Abstract
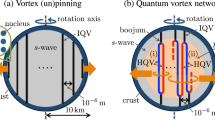
G. Srinivasan et al. (1990) proposed a simple and elegant explanation for the reduction of the neutron star magnetic dipole moment during binary evolution leading to low mass X-ray binaries and eventually to millisecond pulsars: Quantized vortex lines in the neutron star core superfluid will pin against the quantized flux lines of the proton superconductor. As the neutron star spins down in the wind accretion phase of binary evolution, outward motion of vortex lines will reduce the dipole magnetic moment in proportion to the rotation rate. The presence of a toroidal array of flux lines makes this mechanism inevitable and independent of the angle between the rotation and magnetic axes. The incompressibility of the flux-line array (Abrikosov lattice) determines the epoch when the mechanism will be effective throughout the neutron star. Flux vortex pinning will not be effective during the initial young radio pulsar phase. It will, however, be effective and reduce the dipole moment in proportion with the rotation rate during the epoch of spindown by wind accretion as proposed by Srinivasan et al. The mechanism operates also in the presence of vortex creep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, B. P. et al. 2016a, PhRvL, 116, 061102.
Abbott, B. P. et al. 2016b ApJ, 818, L22.
Alpar, M. A. 2008, A new class of radio pulsars – back in 1982, in: A Decade of Accreting Millisecond X-ray Pulsars (AIP Conference Proceedings), edited by R. Wijnands, D. Altamirano & P. Soleri, vol. 1068, pp. 3–8.
Alpar, M. A., Cheng, A. F., Ruderman, M. A., Shaham, J. 1982, Nature, 300, 728.
Alpar, M. A., Anderson, P. W., Pines, D., Shaham, J. 1984a, ApJ, 276, 325.
Alpar, M. A., Langer, S. A., Sauls, J. A. 1984b, ApJ, 282, 533.
Backer, D. C., Kulkarni, S. R., Heiles, C., Davis, M. M., Goss, W. M. 1982, Nature, 300, 615.
Backer D. C., Kulkarni, S. R., Taylor, J. H. 1983, Nature, 301, 314.
Baym, G., Pethick, C. J., Pines, D. 1969, Nature, 224, 673.
Gügercinoğlu, E. 2017, MNRAS, 469, 2313.
Gügercinoğlu, E., Alpar, M. A. 2014, ApJ, 788, L11.
Muslimov, A. G., Tsygan, A. I. 1985, Ap&SS, 115, 43.
Nagae, T. et al. 2004, A&A, 419, 335.
Papitto, A. et al. 2013, Nature, 501, 517.
Patruno, A., Alpar, M. A., van der Klis, M., van den Heuvel, E. P. J. 2012, ApJ, 752, 33.
Passamonti, A, Akgün, T, Pons, J, Miralles, J. A. 2017, arXiv:1704.02016 [astro-ph.HE], accepted by MNRAS.
Pfahl, E., Rappaport, S., Podsiadlowski, P. 2002, ApJ, 571, L37.
Radhakrishnan, V., Srinivasan, G. 1982, Curr. Sci., 51, 1096.
Ruderman, M. A., Zhu, T., Chen, K. 1998, ApJ 492, 267.
Sauls, J. A. 1989, in: Timing Neutron Stars, NATO ASI Series C, 262, edited by H. Ogelman & E. P. J. van den Heuvel, Kluwer, Dordrecht, p. 457.
Sidery, T., Alpar, M. A. 2009, MNRAS, 400, 1859.
Srinivasan, G. 1989, Astron Astrophys Rev., 1, 209.
Srinivasan, G., Bhattacharya, D. , Muslimov, A. G., Tsygan, A. I. 1990, Curr. Sci., 59, 31.
Theuns, T., Bofn, H. M. J., Jorissen, A. 1996, MNRAS, 280, 1264.
Wijnands, R., van der Klis, M. 1998, Nature, 394, 344.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to wish G. Srinivasan a very happy 75th birthday and congratulate and thank him for his many brilliant contributions. The author first met G. Srinivasan in 1973 when he joined the Theory of Condensed Matter Group at the Cavendish Laboratory as a Ph.D. student of Phil Anderson and was charmed by his bright ideas and bright smile. The author also thanks Erbil Gügercinoğlu for his careful reading and suggestions and Onur Akbal for help with the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alpar, M.A. Flux-Vortex Pinning and Neutron Star Evolution. J Astrophys Astron 38, 44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-017-9473-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-017-9473-6