Abstract
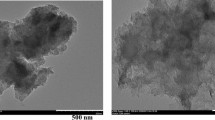
Molybdenum based materials are gaining importance as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction because of their low cost and good electrocatalytic efficiency. Introducing iron nitride with molybdenum nitride as a composite results in efficient hydrogen evolution activity with current density of \({\sim }120\) \(\hbox {mA/cm}^{2}\) at \(-400 \hbox { mV}\) vs. RHE. The nanocomposites were characterized using powder XRD, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Electron Diffraction, Thermogravimetric Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy. The electrochemical investigations suggest that the electrocatalytic activity of the composite increases with iron nitride content. The composite exhibits good electrochemical stability upto 42 hours in acidic medium. The hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) follows Volmer-Heyrovsky mechanism where Volmer reaction is the rate determing step.
Graphical Abstract
SYNOPSIS Introducing iron nitride in composite with molybdenum nitride leads to higher HER activity in acidic media. The in-situ growth of CNTs in the composites enhances the conductivity and decreases the charge transfer resistance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conway B E and Jerkiewicz G 2000 Relation of energies and coverages of underpotential and overpotential deposited H at Pt and other metals to the “volcano curve” for cathodic H 2 evolution kinetics Electrochim. Acta 45 4075
Trasatti S 1972 Work function, electronegativity, and electrochemical behaviour of metals J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 39 163
Wan C, Regmi Y N and Leonard B M 2014 Multiple phases of molybdenum carbide as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53 6407
Pan L F, Li Y H, Yang S, Liu P F, Yu M Q and Yang H G 2014 Molybdenum carbide stabilized on graphene with high electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reaction Chem. Commun. 50 13135
Chen W-F, Wang C-H, Sasaki K, Marinkovic N, Xu W, Muckerman J T, Zhu Y and Adzic R R 2013 Highly active and durable nanostructured molybdenum carbide electrocatalysts for hydrogen production Energy Environ. Sci. 6 943
Chen W-F, Muckerman J T and Fujita E 2013 Recent developments in transition metal carbides and nitrides as hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts Chem. Commun. 49 8896
Popczun E J, Mckone J R, Read C G, Biacchi A J, Wiltrout A M, Lewis N S and Schaak R E 2013 Nanostructured Nickel Phosphide as an Electrocatalyst for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 9267
Xiao P, Sk M A, Thia L, Ge X, Lim R J, Wang J-Y, Lim K H and Wang X 2014 Molybdenum phosphide as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction Energy Environ. Sci. 7 2624
Mahler B, Hoepfner V, Liao K and Ozin G A 2014 Colloidal Synthesis of 1T-WS2 and 2H-WS2 Nanosheets: Applications for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 14121
Youn D H, Han S, Kim J Y, Kim J Y, Park H, Choi S H and Lee J S 2014 Highly Active and Stable Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysts Based on Molybdenum Compounds on Carbon Nanotube À Graphene Hybrid Support ACS Nano 8 5164
Hinnemann B, Moses P G, Bonde J, Jørgensen K P, Nielsen J H, Horch S, Chorkendorff I and Nørskov J K 2005 Biomimetic Hydrogen Evolution: MoS\(_{2}\) Nanoparticles as Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 5308
Casalongue H G S, Benck J D, Tsai C, Karlsson R K B, Kaya S, Ng M L, Pettersson L G M, Abild-pedersen F, Nørskov J K, Ogasawara H, Jaramillo T F and Nilsson A 2014 Operando Characterization of an Amorphous Molybdenum Sulfide Nanoparticle Catalyst during the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction J. Phys. Chem. C 118 29252
Vrubel H and Hu X 2012 Molybdenum boride and carbide catalyze hydrogen evolution in both acidic and basic solutions Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51 12703
Scanlon M D, Bian X, Vrubel H, Amstutz V, Schenk K, Hu X, Liu B and Girault H H 2013 Low-cost industrially available molybdenum boride and carbide as “platinum-like” catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction in biphasic liquid systems Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15 2847
Nørskov J K, Bligaard T, Logadottir A, Kitchin J R, Chen J G, Pandelov S and Stimming U 2005 Trends in the Exchange Current for Hydrogen Evolution J. Electrochem. Soc. 152 J23
Chen W-F, Sasaki K, Ma C, Frenkel A I, Marinkovic N, Muckerman J T, Zhu Y and Adzic R R 2012 Hydrogen-evolution catalysts based on non-noble metal nickel-molybdenum nitride nanosheets Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51 6131
Ojha K, Saha S, Kumar B, Hazra K S and Ganguli A K 2016 Controlling the Morphology and Efficiency of Nanostructured Molybdenum Nitride Electrocatalysts for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction ChemCatChem 8 1218
Xie J, Li S, Zhang X, Zhang J, Wang R, Zhang H, Pan B and Xie Y 2014 Atomically-thin molybdenum nitride nanosheets with exposed active surface sites for efficient hydrogen evolution Chem. Sci. 5 4615
Matanović I, Garzon F H and Henson N J 2014 Electro-reduction of nitrogen on molybdenum nitride: structure, energetics, and vibrational spectra from DFT Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16 3014
Cao B, Veith G M, Neuefeind J C, Adzic R R and Khalifah P G 2013 Mixed Close-Packed Cobalt Molybdenum Nitrides as Non-noble Metal Electrocatalysts for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 19186
Ham D J and Lee J S 2009 Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides as Electrode Materials for Low Temperature Fuel Cells Energies 2 873
Ettmayer P 1970 Das System Molybdan–Stickstoff Monatsh. Chem. 101 127
Wang S, Ge H, Sun S, Zhang J, Liu F, Wen X, Yu X, Wang L, Zhang Y, Xu H, Neuefeind J C, Qin Z, Chen C, Jin C, Li Y, He D and Zhao Y 2015 A New Molybdenum Nitride Catalyst with Rhombohedral MoS 2 Structure for Hydrogenation Applications J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 4815
Dyjak S, Kicinski W and Huczko A 2015 Thermite-driven melamine condensation to CxNyHz graphitic ternary polymers: towards an instant, large-scale synthesis of g-C\(_3\)N\(_4\) J. Mater. Chem. A 3 9621
Bockris J O and Potter E C 1952 The mechanism of the cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction J. Electrochem. Soc. 99 169
Shinagawa T, Garcia-esparza A T and Takanabe K 2015 Insight on Tafel slopes from a microkinetic analysis of aqueous electrocatalysis for energy conversion Sci. Rep. 5 13801
Acknowledgements
AKG thanks DST and DeitY, Govt. of India, for financial support. KO thanks UGC, Govt. of India, for fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of the late Professor Charusita Chakravarty.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ojha, K., Banerjee, S. & Ganguli, A.K. Facile charge transport in \(\hbox {FeN}_{\mathrm{x}}/\hbox {Mo}_{2}\hbox {N/CNT}\) nanocomposites for efficient hydrogen evolution reactions. J Chem Sci 129, 989–997 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-017-1302-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-017-1302-6