (2000) Indian monsoon-ENSO relationship on inter decadal time scales. J Clim 13:579–595
Kumar KK, Rajagopalan KB, Cane MA (1999) On the weakening relationship between the Indian monsoon and ENSO. Science 284:2156–2159
Lau NC, Nath MJ (2000) Impact of ENSO on the variability of the Asian–Australian monsoons as simulated in GCM experiments. J Clim 13:4287–4309
Lau NC, Nath MJ (2003) Atmosphere–ocean variations in the Indo-Pacific sector during ENSO episode. J Clim 16:3–20
Mishra V, Smoliak BV, Lettenmaier DP, Wallace JM (2012) A prominent pattern of year-to-year variability in Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(19):7213–7217
Murtugudde R, McCreary JP, Busalacchi AJ (2000) Oceanic processes associated with anomalous events in the Indian Ocean with relevance to 1997–1998. J Geophys Res 105:3295–3306
Nitta T, Yamada S (1989) Recent warming of tropical sea surface temperature and is relationship to the Northern Hemisphere circulation. J Meteorol Soc Japan 67:375–383
Pai SD, Sridhar L, Rajeevan M, Sreejith OP, Satbhai S, Mukhopadhyay B (2014) Development of a new high spatial resolution (0.25° × 0.25°) long period (1901–2010) daily gridded rainfall data set over India and its comparison with existing data sets over the region. Mausam 65:1–8
Pant GB, Parthasarathy B (1981) Some aspects of an association between the southern oscillation and Indian summer monsoon. Arch Meteorol Geophys Bioklimatol Ser-B 29:245–251
Pillai PA, Annamalai H (2012) Moist dynamics of severe monsoons over south Asia: role of the tropical SST. J Atmos Sci 69:97–115
Rahul S, Gnanaseelan C (2015) Can large scale surface circulation changes modulate the sea surface warming pattern in the Tropical Indian Ocean? Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2790-z
Rasmusson EM, Carpenter TH (1982) Variations in tropical sea surface temperature and surface wind fields associated with the southern oscillation/El Niño. Mon Wea Rev 110:354–384
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108:4407
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363
Sayantani O, Gnanaseelan C (2015) Tropical Indian Ocean subsurface temperature variability and the forcing mechanisms. Clim Dyn 44:2447–2462. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2379-y
Shukla J (1975) Effect of Arabian sea-surface temperature anomaly on Indian summer monsoon: a numerical experiment with the GFDL model. J Atmos Sci 32:503–511
Shukla J (1995) Predictability of the tropical atmosphere, the tropical Oceans and TOGA. In: Proceedings of the international scientific conference on tropical Ocean global atmosphere (TOGA) programme, vol 2, WCRP-91, WMO/TD 717, pp 725–730
Sikka DR (1980) Some aspects of the large-scale fluctuations of summer monsoon rainfall over India in relations to fluctuations in the planetary and regional scale circulation parameters. Proc Indian Natl Acad Sci 89:179–195
Singh P, Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C (2013) Impact of prolonged La Niña events on the Indian Ocean with a special emphasis on southwest Tropical Indian Ocean SST. Glob Planet Chang 100:28–37. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.10.010
Singh P, Vasudevan V, Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C (2015) Subseasonal variations of Indian summer monsoon with special emphasis on drought and excess rainfall years. Int J Climatol 35:570–582. doi:10.1002/joc.4004
Terray P, Dominiak S (2005) Indian Ocean sea surface temperatures and El Niño-southern oscillation: a new perspective. J Clim 18:1351–1368
Torrence C, Webster PJ (1999) Interdecadal changes in the ENSO–monsoon system. J Clim 12:2679–2690
Trenberth KE, Hurrell JW (1994) Decadal atmospheric–ocean variations in the Pacific. Clim Dyn 9:303–319
Wallace JM, Rasmusson EM, Mitchell TP, Kousky VE, Sarachik ES, von Storch H (1998) On the structure and evolution of ENSO related climate variability in the tropical Pacific: lessons from TOGA. J Geophys Res 103:14241–14259
Wang B (1995) Inter decadal changes in El Niño onset in the last four decades. J Clim 8:267–285
Wang B, Wu R, Fu X (2000) Pacific-east Asian teleconnection: how does ENSO affect east Asian climate. J Clim 13:1517–1536
Wang B, Wu R, Li T (2003) Atmosphere–warm Ocean interaction and its impact on Asian–Australian monsoon variability. J Clim 16:1195–1211
Webster PJ (1987) The elementary monsoon. In: Fein JS, Stephens PL (eds) Monsoons. Wiley, New York, pp 3–32
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems. Q J R Meteorol Soc 118:877–926
Webster PJ, Magana VO, Palmer TN, Shukla J, Tomas RA, Yanai M, Yasunari T (1998) Monsoons: processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J Geophys Res: Oceans 103:14451–14510
Webster PJ, Moore AM, Loschnigg JP, Leben RR (1999) Coupled oceanic–atmospheric dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 401:356–360
Wu R, Kirtman BP, Krishnamurthy V (2008) An asymmetric mode of tropical Indian Ocean rainfall variability in boreal spring. J Geophys Res 113:D05104. doi:10.1029/2007JD009316
Xie SP, Hu K, Hafner J, Tokinaga H, Du Y, Huang G, Sampe T (2009) Indian Ocean capacitor effect on Indo-western Pacific climate during the summer following El Niño. J Clim 22(3):730–747
Xie SP, Du Y, Huang G, Zheng XT, Tokinaga H, Hu KM, Liu QY (2010) Decadal shift in El Niño influences on Indo-Western Pacific and East Asian climate in the 1970s. J Clim 23(12):3352–3368. doi:10.1175/2010jcli3429.1
Yang J, Liu Q, Xie S-P, Liu Z, Wu L (2007) Impact of the Indian Ocean SST basin mode on the Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 34:L02708. doi:10.1029/2006GL028571
Yatagai A, Kamiguchi K, Arakawa O, Hamada A, Yasutomi N, Kitoh A (2012) APHRODITE: constructing a long-term daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93:1401–1415. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00122.1
Yeh SW, Kug JS, Dewitte B, Known MH, Kirtman BP, Jin FF (2009) El Nino in a changing climate. Nature 461:511–516
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Ministry of Earth Sciences and Director, ESSO-IITM for support. Soumi acknowledges CSIR, India for JRF/SRF fellowship. We thank D.S. Pai for providing the high resolution rainfall data, H. Annamalai and Jan Hafner for providing the advection code. We thank the anonymous reviewers for valuable suggestions to improve the manuscript. We acknowledge NCEP-NCAR data available at http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/gridded/data.ncep.reanalysis.html, HadISST available at www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadisst, University of Delaware gridded rainfall data available at www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/gridded/data.UDel_AirT_Precip.html and Aphrodite rainfall available at https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/aphrodite-asian-precipitation-highly-resolved-observational-data-integration-towards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakravorty, S., Gnanaseelan, C. & Pillai, P.A. Combined influence of remote and local SST forcing on Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall variability. Clim Dyn 47, 2817–2831 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-2999-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-2999-5