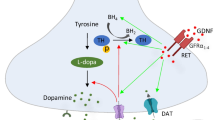
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative movement disorder with unclear etiology and only symptomatic treatment to date. Toward the development of novel disease-modifying agents, neurotrophic factors represent a reasonable and promising therapeutic approach. However, despite the robust preclinical evidence, clinical trials using glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and neurturin have been unsuccessful. In this direction, the therapeutic potential of other trophic factors in PD and the elucidation of the underlying molecular mechanisms are of paramount importance. The liver growth factor (LGF) is an albumin–bilirubin complex acting as a hepatic mitogen, which also exerts regenerative effects on several extrahepatic tissues including the brain. Accumulating evidence suggests that intracerebral and peripheral administration of LGF can enhance the outgrowth of nigrostriatal dopaminergic axonal terminals; promote the survival, migration, and differentiation of neuronal stem cells; and partially protect against dopaminergic neuronal loss in the substantia nigra of PD animal models. In most studies, these effects are accompanied by improved motor behavior of the animals. Potential underlying mechanisms involve transient microglial activation, TNF-α upregulation, and activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) and of the transcription factor cyclic AMP response-element binding protein (CREB), along with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. Herein, we summarize recent preclinical evidence on the potential role of LGF in PD pathogenesis, aiming to shed more light on the underlying molecular mechanisms and reveal novel therapeutic opportunities for this debilitating disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LGF:
-
Liver growth factor
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- GDNF:
-
Glial-derived neurotrophic factor
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CDNF:
-
Cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor
- ERK 1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2
- CREB:
-
Cyclic AMP response-element binding protein
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxy-dopamine
- SVZ:
-
Subventricular zone
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- TGF-α:
-
Tumor growth factor-α
- APOE:
-
Apolipoprotein E
- NSCs:
-
Neuronal stem cells
References
Rizek P, Kumar N, Jog MS (2016) An update on the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. CMAJ 188(16):1157–1165
Angelopoulou E et al (2020) Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3) protein as a possible therapeutic target for Parkinson's disease: Molecular mechanisms connecting neuroinflammation to alpha-synuclein spreading pathology. Biology (Basel):9(4)
Angelopoulou E, Paudel YN, Shaikh MF, Piperi C (2020) Fractalkine (CX3CL1) signaling and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: Potential clinical and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Res 158:104930
Alecu I, Bennett SAL (2019) Dysregulated lipid metabolism and its role in alpha-synucleinopathy in Parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci 13:328
Yuan Y, Sun J, Zhao M, Hu J, Wang X, du G, Chen NH (2010) Overexpression of alpha-synuclein down-regulates BDNF expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30(6):939–946
Palasz, E., et al., BDNF as a promising therapeutic agent in Parkinson's disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2020. 21(3).
Ziebell, M., et al., Striatal dopamine transporter binding correlates with serum BDNF levels in patients with striatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging, 2012. 33(2): p. 428 e1–5.
Sampaio TB, Savall AS, Gutierrez MEZ, Pinton S (2017) Neurotrophic factors in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Neural Regen Res 12(4):549–557
Nevalainen N, Chermenina M, Rehnmark A, Berglöf E, Marschinke F, Strömberg I (2010) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is crucial for long-term maintenance of the nigrostriatal system. Neuroscience 171(4):1357–1366
Lindholm P, Voutilainen MH, Laurén J, Peränen J, Leppänen VM, Andressoo JO, Lindahl M, Janhunen S et al (2007) Novel neurotrophic factor CDNF protects and rescues midbrain dopamine neurons in vivo. Nature 448(7149):73–77
Schrag A, Quinn N (2000) Dyskinesias and motor fluctuations in Parkinson's disease. A community-based study. Brain 123(Pt 11):2297–2305
Sullivan AM, O'Keeffe GW (2016) Neurotrophic factor therapy for Parkinson's disease: Past, present and future. Neural Regen Res 11(2):205–207
Mahato AK, Sidorova YA (2020) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factors (GFLs) and small molecules targeting RET receptor for the treatment of pain and Parkinson's disease. Cell Tissue Res 382:147–160
Yu Y, Lang XY, Li XX, Gu RZ, Liu QS, Lan R, Qin XY (2019) 2,3,5,4'-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-d-glucoside attenuates MPP+/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo by restoring the BDNF-TrkB and FGF2-Akt signaling axis and inhibition of apoptosis. Food Funct 10(9):6009–6019
Sun S et al (2020) GDNF promotes survival and therapeutic efficacy of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Cell Transplant 29:963689720908512
Reyes-Corona D, Vázquez-Hernández N, Escobedo L, Orozco-Barrios CE, Ayala-Davila J, Moreno MG, Amaro-Lara ME, Flores-Martinez YM et al (2017) Neurturin overexpression in dopaminergic neurons induces presynaptic and postsynaptic structural changes in rats with chronic 6-hydroxydopamine lesion. PLoS One 12(11):e0188239
Singh S, Ahmad R, Mathur D, Sagar RK, Krishana B (2006) Neuroprotective effect of BDNF in young and aged 6-OHDA treated rat model of Parkinson disease. Indian J Exp Biol 44(9):699–704
Migliore MM, Ortiz R, Dye S, Campbell RB, Amiji MM, Waszczak BL (2014) Neurotrophic and neuroprotective efficacy of intranasal GDNF in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 274:11–23
Horger BA, Nishimura MC, Armanini MP, Wang LC, Poulsen KT, Rosenblad C, Kirik D, Moffat B et al (1998) Neurturin exerts potent actions on survival and function of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 18(13):4929–4937
Whone A, Luz M, Boca M, Woolley M, Mooney L, Dharia S, Broadfoot J, Cronin D et al (2019) Randomized trial of intermittent intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson's disease. Brain 142(3):512–525
Marks WJ Jr, Bartus RT, Siffert J, Davis CS, Lozano A, Boulis N, Vitek J, Stacy M et al (2010) Gene delivery of AAV2-neurturin for Parkinson's disease: A double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 9(12):1164–1172
Diaz-Gil JJ et al (1986) Purification of a liver DNA-synthesis promoter from plasma of partially hepatectomized rats. Biochem J 235(1):49–55
Diaz-Gil JJ et al (1987) Identification of a liver growth factor as an albumin-bilirubin complex. Biochem J 243(2):443–448
Gonzalo-Gobernado R, Calatrava-Ferreras L, Perucho J, Reimers D, Casarejos MJ, Herranz AS, Jimenez-Escrig A, Diaz-Gil JJ et al (2014) Liver growth factor as a tissue regenerating factor in neurodegenerative diseases. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 9(3):173–180
Gonzalo-Gobernado R, Reimers D, Herranz AS, Díaz-Gil JJ, Osuna C, Asensio MJ, Baena S, Rodríguez-Serrano M et al (2009) Mobilization of neural stem cells and generation of new neurons in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats by intracerebroventricular infusion of liver growth factor. J Histochem Cytochem 57(5):491–502
Perez-Crespo M et al (2011) Effect of liver growth factor on both testicular regeneration and recovery of spermatogenesis in busulfan-treated mice. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 9:21
Calatrava-Ferreras L et al (2016) Liver growth factor (LGF) upregulates frataxin protein expression and reduces oxidative stress in Friedreich's ataxia transgenic mice. Int J Mol Sci:17(12)
Gonzalo-Gobernado R et al (2020) Liver growth factor "LGF" as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol Sci:21(23)
Gonzalo-Gobernado R, Calatrava-Ferreras L, Reimers D, Herranz AS, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Miranda C, Jiménez-Escrig A, Díaz-Gil JJ et al (2013) Neuroprotective activity of peripherally administered liver growth factor in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 8(7):e67771
Gonzalo-Gobernado R et al (2020) Liver growth factor induces glia-associated neuroprotection in an in vitro model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Sci:10(5)
Reimers D, Herranz AS, Diaz-Gil JJ, Lobo MVT, Paíno CL, Alonso R, Asensio MJ, Gonzalo-Gobernado R et al (2006) Intrastriatal infusion of liver growth factor stimulates dopamine terminal sprouting and partially restores motor function in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. J Histochem Cytochem 54(4):457–465
Reimers D, Osuna C, Gonzalo-Gobernado R, S. Herranz A, Jose Diaz-Gil J, Jimenez-Escrig A, Jose Asensio M, Miranda C et al (2012) Liver growth factor promotes the survival of grafted neural stem cells in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 7(1):15–25
O'Keeffe GW, Sullivan AM (2018) Evidence for dopaminergic axonal degeneration as an early pathological process in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 56:9–15
Kordower JH, Olanow CW, Dodiya HB, Chu Y, Beach TG, Adler CH, Halliday GM, Bartus RT (2013) Disease duration and the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson's disease. Brain 136(Pt 8):2419–2431
Connor B, Kozlowski DA, Unnerstall JR, Elsworth JD, Tillerson JL, Schallert T, Bohn MC (2001) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) gene delivery protects dopaminergic terminals from degeneration. Exp Neurol 169(1):83–95
Tieu K (2011) A guide to neurotoxic animal models of Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1(1):a009316
Jeon BS, Jackson-Lewis V, Burke RE (1995) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesion of the rat substantia nigra: Time course and morphology of cell death. Neurodegeneration 4(2):131–137
Sauer H, Oertel WH (1994) Progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons following intrastriatal terminal lesions with 6-hydroxydopamine: A combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 59(2):401–415
Branchi I, D'Andrea I, Armida M, Cassano T, Pèzzola A, Potenza RL, Morgese MG, Popoli P et al (2008) Nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson's disease: Investigating early-phase onset of behavioral dysfunction in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model. J Neurosci Res 86(9):2050–2061
Przedborski S et al (1995) Dose-dependent lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway induced by intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Neuroscience 67(3):631–647
Daubner SC, Le T, Wang S (2011) Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 508(1):1–12
Bilge SS, Günaydin C, Önger ME, Bozkurt A, Avci B (2020) Neuroprotective action of agmatine in rotenone-induced model of Parkinson's disease: Role of BDNF/cREB and ERK pathway. Behav Brain Res 392:112692
Gu X, Liu L, Shen Q, Xing D (2017) Photoactivation of ERK/CREB/VMAT2 pathway attenuates MPP(+)-induced neuronal injury in a cellular model of Parkinson's disease. Cell Signal 37:103–114
Feng Z, Zhang L, Wang S, Hong Q (2020) Circular RNA circDLGAP4 exerts neuroprotective effects via modulating miR-134-5p/CREB pathway in Parkinson's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 522(2):388–394
Ralay Ranaivo H, Wainwright MS (2010) Albumin activates astrocytes and microglia through mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Brain Res 1313:222–231
Lee HT, Chang YC, Tu YF, Huang CC (2010) CREB activation mediates VEGF-A's protection of neurons and cerebral vascular endothelial cells. J Neurochem 113(1):79–91
Zhao X, Moore DL (2018) Neural stem cells: Developmental mechanisms and disease modeling. Cell Tissue Res 371(1):1–6
Lu Q et al (2020) Icariin sustains the proliferation and differentiation of Abeta25-35-treated hippocampal neural stem cells via the BDNF-TrkB-ERK/Akt signaling pathway. Neurol Res:1–10
Dong Z, Su L, Mino J (2007) Effects of endothelial cells on renewal and differentiation of neural stem cells. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 24(5):1184–1186
Shen Q et al (2004) Endothelial cells stimulate self-renewal and expand neurogenesis of neural stem cells. Science 304(5675):1338–1340
Yang M, Stull ND, Berk MA, Snyder EY, Iacovitti L (2002) Neural stem cells spontaneously express dopaminergic traits after transplantation into the intact or 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat. Exp Neurol 177(1):50–60
Liste I, Garcia-Garcia E, Martinez-Serrano A (2004) The generation of dopaminergic neurons by human neural stem cells is enhanced by Bcl-XL, both in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci 24(48):10786–10795
Bernaus A, Blanco S, Sevilla A (2020) Glia crosstalk in neuroinflammatory diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 14:209
Hampel H, Caraci F, Cuello AC, Caruso G, Nisticò R, Corbo M, Baldacci F, Toschi N et al (2020) A path toward precision medicine for neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease. Front Immunol 11:456
Probert L (2015) TNF and its receptors in the CNS: The essential, the desirable and the deleterious effects. Neuroscience 302:2–22
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2008) Glial reactions in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 23(4):474–483
Yasuhara T, Shingo T, Kobayashi K, Takeuchi A, Yano A, Muraoka K, Matsui T, Miyoshi Y et al (2004) Neuroprotective effects of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) upon dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurosci 19(6):1494–1504
Batchelor PE, Liberatore GT, Wong JYF, Porritt MJ, Frerichs F, Donnan GA, Howells DW (1999) Activated macrophages and microglia induce dopaminergic sprouting in the injured striatum and express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci 19(5):1708–1716
Cui M, Aras R, Christian WV, Rappold PM, Hatwar M, Panza J, Jackson-Lewis V, Javitch JA et al (2009) The organic cation transporter-3 is a pivotal modulator of neurodegeneration in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(19):8043–8048
Mizuno Y, Sone N, Saitoh T (1987) Effects of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion on activities of the enzymes in the electron transport system in mouse brain. J Neurochem 48(6):1787–1793
Cho SG, Yi SY, Yoo YS (2005) IFNgamma and TNFalpha synergistically induce neurite outgrowth on PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 378(1):49–54
Remy S et al (2003) Lipopolysaccharide and TNFalpha regulate the expression of GDNF, neurturin and their receptors. Neuroreport 14(11):1529–1534
Sriram K, Matheson JM, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, Luster MI, O'Callaghan JP (2006) Deficiency of TNF receptors suppresses microglial activation and alters the susceptibility of brain regions to MPTP-induced neurotoxicity: Role of TNF-alpha. FASEB J 20(6):670–682
Kuno, R., Yoshida Y., Nitta A., Nabeshima T., Wang J., Sonobe Y., Kawanokuchi J., Takeuchi H., Mizuno T., Suzumura A., The role of TNF-alpha and its receptors in the production of NGF and GDNF by astrocytes. Brain Res, 2006. 1116(1): p. 12–18.
Diaz-Gil JJ et al (2003) The mitogenic activity of the liver growth factor is mediated by tumor necrosis factor alpha in rat liver. J Hepatol 38(5):598–604
Desai Bradaric B, Patel A, Schneider JA, Carvey PM, Hendey B (2012) Evidence for angiogenesis in Parkinson's disease, incidental Lewy body disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 119(1):59–71
Faucheux BA, Agid Y, Hirsch EC, Bonnet AM (1999) Blood vessels change in the mesencephalon of patients with Parkinson's disease. Lancet 353(9157):981–982
Barcia C, Bautista V, Sánchez-Bahillo Á, Fernández-Villalba E, Faucheux B, Poza y Poza M, Fernandez Barreiro A, Hirsch EC et al (2005) Changes in vascularization in substantia nigra pars compacta of monkeys rendered parkinsonian. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 112(9):1237–1248
Westin JE, Lindgren HS, Gardi J, Nyengaard JR, Brundin P, Mohapel P, Cenci MA (2006) Endothelial proliferation and increased blood–brain barrier permeability in the basal ganglia in a rat model of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine-induced dyskinesia. J Neurosci 26(37):9448–9461
Janelidze S, Lindqvist D, Francardo V, Hall S, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Adler CH, Beach TG et al (2015) Increased CSF biomarkers of angiogenesis in Parkinson disease. Neurology 85(21):1834–1842
Giron-Martinez A et al (2014) Proliferative activity of liver growth factor is associated with an improvement of cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. PLoS One 9(11):e112995
Hwang O (2013) Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurobiol 22(1):11–17
Chung SY, Kishinevsky S, Mazzulli JR, Graziotto J, Mrejeru A, Mosharov EV, Puspita L, Valiulahi P et al (2016) Parkin and PINK1 patient iPSC-derived midbrain dopamine neurons exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction and alpha-synuclein accumulation. Stem Cell Reports 7(4):664–677
Condezo-Hoyos L, Abderrahim F, Conde MV, Susín C, Díaz-Gil JJ, González MC, Arribas SM (2009) Antioxidant activity of liver growth factor, a bilirubin covalently bound to albumin. Free Radic Biol Med 46(5):656–662
Simitsi A, Koros C, Moraitou M, Papagiannakis N, Antonellou R, Bozi M, Angelopoulou E, Stamelou M et al (2018) Phenotypic characteristics in GBA-associated Parkinson's disease: A study in a Greek population. J Parkinsons Dis 8(1):101–105
Gegg ME, Burke D, Heales SJR, Cooper JM, Hardy J, Wood NW, Schapira AHV (2012) Glucocerebrosidase deficiency in substantia nigra of Parkinson disease brains. Ann Neurol 72(3):455–463
Pepin E et al (2020) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors modulators decrease signs of neuroinflammation and prevent Parkinson's disease symptoms in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model. Front Pharmacol 11:77
Hong CT, Hu HH, Chan L, Bai CH (2018) Prevalent cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease in people with Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis. Clin Epidemiol 10:1147–1154
Huang X, Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, Mailman RB, Ross GW (2008) Low LDL cholesterol and increased risk of Parkinson's disease: Prospective results from Honolulu-Asia aging study. Mov Disord 23(7):1013–1018
Navarrete A, Rupérez FJ, Mendes TO, Pérez-Rial S, Girón-Martínez A, Terrón-Expósito R, Díaz-Gil JJ, Peces-Barba G et al (2017) A metabolomic approach shows sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophospholipids as mediators of the therapeutic effect of liver growth factor in emphysema. J Pharm Biomed Anal 139:238–246
Adibhatla RM, Hatcher JF (2008) Altered lipid metabolism in brain injury and disorders. Subcell Biochem 49:241–268
Huang M, Wang Y, Wang L, Chen B, Wang X, Hu Y (2020) APOE rs405509 polymorphism and Parkinson's disease risk in the Chinese population. Neurosci Lett 736:135256
Davis AA et al (2020) APOE genotype regulates pathology and disease progression in synucleinopathy. Sci Transl Med:12(529)
Surra JC, Guillén N, Barranquero C, Arbonés-Mainar JM, Navarro MA, Gascón S, Arnal C, Godino J et al (2010) Sex-dependent effect of liver growth factor on atherosclerotic lesions and fatty liver disease in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Histol Histopathol 25(5):609–618
Blandini F, Porter RH, Greenamyre JT (1996) Glutamate and Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol 12(1):73–94
Meredith GE, Totterdell S, Beales M, Meshul CK (2009) Impaired glutamate homeostasis and programmed cell death in a chronic MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol 219(1):334–340
Wang J, Wang F, Mai D, Qu S (2020) Molecular mechanisms of glutamate toxicity in Parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci 14:585584
Calatrava-Ferreras L, Gonzalo-Gobernado R, Reimers D, Herranz A, Jiménez-Escrig A, Díaz-Gil J, Casarejos M, Montero-Vega M et al (2014) Neuroprotective role of liver growth factor "LGF" in an experimental model of cerebellar ataxia. Int J Mol Sci 15(10):19056–19073
Iovino L, Tremblay ME, Civiero L (2020) Glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in Parkinson's disease: The role of glial cells. J Pharmacol Sci 144:151–164
Decressac M, Mattsson B, Bjorklund A (2012) Comparison of the behavioural and histological characteristics of the 6-OHDA and alpha-synuclein rat models of Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol 235(1):306–315
Visanji NP, Brotchie JM, Kalia LV, Koprich JB, Tandon A, Watts JC, Lang AE (2016) Alpha-Synuclein-based animal models of Parkinson's disease: Challenges and opportunities in a new era. Trends Neurosci 39(11):750–762
Chung HK, Ho HA, Pérez-Acuña D, Lee SJ (2019) Modeling alpha-synuclein propagation with preformed fibril injections. J Mov Disord 12(3):139–151
Karampetsou M, Ardah MT, Semitekolou M, Polissidis A, Samiotaki M, Kalomoiri M, Majbour N, Xanthou G et al (2017) Phosphorylated exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils exacerbate pathology and induce neuronal dysfunction in mice. Sci Rep 7(1):16533
Diaz-Gil JJ et al (1989) Liver growth factor purified from human plasma is an albumin–bilirubin complex. Mol Biol Med 6(3):197–207
Kang SS, Zhang Z, Liu X, Manfredsson FP, Benskey MJ, Cao X, Xu J, Sun YE et al (2017) TrkB neurotrophic activities are blocked by alpha-synuclein, triggering dopaminergic cell death in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(40):10773–10778
Wang Y, Liu H, Zhang BS, Soares JC, Zhang XY (2016) Low BDNF is associated with cognitive impairments in patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 29:66–71
A controlled trial of recombinant methionyl human BDNF in ALS: the BDNF Study Group (Phase III). Neurology, 1999. 52(7): p. 1427–33.
Ochs G, Penn RD, York M, Giess R, Beck M, Tonn J, Haigh J, Malta E et al (2000) A phase I/II trial of recombinant methionyl human brain derived neurotrophic factor administered by intrathecal infusion to patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(3):201–206
Lahteinen S et al (2003) Exacerbated status epilepticus and acute cell loss, but no changes in epileptogenesis, in mice with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling. Neuroscience 122(4):1081–1092
Ito K, Enomoto H (2016) Retrograde transport of neurotrophic factor signaling: Implications in neuronal development and pathogenesis. J Biochem 160(2):77–85
d’Anglemont de Tassigny X, Pascual A, Lopez-Barneo J (2015) GDNF-based therapies, GDNF-producing interneurons, and trophic support of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway. Implications for Parkinson's disease. Front Neuroanat 9:10
Perez-Rial S et al (2014) Liver growth factor treatment reverses emphysema previously established in a cigarette smoke exposure mouse model. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307(9):L718–L726
Kustrimovic N, Comi C, Magistrelli L, Rasini E, Legnaro M, Bombelli R, Aleksic I, Blandini F et al (2018) Parkinson's disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: Cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naive and drug-treated patients. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):205
Mehta D, Malik AB (2006) Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev 86(1):279–367
Thornalley PJ (1998) Cell activation by glycated proteins. AGE receptors, receptor recognition factors and functional classification of AGEs. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 44(7):1013–1023
Aly AE et al (2019) Intranasal delivery of pGDNF DNA nanoparticles provides neuroprotection in the rat 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol 56(1):688–701
Ji R, Smith M, Niimi Y, Karakatsani ME, Murillo MF, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S, Konofagou EE (2019) Focused ultrasound enhanced intranasal delivery of brain derived neurotrophic factor produces neurorestorative effects in a Parkinson's disease mouse model. Sci Rep 9(1):19402
Diaz Gil JJ et al (1994) Hepatic growth induced by injection of the liver growth factor into normal rats. Growth Regul 4(3):113–122
Sun M, Kong L, Wang X, Lu XG, Gao Q, Geller AI (2005) Comparison of the capability of GDNF, BDNF, or both, to protect nigrostriatal neurons in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 1052(2):119–129
Onyango IG, Tuttle JB, Bennett JP Jr (2005) Brain-derived growth factor and glial cell line-derived growth factor use distinct intracellular signaling pathways to protect PD cybrids from H2O2-induced neuronal death. Neurobiol Dis 20(1):141–154
Krakora D, Mulcrone P, Meyer M, Lewis C, Bernau K, Gowing G, Zimprich C, Aebischer P et al (2013) Synergistic effects of GDNF and VEGF on lifespan and disease progression in a familial ALS rat model. Mol Ther 21(8):1602–1610
Lindgren N, Leak RK, Carlson KM, Smith AD, Zigmond MJ (2008) Activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and its relation to neuroprotection in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res 86(9):2039–2049
McFarthing K, Buff S, Rafaloff G, Dominey T, Wyse RK, Stott SR (2020) Parkinson’s disease drug therapies in the clinical trial pipeline: 2020. J Parkinsons Dis 10(3):757–774
Kalia LV, Kalia SK, Lang AE (2015) Disease-modifying strategies for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 30(11):1442–1450
Barker RA, Björklund A, Gash DM, Whone A, van Laar A, Kordower JH, Bankiewicz K, Kieburtz K et al (2020) GDNF and Parkinson's disease: Where next? A summary from a recent workshop. J Parkinsons Dis 10(3):875–891
Riboldi GM, Di Fonzo AB (2019) GBA, Gaucher disease, and Parkinson's disease: From genetic to clinic to new therapeutic approaches. Cells:8(4)
Michalowska M et al (2020) Gene polymorphisms and motor levodopa-induced complications in Parkinson's disease. Brain Behav 10(3):e01537
Wang Q, Liu J, Guo Y, Dong G, Zou W, Chen Z (2019) Association between BDNF G196A (Val66Met) polymorphism and cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis. Braz J Med Biol Res 52(8):e8443
Acknowledgments
Y.N.P. would like to acknowledge Monash University Malaysia for supporting with HDR Scholarship.
Funding Sources
This research has not received any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.A. carried out the literature review, conceptualized, and prepared the initial draft. Y.N.P. edited and contributed in the final manuscript. C.P. provided critical inputs, edited, and contributed to the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelopoulou, E., Paudel, Y.N. & Piperi, C. Role of Liver Growth Factor (LGF) in Parkinson’s Disease: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Mol Neurobiol 58, 3031–3042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02326-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02326-9