Abstract
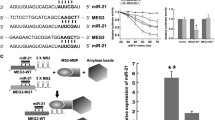
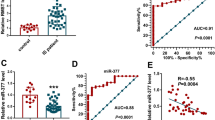
Much efforts have been made to probe the mechanism underlying ischemic stroke (IS). This study was proposed to uncover the role of long non-coding RNA rhabdomyosarcoma 2 related transcript (RMST) in IS through microRNA-221-3p (miR-221-3p)/phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 1 (PIK3R1)/transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) axis. Neurological behavioral function, pathological changes in brain tissue, oxidative stress, and inflammation responses in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice were tested. RMST, miR-221-3p, PIK3R1, and TGF-β signaling-related protein expression in brain tissues of MCAO mice were detected. RMST and PIK3R1 were elevated, miR-221-3p was downregulated, and TGF-β pathway was activated in mice after MCAO. Restored miR-221-3p or depleted RMST improved neurological behavioral functions, relieved pathological injury in brain tissue, and repressed oxidative stress and inflammation in mice after MCAO. Depleted PIK3R1 or restored miR-221-3p offsets the negative effects of overexpressed RMST on mice with MCAO. The present work highlights that RMST augments IS through reducing miR-221-3p-mediated regulation of PIK3R1 and activating TGF-β pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Chen C et al (2020) Electroacupuncture pretreatment prevents ischemic stroke and inhibits Wnt signaling-mediated autophagy through the regulation of GSK-3beta phosphorylation. Brain Res Bull 158:90–98
Li X et al (2020) Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde in ischemic stroke. Int Immunopharmacol 82:106353
Xu T et al (2020) Serum omentin-1 and risk of one-year mortality in patients with ischemic stroke. Clin Chim Acta 505:167–171
Feng H et al (2020) Repurposing antimycotic ciclopirox olamine as a promising anti-ischemic stroke agent. Acta Pharm Sin B 10(3):434–446
Hou XX, Cheng H (2018) Long non-coding RNA RMST silencing protects against middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced ischemic stroke. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(4):2602–2608
Cheng H et al (2020) LncRNA RMST-mediated miR-107 transcription promotes OGD-induced neuronal apoptosis via interacting with hnRNPK. Neurochem Int 133:104644
Sun XL et al (2019) LncRNA RMST activates TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB signaling and promotes activation of microglial cells via competitively binding with hnRNPK. IUBMB Life 71(11):1785–1793
Wu J et al (2019) MicroRNA target gene prediction of ischemic stroke by using variational Bayesian inference for Gauss mixture model. Exp Ther Med 17(4):2734–2740
Peng H et al (2020) MuicroRNA-221 participates in cerebral ischemic stroke by modulating endothelial cell function by regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Ther Med 19(1):443–450
Zhou XB et al (2020) LncRNAGAS5 sponges miRNA-221 to promote neurons apoptosis by up-regulated PUMA under hypoxia condition. Neurol Res 42(1):8–16
Chang TY et al (2014) miRNome traits analysis on endothelial lineage cells discloses biomarker potential circulating microRNAs which affect progenitor activities. BMC Genomics 15:802
Prasad SS et al (2010) Retinal gene expression after central retinal artery ligation: effects of ischemia and reperfusion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(12):6207–6219
Eyileten C et al. (2018) MicroRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in ischemic stroke-a comprehensive review and bioinformatic analysis. Cells 7(12)
Zhang K et al (2019) ALK5 signaling pathway mediates neurogenesis and functional recovery after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats via Gadd45b. Cell Death Dis 10(5):360
Meng H et al (2016) LRG1 promotes angiogenesis through upregulating the TGFbeta1 pathway in ischemic rat brain. Mol Med Rep 14(6):5535–5543
Jin J et al (2019) LRG1 promotes apoptosis and autophagy through the TGFbeta-smad1/5 signaling pathway to exacerbate ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neuroscience 413:123–134
Li J et al (2019) miR-219-5p inhibits tau phosphorylation by targeting TTBK1 and GSK-3beta in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Biochem 120(6):9936–9946
Xie YL, Zhang B, Jing L (2018) MiR-125b blocks Bax/cytochrome C/caspase-3 apoptotic signaling pathway in rat models of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting p53. Neurol Res 40(10):828–837
Liu XH et al (2019) Early constraint-induced movement therapy affects behavior and neuronal plasticity in ischemia-injured rat brains. Neural Regen Res 14(5):775–782
Doeppner TR et al (2014) Effects of neural progenitor cells on post-stroke neurological impairment-a detailed and comprehensive analysis of behavioral tests. Front Cell Neurosci 8:338
Hua Y et al (2002) Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 33(10):2478–2484
Wang Y et al (2019) Methylation-dependent transcriptional repression of RUNX3 by KCNQ1OT1 regulates mouse cardiac microvascular endothelial cell viability and inflammatory response following myocardial infarction. FASEB J 33(12):13145–13160
Qiao P, Yan H, Wang J (2020) EGb761 protects brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury through lncRNA Rmst/miR-150 axis. Neurochem Res 45(10):2398–2408
Jia L et al (2015) Circulating miR-145 is associated with plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in acute ischemic stroke patients. Cell Biochem Funct 33(5):314–319
Tsai PC et al (2013) Serum microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 as potential biomarkers for cerebrovascular disease. J Vasc Res 50(4):346–354
Zhao D et al (2018) miR-221 alleviates the inflammatory response and cell apoptosis of neuronal cell through targeting TNFAIP2 in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion. NeuroReport 29(8):655–660
Oh SE et al (2018) The Parkinson’s disease gene product DJ-1 modulates miR-221 to promote neuronal survival against oxidative stress. Redox Biol 19:62–73
Zhou Y, Richards AM, Wang P (2019) MicroRNA-221 is cardioprotective and anti-fibrotic in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 17:185–197
Cai W et al (2019) MicroRNA-24 attenuates vascular remodeling in diabetic rats through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 29(6):621–632
Zhu H et al (2017) TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling pathway suppresses cell apoptosis in cerebral ischemic stroke rats. Med Sci Monit 23:366–376
Lou Z et al (2018) Upregulation of NOX2 and NOX4 mediated by TGF-beta signaling pathway exacerbates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion oxidative stress injury. Cell Physiol Biochem 46(5):2103–2113
Acknowledgements
We thank the associate editor and the reviewers for their useful feedback that improved this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Fund of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, subject No. Kybs2015-02 and Funds for postdoctoral research in Heilongjiang Province and Heilongjiang Health and Family Planning Commission Research Project (2017–078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wenjuan Liu and Kuo Tian contributed to study design; Jie Li and Ning Wang contributed to manuscript editing; Huan Nie and Shan Wang contributed to experimental studies; Tongtong Jiang and Xuehan Ma contributed to data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This experiment was reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethics Association of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University. Great efforts have been made to relieve pain of animals.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jie Li and Ning Wang are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, N., Nie, H. et al. Long Non-coding RNA RMST Worsens Ischemic Stroke via MicroRNA-221-3p/PIK3R1/TGF-β Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 59, 2808–2821 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02632-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02632-2