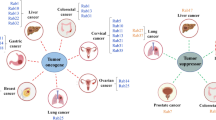
Abstract
Rab proteins are important components of small GTPases and play crucial roles in regulating intracellular transportation and cargo delivery. Maintaining the proper functions of Rab proteins is essential for normal cellular activities such as cell signaling, division, and survival. Due to their vital and irreplaceable role in regulating intracellular vesicle transportation, accumulated researches have shown that the abnormalities of Rab proteins and their effectors are closely related to human diseases. Here, this review focused on Rab21, a member of the Rab family, and introduced the structures and functions of Rab21, as well as the regulatory mechanisms of Rab21 in human diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and inflammation. In summary, we described in detail the role of Rab21 in human diseases and provide insights into the potential of Rab21 as a therapeutic target for diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data availability is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
Li G, Marlin MC (2015) Rab family of GTPases. Methods Mol Biol 1298:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2569-8_1
Brennwald P, Novick P (1993) Interactions of 3 domains distinguishing the RAS-related GTP-binding proteins YPT1 and SEC4. Nature 362(6420):560–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/362560a0
Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC (2001) Evolution of the Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins. J Mol Biol 313(4):889–901. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.5072
Seabra MC, Wasmeier C (2004) Controlling the location and activation of Rab GTPases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(4):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2004.06.014
Grosshans BL, Ortiz D, Novick P (2006) Rabs and their effectors: achieving specificity in membrane traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A 103(32):11821–11827. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601617103
Guadagno NA, Progida C (2019) Rab GTPases: switching to human diseases. Cells 8(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080909
Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ (2011) Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev 91(1):119–149. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00059.2009
Veleri S, Punnakkal P, Dunbar GL, Maiti P (2018) Molecular insights into the roles of Rab proteins in intracellular dynamics and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuromolecular Med 20(1):18–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8479-9
Kiral FR, Kohrs FE, Jin EJ, Hiesinger PR (2018) Rab GTPases and membrane trafficking in neurodegeneration. Curr Biol 28(8):R471–R486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.010
Tzeng HT, Wang YC (2016) Rab-mediated vesicle trafficking in cancer. J Biomed Sci 23(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-016-0287-7
Prashar A, Schnettger L, Bernard EM, Gutierrez MG (2017) Rab GTPases in immunity and inflammation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:435. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00435
Langemeyer L, Frohlich F, Ungermann C (2018) Rab GTPase function in endosome and lysosome biogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 28(11):957–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2018.06.007
Guerra F, Bucci C (2016) Multiple roles of the small GTPase Rab7. Cells 5(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5030034
Guichard A, Nizet V, Bier E (2014) RAB11-mediated trafficking in host-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 12(9):624–634. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3325
Sultana P, Novotny J (2022) Rab11 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. ASN Neuro 14:17590914221142360. https://doi.org/10.1177/17590914221142360
Chavrier P, Simons K, Zerial M (1992) The complexity of the Rab and Rho GTP-binding protein subfamilies revealed by a PCR cloning approach. Gene 112(2):261–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(92)90387-5
Olkkonen VM, Dupree P, Killisch I, Lutcke A, Zerial M, Simons K (1993) Molecular-cloning and subcellular-localization of 3 GTP-binding proteins of the rab subfamily. J Cell Sci 106:1249–1261
Opdam FJM, Kamps G, Croes H, van Bokhoven H, Ginsel LA, Fransen JAM (2000) Expression of Rab small GTPases in epithelial Caco-2 cells: Rab21 is an apically located GTP-binding protein in polarised intestinal epithelial cells. Eur J Cell Biol 79(5):308–316. https://doi.org/10.1078/s0171-9335(04)70034-5
Zhang X, He X, Fu XY, Chang Z (2006) Varp is a Rab21 guanine nucleotide exchange factor and regulates endosome dynamics. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 6):1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02810
Delprato A, Lambright DG (2007) Structural basis for Rab GTPase activation by VPS9 domain exchange factors. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14(5):406–412. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1232
Delprato A, Merithew E, Lambright DG (2004) Structure, exchange determinants, and family-wide rab specificity of the tandem helical bundle and Vps9 domains of Rabex-5. Cell 118(5):607–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.009
Jean S, Cox S, Schmidt EJ, Robinson FL, Kiger A (2012) Sbf/MTMR13 coordinates PI(3)P and Rab21 regulation in endocytic control of cellular remodeling. Mol Biol Cell 23(14):2723–2740. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-05-0375
Sohn YS, Shin HC, Park WS, Ge J, Kim CH, Lee BL, Heo WD, Jung JU et al (2015) Lpg0393 of Legionella pneumophila is a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor for Rab5, Rab21 and Rab22. PLoS One 10(3):e0118683. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118683
Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC (2000) The mammalian Rab family of small GTPases: definition of family and subfamily sequence motifs suggests a mechanism for functional specificity in the Ras superfamily. J Mol Biol 301(4):1077–1087. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4010
Saito K, Murai J, Kajiho H, Kontani K, Kurosu H, Katada T (2002) A novel binding protein composed of homophilic tetramer exhibits unique properties for the small GTPase Rab5. J Biol Chem 277(5):3412–3418. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106276200
Kajiho H, Saito K, Tsujita K, Kontani K, Araki Y, Kurosu H, Katada T (2003) RIN3: a novel Rab5 GEF interacting with amphiphysin II involved in the early endocytic pathway. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 20):4159–4168. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00718
Tall GG, Barbieri MA, Stahl PD, Horazdovsky BF (2001) Ras-activated endocytosis is mediated by the Rab5 guanine nucleotide exchange activity of RIN1. Dev Cell 1(1):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1534-5807(01)00008-9
Kajiho H, Sakurai K, Minoda T, Yoshikawa M, Nakagawa S, Fukushima S, Kontani K, Katada T (2011) Characterization of RIN3 as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the Rab5 subfamily GTPase Rab31. J Biol Chem 286(27):24364–24373. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.172445
Simpson JC, Griffiths G, Wessling-Resnick M, Fransen JAM, Bennett H, Jones AT (2004) A role for the small GTPase Rab21 in the early endocytic pathway. J Cell Sci 117(26):6297–6311. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01560
Khurana T, Brzostowski JA, Kimmel AR (2005) A Rab21/LIM-only/CH-LIM complex regulates phagocytosis via both activating and inhibitory mechanisms. EMBO J 24(13):2254–2264. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600716
Pellinen T, Arjonen A, Vuoriluoto K, Kallio K, Fransen JA, Ivaska J (2006) Small GTPase Rab21 regulates cell adhesion and controls endosomal traffic of beta1-integrins. J Cell Biol 173(5):767–780. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200509019
Moreno-Layseca P, Jantti NZ, Godbole R, Sommer C, Jacquemet G, Al-Akhrass H, Conway JRW, Kronqvist P et al (2021) Cargo-specific recruitment in clathrin- and dynamin-independent endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol 23(10):1073–1084. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00767-x
Del Olmo T, Lauzier A, Normandin C, Larcher R, Lecours M, Jean D, Lessard L, Steinberg F et al (2019) APEX2-mediated RAB proximity labeling identifies a role for RAB21 in clathrin-independent cargo sorting. EMBO Rep 20(2). https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201847192
Pei Y, Lv S, Shi Y, Jia J, Ma M, Han H, Zhang R, Tan J et al (2022) RAB21 controls autophagy and cellular energy homeostasis by regulating retromer-mediated recycling of SLC2A1/GLUT1. Autophagy 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2022.2114271
Tower-Gilchrist C, Lee E, Sztul E (2011) Endosomal trafficking of the G protein-coupled receptor somatostatin receptor 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 413(4):555–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.137
Zhu G, Chen J, Liu J, Brunzelle JS, Huang B, Wakeham N, Terzyan S, Li X et al (2007) Structure of the APPL1 BAR-PH domain and characterization of its interaction with Rab5. EMBO J 26(14):3484–3493. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601771
Egami Y, Araki N (2008) Characterization of Rab21-positive tubular endosomes induced by PI3K inhibitors. Exp Cell Res 314(4):729–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.11.018
Yang X, Zhang Y, Li S, Liu C, Jin Z, Wang Y, Ren F, Chang Z (2012) Rab21 attenuates EGF-mediated MAPK signaling through enhancing EGFR internalization and degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 421(4):651–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.04.049
Wu AP, Qing H, Quan ZZ (2021) The roles of Rab protein family in neurological diseases. Yi Chuan 43(1):16–29. https://doi.org/10.16288/j.yczz.20-318
Alberts P, Rudge R, Hinners I, Muzerelle A, Martinez-Arca S, Irinopoulou T, Marthiens V, Tooze S et al (2003) Cross talk between tetanus neurotoxin-insensitive vesicle-associated membrane protein-mediated transport and L1-mediated adhesion. Mol Biol Cell 14(10):4207–4220. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e03-03-0147
Martinez-Arca S, Coco S, Mainguy G, Schenk U, Alberts P, Bouille P, Mezzina M, Prochiantz A et al (2001) A common exocytotic mechanism mediates axonal and dendritic outgrowth. J Neurosci 21(11):3830–3838. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.21-11-03830.2001
Martinez-Arca S, Rudge R, Vacca M, Raposo G, Camonis J, Proux-Gillardeaux V, Daviet L, Formstecher E et al (2003) A dual mechanism controlling the localization and function of exocytic v-SNAREs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A 100(15):9011–9016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1431910100
Burgo A, Sotirakis E, Simmler MC, Verraes A, Chamot C, Simpson JC, Lanzetti L, Proux-Gillardeaux V et al (2009) Role of Varp, a Rab21 exchange factor and TI-VAMP/VAMP7 partner, in neurite growth. EMBO Rep 10(10):1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2009.186
Shikanai M, Ito S, Nishimura YV, Akagawa R, Fukuda M, Yuzaki M, Nabeshima YI, Kawauchi T (2023) Rab21 regulates caveolin-1-mediated endocytic trafficking to promote immature neurite pruning. EMBO Rep 24(3):e54701. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202254701
O'Brien RJ, Wong PC (2011) Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:185–204. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113613
De Strooper B (2003) Aph-1, Pen-2, and nicastrin with presenilin generate an active gamma-secretase complex. Neuron 38(1):9–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00205-8
Sun ZZ, Xie YJ, Chen YT, Yang QH, Quan ZZ, Dai RJ, Qing H (2018) Rab21, a novel PS1 interactor, regulates gamma-secretase activity via PS1 subcellular distribution. Mol Neurobiol 55(5):3841–3855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0606-3
Liu P, Wu A, Li H, Zhang J, Ni J, Quan Z, Qing H (2022) Rab21 protein is degraded by both the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Int J Mol Sci 23(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031131
Popoff V, Adolf F, Brugger B, Wieland F (2011) COPI budding within the Golgi stack. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(11):a005231. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005231
Pastor-Cantizano N, Montesinos JC, Bernat-Silvestre C, Marcote MJ, Aniento F (2016) p24 family proteins: key players in the regulation of trafficking along the secretory pathway. Protoplasma 253(4):967–985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0858-6
Pardossi-Piquard R, Bohm C, Chen F, Kanemoto S, Checler F, Schmitt-Ulms G, St George-Hyslop P, Fraser PE (2009) TMP21 transmembrane domain regulates gamma-secretase cleavage. J Biol Chem 284(42):28634–28641. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.059345
Del Olmo T, Lacarriere-Keita C, Normandin C, Jean D, Boisvert F-M, Jean S (2019) RAB21 interacts with TMED10 and modulates its localization and abundance. Biol Open 8(9). https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.045336
Anand S, Khan MA, Khushman M, Dasgupta S, Singh S, Singh AP (2020) Comprehensive analysis of expression, clinicopathological association and potential prognostic significance of RABs in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155580
Hognas G, Tuomi S, Veltel S, Mattila E, Murumagi A, Edgren H, Kallioniemi O, Ivaska J (2012) Cytokinesis failure due to derailed integrin traffic induces aneuploidy and oncogenic transformation in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 31(31):3597–3606. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.527
Ma X, Wang Z, Ren H, Bao X, Zhang Y, Wang B, Ruan D (2020) Long non-coding RNA GAS5 suppresses tumor progression and enhances the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer through the miR-320a/RAB21 axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:8833–8845. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S244123
Liu H (2012) MicroRNAs in breast cancer initiation and progression. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(21):3587–3599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1128-9
Ye F, Tang H, Liu Q, Xie X, Wu M, Liu X, Chen B, Xie X (2014) miR-200b as a prognostic factor in breast cancer targets multiple members of RAB family. J Transl Med 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-12-17
Li P, Sheng C, Huang L, Zhang H, Huang L, Cheng Z, Zhu Q (2014) MiR-183/-96/-182 cluster is up-regulated in most breast cancers and increases cell proliferation and migration. Breast Cancer Res 16(6). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-014-0473-z
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110(6):673–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00971-6
Pellinen T, Tuomi S, Arjonen A, Wolf M, Edgren H, Meyer H, Grosse R, Kitzing T et al (2008) Integrin trafficking regulated by Rab21 is necessary for cytokinesis. Dev Cell 15(3):371–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.08.001
Alanko J, Mai A, Jacquemet G, Schauer K, Kaukonen R, Saari M, Goud B, Ivaska J (2015) Integrin endosomal signalling suppresses anoikis. Nat Cell Biol 17(11):1412–1421. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3250
Alanko J, Ivaska J (2016) Endosomes: emerging platforms for integrin-mediated FAK signalling. Trends Cell Biol 26(6):391–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.02.001
Xu W, Wang P, Petri B, Zhang Y, Tang W, Sun L, Kress H, Mann T et al (2010) Integrin-induced PIP5K1C kinase polarization regulates neutrophil polarization, directionality, and in vivo infiltration. Immunity 33(3):340–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.08.015
Sadik CD, Kim ND, Luster AD (2011) Neutrophils cascading their way to inflammation. Trends Immunol 32(10):452–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2011.06.008
Nourshargh S, Alon R (2014) Leukocyte migration into inflamed tissues. Immunity 41(5):694–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.008
Yuan Q, Ren C, Xu W, Petri B, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Kubes P, Wu D et al (2017) PKN1 directs polarized RAB21 vesicle trafficking via RPH3A and is important for neutrophil adhesion and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Rep 19(12):2586–2597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.080
Li P, Wu YH, Zhu YT, Li MX, Pei HH (2019) Requirement of Rab21 in LPS-induced TLR4 signaling and pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages and monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508(1):169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.074
Wang N, Meng W, Jia R, Xiang S (2019) Rab GTPase 21 mediates caerulin-induced TRAF3-MKK3-p38 activation and acute pancreatitis response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 518(1):50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.007
Chan CS, Weeber EJ, Zong L, Fuchs E, Sweatt JD, Davis RL (2006) Beta 1-integrins are required for hippocampal AMPA receptor-dependent synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity, and working memory. J Neurosci 26(1):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4110-05.2006
Mathys H, Davila-Velderrain J, Peng Z, Gao F, Mohammadi S, Young JZ, Menon M, He L et al (2019) Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 570(7761):332–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1195-2
Acknowledgements
We thank the Biological and Medical Engineering Core Facilities of Beijing Institute of Technology for supplying our experimental equipment.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology major projects (STI2030-Major Projects 2022ZD0206800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 92049102), Beijing Nova Program (Grant No. 20220484083), and Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 7222113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XJ.L and ZZ. Q conceived and designed the studies and wrote the manuscript. JJ. N provided some valuable advice for this article. H. Q edited and advised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the data analysis and presentation in the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Ni, J., Qing, H. et al. The Regulatory Mechanism of Rab21 in Human Diseases. Mol Neurobiol 60, 5944–5953 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03454-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03454-0