Abstract
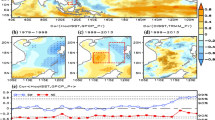
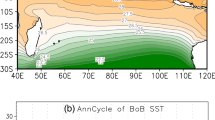
We use daily satellite estimates of sea surface temperature (SST) and rainfall during 1998–2005 to show that onset of convection over the central Bay of Bengal (88–92°E, 14–18°N) during the core summer monsoon (mid-May to September) is linked to the meridional gradient of SST in the bay. The SST gradient was computed between two boxes in the northern (88–92°E, 18–22°N) and southern (82–88°E, 4–8°N) bay; the latter is the area of the cold tongue in the bay linked to the Summer Monsoon Current. Convection over central bay followed the SST difference between the northern and southern bay (ΔT) exceeding 0.75°C in 28 cases. There was no instance of ΔT exceeding this threshold without a burst in convection. There were, however, five instances of convection occurring without this SST gradient. Long rainfall events (events lasting more than a week) were associated with an SST event (ΔT ≥ 0.75°C); rainfall events tended to be short when not associated with an SST event. The SST gradient was important for the onset of convection, but not for its persistence: convection often persisted for several days even after the SST gradient weakened. The lag between ΔT exceeding 0.75°C and the onset of convection was 0–18 days, but the lag histogram peaked at one week. In 75% of the 28 cases, convection occurred within a week of ΔT exceeding the threshold of 0.75°C. The northern bay SST, T N , contributed more to ΔT, but it was a weaker criterion for convection than the SST gradient. A sensitivity analysis showed that the corresponding threshold for T N was 29°C. We hypothesise that the excess heating (∼1°C above the threshold for deep convection) required in the northern bay to trigger convection is because this excess in SST is what is required to establish the critical SST gradient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat G S, Gadgil S, Kumar P V H, Kalsi S R and Madhusoodanan P et al 2001 BOBMEX — The Bay of Bengal Monsoon Experiment; Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 82 2217–2243.
Bhat G S, Vecchi G A and Gadgil S 2004 Sea surface temperature of the Bay of Bengal derived from the TRMM Microwave Imager; J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 21 1283–1290.
Charney J G 1969 The Inter-tropical convergence Zone and the Hadley circulation of the atmosphere; In: Proc. WMO/IUGG Symposium on Numerical Weather Prediction, 3, 73–79, Japan Meteorol. Agency.
Flatau M, Flatau P, Schmidt J and Kiladys G 2003 Delayed onset of the 2002 Indian monsoon; Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 1768.
Gadgil S 2000 Monsoon-ocean coupling; Curr. Sci. 78 309–323.
Gadgil S 2003 The Indian monsoon and its variability; Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 31 429–467.
Gadgil S, Joseph P V and Joshi N V 1984 Ocean-atmosphere coupling over monsoon regions; Nature 312 141–143.
Gadgil S, Srinivasan J, Nanjundiah R S, Krishnakumar K, Munot A A and Rupakumar K 2002 On forecasting the Indian summer monsoon: the intriguing season of 2002; Curr. Sci. 83 394–403.
Goswami B N 1987 A mechanism for the west-northwest movement of monsoon depressions; Nature 326 376–377.
Graham N E and Barnett T P 1987 Sea surface temperature, surface wind divergence, and convection over tropical oceans; Science 238 657–659.
Halley E 1686 A historical account of the trade winds and monsoon observable in the seas between and near the tropics with an attempt to assign a physical cause of the said winds; Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London 16 153–168.
Harrison D E and Vecchi G A 2001 Indian Ocean cooling event; Geophys. Res. Lett. 28 3717–3720.
Held I M and Hou A Y 1980 Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere; J. Atmos. Sci. 37 515–533.
Huffman G J, Adler R F, Morrissey M, Bolvin D T, Curtis S, McGavock R J B and Susskind J 2001 Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multi-satellite observations; J. Hydrometeor. 2 36–50.
Joseph P V and Sijikumar S 2004 Intraseasonal variability of the low-level jet stream of the Asian summer monsoon; J. Climate 17 1449–1458.
Joseph P V, Sooraj K P, Babu C A and Sabin T P 2005 A cold pool in the Bay of Bengal and its interaction with the active-break cycle of the monsoon; CLIVAR Exchanges 34, Southampton, U.K. 10 10–12.
Joseph P V and Sabin T P 2007 An ocean-atmosphere interaction mechanism for the active break cycle of the Indian summer monsoon; Climate Dynamics (in press) doi:10.107/s00382-007-0305-2.
Krishnamurti T N and Bhalme H N 1976 Oscillations of a monsoon system. Part I: Observational aspects; J. Atmos. Sci. 33 1937–1954.
McCreary J P, Kundu P K and Molinari R L 1993 A numerical investigation of the dynamics, thermodynamics and mixed-layer processes in the Indian Ocean; Prog. Oceanogr. 31 181–244.
Mooley D and Shukla J 1989 Main features of the westwardmoving low pressure systems which form over the Indian region during the summer monsoon season and their relation to the monsoon rainfall; Mausam 40 137–152.
Nanjundiah R S, Srinivasan J and Gadgil S 1992 Intraseasonal variation of the Indian summer monsoon. II: Theoretical aspects; J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 70 529–549.
Premkumar K, Ravichandran M, Kalsi S R, Sengupta D and Gadgil S 2000 First results from a new observational system over the Indian seas; Curr. Sci. 78 323–331.
Ramamurthy K 1969 Monsoon of India: Some aspects of the ‘break’ in the Indian southwest monsoon during July and August; India Meteorol. Dept., Poona, India.
Rao R R, Ramam K V S, Rao D S and Joseph M X 1985 Surface heat budget estimates at selected areas of north Indian Ocean during Monsoon-77; Mausam 36 21–32.
Rao R R, Kumar M S G, Ravichandran M, Samala B K and Anitha G 2006a Observed intra-seasonal variability of mini-cold pool off the southern tip of India and its intrusion into the south central Bay of Bengal during summer monsoon season; Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 doi:10.1029/2006GL026086.
Rao R R, Kumar M S G, Ravichandran M, Samala B K and Sreedevi N 2006b Observed mini-cold pool off the southern tip of India and its intrusion into the south central Bay of Bengal during summer monsoon season; Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 doi:10.1029/2005GL025382
Rao Y P 1976 Southwest monsoon; Meteorological monograph, India Meteorological Department, New Delhi, India.
Riehl H 1979 Climate and weather in the tropics; Academic Press, San Diego.
Sanilkumar K V, Mohankumar N, Joseph M X and Rao R R 1994 Genesis of meteorological disturbances and thermohaline variability of the upper layers in the head Bay of Bengal during MONsoon Trough Boundary Layer EXperiment (MONTBLEX-90); Deep-Sea Res., Part I 41 1569–1581.
Schneider E K and Lindzen R S 1976 Axially symmetric steady-state models of the basic state for instability and climate studies. Part I: Linearized calculations; J. Atmos. Sci. 34 263–279.
Sengupta D and Ravichandran M 2001 Oscillations of Bay of Bengal sea surface temperature during the 1998 summer monsoon; Geophys. Res. Lett. 28 2033–2036.
Sengupta D, Goswami B N and Senan R 2001 Coherent intraseasonal oscillation of ocean and atmosphere during the Asian summer monsoon; Geophys. Res. Lett. 28 4127–4130.
Shankar D, Vinayachandran P N and Unnikrishnan A S 2002 The monsoon currents in the north Indian Ocean; Prog. Oceanogr. 52 63–120.
Shenoi S S C, Shankar D and Shetye S R 2002 Differences in heat budgets of the near-surface Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal: Implications for the summer monsoon; J. Geophys. Res. 107 doi:10.1029/2000JC000679
Sikka D R and Gadgil S 1980 On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over India longitude during the southwest monsoon; Mon. Wea. Rev. 108 1840–1853.
Srinivasan J S, Nanjundiah R S and Gadgil S 1993 Meridional propagation of large-scale monsoon convective zones; Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 52 15–35.
Sud Y C, Walker G K and Lau K-M 1999 Mechanisms regulating sea surface temperatures and deep convection in the tropics; Geophys. Res. Lett. 26 1019–1022.
Vecchi G A and Harrison D E 2002 Monsoon breaks and subseasonal sea surface temperature variability in the Bay of Bengal; J. Climate 15 1485–1493.
Vinayachandran P N and Yamagata T 1998 Monsoon response of the sea around Sri Lanka: Generation of thermal domes and anticylonic vortices; J. Phys. Oceanogr. 28 1946–1960.
Vinayachandran P N, Masumoto Y, Mikawa T and Yamagata T 1999 Intrusion of the Southwest Monsoon Current into the Bay of Bengal; J. Geophys. Res. 104 11,077–11,085.
Vinayachandran P N, Murty V S N and Babu V R 2002 Observations of barrier layer formation in the Bay of Bengal during summer monsoon; J. Geophys. Res. 107 10.1029/2001JC000831
Webster P J 1987 The elementary monsoon; In: Monsoons (eds) Fein J S and Stephens P S, 3–32, (New York: Wiley).
Wentz F J 1998 Algorithm theoretical basis document: AMSR Ocean Algorithm; Tech. Rep. 110398 Remote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, CA.
Xie S-P and Saiki N 1999 Abrupt onset and slow seasonal evolution of summer monsoon in an idealized GCM simulation; J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 77 949–968.
Yasunari T 1979 Cloudiness fluctuations associated with the northern hemisphere summer monsoon; J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 57 227–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, D., Shetye, S.R. & Joseph, P.V. Link between convection and meridional gradient of sea surface temperature in the Bay of Bengal. J Earth Syst Sci 116, 385–406 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0038-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0038-y