Abstract
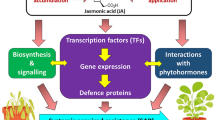
A sustainable balance between defence and growth is essential for optimal fitness under pathogen stress. Plants activate immune response at the cost of normal metabolic requirements. Thus, plants that constitutively activate defence are deprived of growth. Arabidopsis thaliana mutant constitutive defence without defect in growth and development1 (cdd1) is an exception. The cdd1 mutant is constitutive for salicylic acid accumulation, signalling, and defence against biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens, without having much impact on growth. Thus, cdd1 offers an ideal genetic background to identify novel regulators of plant defence. Here we report the differential gene expression profile between cdd1 and wild-type plants as obtained by microarray hybridization. Expression of several defence-related genes also supports constitutive activation of defence in cdd1. We screened T-DNA insertion mutant lines of selected genes, for resistance against virulent bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000). Through bacterial resistance, callose deposition and pathogenesis-associated expression analyses, we identified four novel regulators of plant defence. Resistance levels in the mutants suggest that At2g19810 and [rom] At5g05790 are positive regulators, whereas At1g61370 and At3g42790 are negative regulators of plant defence against bacterial pathogens.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, et al. 2002 MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415 977–983
Bari R and Jones JD 2009 Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 69 473–488
Barth C and Jander G 2006 Arabidopsis myrosinases TGG1 and TGG2 have redundant function in glucosinolate breakdown and insect defense. Plant J. 46 549–562
Bent AF and Mackey D 2007 Elicitors, effectors, and R genes: the new paradigm and a lifetime supply of questions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 45 399–436
Bowling SA, Clarke JD, Liu Y, Klessig DF and Dong X 1997 The cpr5 mutant of Arabidopsis expresses both NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent resistance. Plant Cell 9 1573–1584
Cheng YT, Germain H, Wiermer M, Bi D, Xu F, Garcia AV, Wirthmueller L, Despres C, et al. 2009 Nuclear pore complex component MOS7/Nup88 is required for innate immunity and nuclear accumulation of defense regulators in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21 2503–2516
Choi J, Huh SU, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Paek KH and Hwang I 2010 The cytokinin-activated transcription factor ARR2 promotes plant immunity via TGA3/NPR1-dependent salicylic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 19 284–295
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N 1987 Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162 156–159
Desclos-Theveniau M, Arnaud D, Huang TY, Lin GJC, Chen WY, Lin YC and Zimmerli L 2012 The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-V.5 represses stomatal immunity induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. PLoS Pathog. 8 e1002513
Dong X, Mindrinos M, Davis KR and Ausubel FM 1991 Induction of Arabidopsis defense genes by virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas syringae strains and by a cloned avirulence gene. Plant Cell 3 61–72
Ellis C and Turner JG 2001 The Arabidopsis mutant cev1 has constitutively active jasmonate and ethylene signal pathways and enhanced resistance to pathogens. Plant Cell 13 1025–1033
Giri MK, Swain S, Gautam JK, Singh S, Singh N, Bhattacharjee L and Nandi AK 2014 The Arabidopsis thaliana At4g13040 gene, a unique member of the AP2/EREBP family, is a positive regulator for salicylic acid accumulation and basal defense against bacterial pathogens. J. Plant Physiol. 171 860–867
Gomez-Gomez L, Felix G and Boller T 1999 A single locus determines sensitivity to bacterial flagellin in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 18 277–284
Hofstetter SS, Dudnik A, Widmer H and Dudler R 2013 Arabidopsis YELLOW STRIPE-LIKE7 (YSL7) and YSL8 transporters mediate uptake of Pseudomonas virulence factor syringolin A into plant cells. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 26 1302–1311
Huang P, Chung MS, Ju HW, Na HS, Lee DJ, Cheong HS and Kim CS 2010 Physiological characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana oxidation-related zinc finger 1, a plasma membrane protein involved in oxidative stress. J. Plant Res. 124 699–705
Ishikawa K, Yoshimura K, Harada K, Fukusaki E, Ogawa T, Tamoi M and Shigeoka S 2010 AtNUDX6, an ADP-ribose/NADH pyrophosphohydrolase in Arabidopsis, positively regulates NPR1-dependent salicylic acid signaling. Plant Physiol. 152 2000–2012
Jirage D, Zhou N, Cooper B, Clarke JD, Dong X and Glazebrook J 2001 Constitutive salicylic acid-dependent signaling in cpr1 and cpr6 mutants requires PAD4. Plant J. 26 395–407
Jones JD and Dangl JL 2006 The plant immune system. Nature 444 323–329
Kachroo P, Shanklin J, Shah J, Whittle EJ and Klessig DF 2001 A fatty acid desaturase modulates the activation of defense signaling pathways in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 98 9448–9453
Knoth C and Eulgem T 2008 The oomycete response gene LURP1 is required for defense against Hyaloperonospora parasitica in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 55 53–64
Lee SJ, Jung HJ, Kang H and Kim SY 2012 Arabidopsis zinc finger proteins AtC3H49/AtTZF3 and AtC3H20/AtTZF2 are involved in ABA and JA responses. Plant Cell Physiol. 53 673–686
Lee WY, Lee D, Chung WI and Kwon CS 2009 Arabidopsis ING and Alfin1-like protein families localize to the nucleus and bind to H3K4me3/2 via plant homeodomain fingers. Plant J. 58 511–524
Lu H, Zou Y and Feng N 2010 Overexpression of AHL20 negatively regulates defenses in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 52 801–808
Mir R, Hernandez ML, Abou-Mansour E, Martinez-Rivas JM, Mauch F, Metraux JP and Leon J 2013 Pathogen and Circadian Controlled 1 (PCC1) regulates polar lipid content, ABA-related responses, and pathogen defence in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 64 3385–3395
Monaghan J and Zipfel C 2012 Plant pattern recognition receptor complexes at the plasma membrane. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15 349–357
Monaghan J, Xu F, Gao M, Zhao Q, Palma K, Long C, Chen S, Zhang Y, et al. 2009 Two Prp19-like U-box proteins in the MOS4-associated complex play redundant roles in plant innate immunity. PLoS Pathog. 5 e1000526
Navarro L, Zipfel C, Rowland O, Keller I, Robatzek S, Boller T and Jones JD 2004 The transcriptional innate immune response to flg22. Interplay and overlap with Avr gene-dependent defense responses and bacterial pathogenesis. Plant Physiol. 135 1113–1128
Pieterse CM, Van der Does D, Zamioudis C, Leon-Reyes A and Van Wees SC 2012 Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 28 489–521
Po-Wen C, Singh P and Zimmerli L 2013 Priming of the Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity response upon infection by necrotrophic Pectobacterium carotovorum bacteria. Mol. Plant Pathol. 14 58–70
Qutob D, Kemmerling B, Brunner F, Kufner I, Engelhardt S, Gust AA, Luberacki B, Seitz HU, et al. 2006 Phytotoxicity and innate immune responses induced by Nep1-like proteins. Plant Cell 18 3721–3744
Santner A, Calderon-Villalobos LI and Estelle M 2009 Plant hormones are versatile chemical regulators of plant growth. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 301–307
Seo PJ, Lee AK, Xiang F and Park CM 2008 Molecular and functional profiling of Arabidopsis pathogenesis-related genes: insights into their roles in salt response of seed germination. Plant Cell Physiol. 49 334–344
Shah J, Kachroo P and Klessig DF 1999 The Arabidopsis ssi1 mutation restores pathogenesis-related gene expression in npr1 plants and renders defensin gene expression salicylic acid dependent. Plant Cell 11 191–206
Singh V, Roy S, Singh D and Nandi AK 2014 Arabidopsis flowering locus D influences systemic-acquired-resistance- induced expression and histone modifications of WRKY genes. J. Biosci. 39 119–126
Singh V, Roy S, Giri MK, Chaturvedi R, Chowdhury Z, Shah J and Nandi AK 2013 Arabidopsis thaliana FLOWERING LOCUS D is required for systemic acquired resistance. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 26 1079–1088
Staswick PE, Su W and Howell SH 1992 Methyl jasmonate inhibition of root growth and induction of a leaf protein are decreased in an Arabidopsis thaliana mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 89 6837–6840
Swain S, Roy S, Shah J, Van Wees S, Pieterse CM and Nandi AK 2011 Arabidopsis thaliana cdd1 mutant uncouples the constitutive activation of salicylic acid signalling from growth defects. Mol. Plant Pathol. 12 855–865
Wang D, Guo Y, Wu C, Yang G, Li Y and Zheng C 2008 Genome-wide analysis of CCCH zinc finger family in Arabidopsis and rice. BMC Genomics 9 44
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Ding P, Johnson K and Li X 2012 The ankyrin-repeat transmembrane protein BDA1 functions downstream of the receptor-like protein SNC2 to regulate plant immunity. Plant Physiol. 159 1857–1865
Zhang X, Zhao H, Gao S, Wang WC, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Huang HD, Raikhel N and Jin H 2011 Arabidopsis Argonaute 2 regulates innate immunity via miRNA393(*)-mediated silencing of a Golgi-localized SNARE gene, MEMB12. Mol. Cell 42 356–366
Zheng XY, Spivey NW, Zeng W, Liu PP, Fu ZQ, Klessig DF, He SY and Dong X 2012 Coronatine promotes Pseudomonas syringae virulence in plants by activating a signaling cascade that inhibits salicylic acid accumulation. Cell Host Microbe 11 587–596
Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D, Caniard A, Jones JD, Boller T and Felix G 2006 Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125 749–760
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center, Ohio State University, USA, for mutant seed lines, and Genotypic Technology, Bangalore, India, for microarray experiment. This work is supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India, Grant (No. 38(1358)/13/EMR-II), and UGC grant (F.No. 40-398/2011(SR)) to AKN, and CSIR fellowships to SS and NS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Utpal Nath
[Swain S, Singh N and Nandi AK 2015 Identification of plant defence regulators through transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana cdd1 mutant. J. Biosci. 40 1–10] DOI 10.1007/s12038-014-9498-9
Supplementary materials pertaining to this article are available on the Journal of Biosciences Website at http://www.ias.ac.in/jbiosci/mar2015/supp/Swain.pdf
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1.34 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swain, S., Singh, N. & Nandi, A.K. Identification of plant defence regulators through transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana cdd1 mutant. J Biosci 40, 137–146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-014-9498-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-014-9498-9