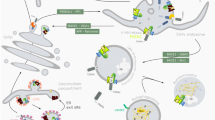
Abstract
Since its discovery as a genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, the APOE4 allele has been linked to the majority of the pathological findings associated with the disease progression. These include abnormalities of the endocytic, autophagic, and lysosomal machineries, which begin at the most early stages of Alzheimer’s disease development. Considering that these three vesicular systems share common features and, in fact, comprise an interconnected cargo-trafficking and degradation network, some of the effects of APOE4 are interrelated, while others are system-specific. In turn, APOE4-driven impairments of endocytosis, autophagy, and lysosomal activity influence various aspects of Alzheimer’s disease pathology, ranging from Aβ generation and clearance to neuronal loss and cognitive deficits. This review discusses the detrimental effects of APOE4 on the endocytic–autophagic–lysosomal axis in the context of Alzheimer’s disease, as well as the various mechanisms underlying them.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
amyloid beta
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
amyloid precursor protein
- apoE:
-
apolipoprotein E
- Atg:
-
autophagy-related protein
- FAD:
-
familial AD
- mTOR1:
-
mammalian target of rapamycin (complex 1)
- NFT:
-
neurofibrillary tangles
- PI3K:
-
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PIP2:
-
phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate
- PS1 and PS2:
-
presenilin 1 and 2
- SAD:
-
sporadic AD
- synj1:
-
synaptojanin 1
- TR:
-
target replacement
- VLDL:
-
very low density lipoprotein
References
Nixon RA, Cataldo AM, Mathews PM (2000) The endosomal-lysosomal system of neurons in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: a review. Neurochem Res 25(9–10):1161–1172. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007675508413
Nixon RA (2005) Endosome function and dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging 26(3):373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.09.018
Orr ME, Oddo S (2013) Autophagic/lysosomal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 5(5):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt217
Placido AI, Pereira CM, Duarte AI, Candeias E, Correia SC, Santos RX, Carvalho C, Cardoso S et al (2014) The role of endoplasmic reticulum in amyloid precursor protein processing and trafficking: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(9):1444–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.003
Vetrivel KS, Thinakaran G (2010) Membrane rafts in Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid production. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801(8):860–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.03.007
Kim J, Basak JM, Holtzman DM (2009) The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 63(3):287–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.026
Michaelson DM (2014) APOE epsilon4: the most prevalent yet understudied risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer's Dement : J Alzheimer's Assoc 10(6):861–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.06.015
Bu G (2009) Apolipoprotein E and its receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: pathways, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(5):333–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2620
Aoki K, Uchihara T, Sanjo N, Nakamura A, Ikeda K, Tsuchiya K, Wakayama Y (2003) Increased expression of neuronal apolipoprotein E in human brain with cerebral infarction. Stroke 34(4):875–880. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000064320.73388.C6
Xu Q, Bernardo A, Walker D, Kanegawa T, Mahley RW, Huang Y (2006) Profile and regulation of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) expression in the CNS in mice with targeting of green fluorescent protein gene to the ApoE locus. J Neurosci 26(19):4985–4994. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5476-05.2006
Kanekiyo T, Xu H, Bu G (2014) ApoE and Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease: accidental encounters or partners? Neuron 81(4):740–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.045
Perugini MA, Schuck P, Howlett GJ (2002) Differences in the binding capacity of human apolipoprotein E3 and E4 to size-fractionated lipid emulsions. Eur J Biochem 269(23):5939–5949
Steinmetz A, Jakobs C, Motzny S, Kaffarnik H (1989) Differential distribution of apolipoprotein E isoforms in human plasma lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis 9(3):405–411. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.9.3.405
Youmans KL, Tai LM, Nwabuisi-Heath E, Jungbauer L, Kanekiyo T, Gan M, Kim J, Eimer WA et al (2012) APOE4-specific changes in Abeta accumulation in a new transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 287(50):41774–41786. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.407957
Fu Y, Zhao J, Atagi Y, Nielsen HM, Liu CC, Zheng H, Shinohara M, Kanekiyo T et al (2016) Apolipoprotein E lipoprotein particles inhibit amyloid-beta uptake through cell surface heparan sulphate proteoglycan. Mol Neurodegener 11(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-016-0099-y
Boehm-Cagan A, Bar R, Liraz O, Bielicki JK, Johansson JO, Michaelson DM (2016) ABCA1 agonist reverses the ApoE4-driven cognitive and brain pathologies. J Alzheimer's Dis: JAD 54(3):1219–1233. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160467
Carter AY, Letronne F, Fitz NF, Mounier A, Wolfe CM, Nam KN, Reeves VL, Kamboh H et al (2017) Liver X receptor agonist treatment significantly affects phenotype and transcriptome of APOE3 and APOE4 Abca1 haplo-deficient mice. PLoS One 12(2):e0172161. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172161
Ruiz J, Kouiavskaia D, Migliorini M, Robinson S, Saenko EL, Gorlatova N, Li D, Lawrence D et al (2005) The apoE isoform binding properties of the VLDL receptor reveal marked differences from LRP and the LDL receptor. J Lipid Res 46(8):1721–1731. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M500114-JLR200
Hatters DM, Peters-Libeu CA, Weisgraber KH (2006) Apolipoprotein E structure: insights into function. Trends Biochem Sci 31(8):445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.008
Dose J, Huebbe P, Nebel A, Rimbach G (2016) APOE genotype and stress response—a mini review. Lipids Health Dis 15(1):121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-016-0288-2
Holtzman DM, Herz J, Bu G (2012) Apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein E receptors: normal biology and roles in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(3):a006312. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006312
Parcon PA, Balasubramaniam M, Ayyadevara S, Jones RA, Liu L, Shmookler Reis RJ, Barger SW, Mrak RE et al (2017) Apolipoprotein E4 inhibits autophagy gene products through direct, specific binding to CLEAR motifs. Alzheimer's Dement: J Alzheimer's Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.07.754
Chang S, ran Ma T, Miranda RD, Balestra ME, Mahley RW, Huang Y (2005) Lipid- and receptor-binding regions of apolipoprotein E4 fragments act in concert to cause mitochondrial dysfunction and neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(51):18694–18699. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508254102
Mahley RW, Huang Y (2012) Small-molecule structure correctors target abnormal protein structure and function: structure corrector rescue of apolipoprotein E4-associated neuropathology. J Med Chem 55(21):8997–9008. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm3008618
Mahley RW, Huang Y (2012) Apolipoprotein e sets the stage: response to injury triggers neuropathology. Neuron 76(5):871–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.11.020
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M, Korolchuk VI et al (2010) Regulation of mammalian autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 90(4):1383–1435. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00030.2009
Codogno P, Meijer AJ (2005) Autophagy and signaling: their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1509–1518. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401751
Liang JH, Jia JP (2014) Dysfunctional autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenic roles and therapeutic implications. Neurosci Bull 30(2):308–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1418-8
Frake RA, Ricketts T, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2015) Autophagy and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 125(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI73944
Lamark T, Johansen T (2012) Aggrephagy: selective disposal of protein aggregates by macroautophagy. Int J Cell Biol 2012:736905. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/736905
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A, Bruun JA, Outzen H, Overvatn A, Bjorkoy G et al (2007) p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem 282(33):24131–24145. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M702824200
Ding WX, Yin XM (2012) Mitophagy: mechanisms, pathophysiological roles, and analysis. Biol Chem 393(7):547–564. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2012-0119
Barnett A, Brewer GJ (2011) Autophagy in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: pathologic or protective? J Alzheimer's Dis: JAD 25(3):385–394. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2011-101989
Funderburk SF, Marcellino BK, Yue Z (2010) Cell “self-eating” (autophagy) mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Mount Sinai J Med, N Y 77(1):59–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.20161
Ling D, Salvaterra PM (2011) Autophagy-derived Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. In: Monte SDL (ed) Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis—core concepts, shifting paradigms and therapeutic targets. InTech. pp 539–560. doi:https://doi.org/10.5772/951
Wojtkowiak JW, Sane KM, Kleinman M, Sloane BF, Reiners JJ Jr, Mattingly RR (2011) Aborted autophagy and nonapoptotic death induced by farnesyl transferase inhibitor and lovastatin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.110.174573
Schmukler E, Shai B, Ehrlich M, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2012) Neuregulin promotes incomplete autophagy of prostate cancer cells that is independent of mTOR pathway inhibition. PLoS One 7(5):e36828. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036828
Pickford F, Masliah E, Britschgi M, Lucin K, Narasimhan R, Jaeger PA, Small S, Spencer B et al (2008) The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid beta accumulation in mice. J Clin Invest 118(6):2190–2199. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI33585
Shin JY, Park HJ, Kim HN, Oh SH, Bae JS, Ha HJ, Lee PH (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells enhance autophagy and increase beta-amyloid clearance in Alzheimer disease models. Autophagy 10(1):32–44. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.26508
Erlich S, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2007) Rapamycin is a neuroprotective treatment for traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis 26(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.12.003
Diskin T, Tal-Or P, Erlich S, Mizrachy L, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2005) Closed head injury induces upregulation of Beclin 1 at the cortical site of injury. J Neurotrauma 22(7):750–762. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2005.22.750
Erlich S, Shohami E, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2006) Neurodegeneration induces upregulation of Beclin 1. Autophagy 2(1):49–51
Ling D, Song HJ, Garza D, Neufeld TP, Salvaterra PM (2009) Abeta42-induced neurodegeneration via an age-dependent autophagic-lysosomal injury in Drosophila. PLoS One 4(1):e4201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004201
Keating DJ, Chen C, Pritchard MA (2006) Alzheimer’s disease and endocytic dysfunction: clues from the Down syndrome-related proteins, DSCR1 and ITSN1. Ageing Res Rev 5(4):388–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2005.11.001
Wu F, Yao PJ (2009) Clathrin-mediated endocytosis and Alzheimer’s disease: an update. Ageing Res Rev 8(3):147–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2009.03.002
Ries M, Sastre M (2016) Mechanisms of Abeta clearance and degradation by glial cells. Front Aging Neurosci 8:160. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00160
Kanekiyo T, Bu G (2014) The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 and amyloid-beta clearance in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 6:93. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00093
Funk KE, Kuret J (2012) Lysosomal fusion dysfunction as a unifying hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:752894. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/752894
Hartley SL, Handen BL, Devenny DA, Hardison R, Mihaila I, Price JC, Cohen AD, Klunk WE et al (2014) Cognitive functioning in relation to brain amyloid-beta in healthy adults with Down syndrome. Brain J Neurol 137(Pt 9):2556–2563. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu173
Simonovitch S, Schmukler E, Bespalko A, Iram T, Frenkel D, Holtzman DM, Masliah E, Michaelson DM et al (2016) Impaired autophagy in APOE4 astrocytes. J Alzheimer's Dis: JAD 51(3):915–927. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-151101
Lin AL, Jahrling JB, Zhang W, DeRosa N, Bakshi V, Romero P, Galvan V, Richardson A (2017) Rapamycin rescues vascular, metabolic and learning deficits in apolipoprotein E4 transgenic mice with pre-symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37(1):217–226. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X15621575
Zhu L, Zhong M, Elder GA, Sano M, Holtzman DM, Gandy S, Cardozo C, Haroutunian V et al (2015) Phospholipid dysregulation contributes to ApoE4-associated cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(38):11965–11970. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1510011112
Ji ZS, Miranda RD, Newhouse YM, Weisgraber KH, Huang Y, Mahley RW (2002) Apolipoprotein E4 potentiates amyloid beta peptide-induced lysosomal leakage and apoptosis in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 277(24):21821–21828. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112109200
Itzhaki RF, Cosby SL, Wozniak MA (2008) Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: the autophagy connection. J Neurovirol 14(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280701802543
Cataldo AM, Peterhoff CM, Troncoso JC, Gomez-Isla T, Hyman BT, Nixon RA (2000) Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations. Am J Pathol 157(1):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64538-5
Li J, Kanekiyo T, Shinohara M, Zhang Y, LaDu MJ, Xu H, Bu G (2012) Differential regulation of amyloid-beta endocytic trafficking and lysosomal degradation by apolipoprotein E isoforms. J Biol Chem 287(53):44593–44601. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.420224
Yamauchi K, Tozuka M, Hidaka H, Nakabayashi T, Sugano M, Katsuyama T (2002) Isoform-specific effect of apolipoprotein E on endocytosis of beta-amyloid in cultures of neuroblastoma cells. Ann Clin Lab Sci 32(1):65–74
He X, Cooley K, Chung CH, Dashti N, Tang J (2007) Apolipoprotein receptor 2 and X11 alpha/beta mediate apolipoprotein E-induced endocytosis of amyloid-beta precursor protein and beta-secretase, leading to amyloid-beta production. J Neurosci 27(15):4052–4060. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3993-06.2007
Ye S, Huang Y, Mullendorff K, Dong L, Giedt G, Meng EC, Cohen FE, Kuntz ID et al (2005) Apolipoprotein (apo) E4 enhances amyloid beta peptide production in cultured neuronal cells: apoE structure as a potential therapeutic target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(51):18700–18705. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508693102
Chen Y, Durakoglugil MS, Xian X, Herz J (2010) ApoE4 reduces glutamate receptor function and synaptic plasticity by selectively impairing ApoE receptor recycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(26):12011–12016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914984107
Jiang Q, Lee CY, Mandrekar S, Wilkinson B, Cramer P, Zelcer N, Mann K, Lamb B et al (2008) ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron 58(5):681–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.010
Cash JG, Kuhel DG, Basford JE, Jaeschke A, Chatterjee TK, Weintraub NL, Hui DY (2012) Apolipoprotein E4 impairs macrophage efferocytosis and potentiates apoptosis by accelerating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 287(33):27876–27884. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.377549
Zhao W, Dumanis SB, Tamboli IY, Rodriguez GA, Jo Ladu M, Moussa CE, William Rebeck G (2014) Human APOE genotype affects intraneuronal Abeta1-42 accumulation in a lentiviral gene transfer model. Hum Mol Genet 23(5):1365–1375. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt525
van Niel G, Bergam P, Di Cicco A, Hurbain I, Lo Cicero A, Dingli F, Palmulli R, Fort C et al (2015) Apolipoprotein E regulates amyloid formation within endosomes of pigment cells. Cell Rep 13(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.057
Belinson H, Lev D, Masliah E, Michaelson DM (2008) Activation of the amyloid cascade in apolipoprotein E4 transgenic mice induces lysosomal activation and neurodegeneration resulting in marked cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 28(18):4690–4701. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5633-07.2008
Mazur-Kolecka B, Kowal D, Sukontasup T, Dickson D, Frackowiak J (2003) The effect of oxidative stress on accumulation of apolipoprotein E3 and E4 in a cell culture model of beta-amyloid angiopathy (CAA). Brain Res 983(1–2):48–57
Mazur-Kolecka B, Dickson D, Frackowiak J (2006) Induction of vascular amyloidosis-beta by oxidative stress depends on APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging 27(6):804–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.04.012
Fu R, Yanjanin NM, Elrick MJ, Ware C, Lieberman AP, Porter FD (2012) Apolipoprotein E genotype and neurological disease onset in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1. Am J Med Genet A 158A(11):2775–2780. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.35395
Persson T, Lattanzio F, Calvo-Garrido J, Rimondini R, Rubio-Rodrigo M, Sundstrom E, Maioli S, Sandebring-Matton A et al (2017) Apolipoprotein E4 elicits lysosomal cathepsin D release, decreased thioredoxin-1 levels, and apoptosis. J Alzheimer's Dis: JAD 56(2):601–617. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-150738
Ji ZS, Mullendorff K, Cheng IH, Miranda RD, Huang Y, Mahley RW (2006) Reactivity of apolipoprotein E4 and amyloid beta peptide: lysosomal stability and neurodegeneration. J Biol Chem 281(5):2683–2692. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M506646200
Cai Z, Yan LJ (2013) Rapamycin, autophagy, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Biochem Pharmacol Res 1(2):84–90
Dall'Armi C, Devereaux KA, Di Paolo G (2013) The role of lipids in the control of autophagy. Curr Biol: CB 23(1):R33–R45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.10.041
George AA, Hayden S, Stanton GR, Brockerhoff SE (2016) Arf6 and the 5'phosphatase of synaptojanin 1 regulate autophagy in cone photoreceptors. BioEssays: news and reviews in molecular, cellular and developmental biology 38 Suppl 1:S119-135. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201670913
Zhu L, Zhong M, Zhao J, Rhee H, Caesar I, Knight EM, Volpicelli-Daley L, Bustos V et al (2013) Reduction of synaptojanin 1 accelerates Abeta clearance and attenuates cognitive deterioration in an Alzheimer mouse model. J Biol Chem 288(44):32050–32063. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.504365
Kim WS, Elliott DA, Kockx M, Kritharides L, Rye KA, Jans DA, Garner B (2008) Analysis of apolipoprotein E nuclear localization using green fluorescent protein and biotinylation approaches. Biochem J 409(3):701–709. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20071261
Theendakara V, Peters-Libeu CA, Spilman P, Poksay KS, Bredesen DE, Rao RV (2016) Direct transcriptional effects of apolipoprotein E. J Neurosci 36(3):685–700. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3562-15.2016
Cai Z, Chen G, He W, Xiao M, Yan LJ (2015) Activation of mTOR: a culprit of Alzheimer’s disease? Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:1015–1030. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S75717
Herz J, Chen Y (2006) Reelin, lipoprotein receptors and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(11):850–859. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2009
Rebeck GW, LaDu MJ, Estus S, Bu G, Weeber EJ (2006) The generation and function of soluble apoE receptors in the CNS. Mol Neurodegener 1(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-1-15
Yates SC, Zafar A, Hubbard P, Nagy S, Durant S, Bicknell R, Wilcock G, Christie S et al (2013) Dysfunction of the mTOR pathway is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 1(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2051-5960-1-3
Huang YA, Zhou B, Wernig M, Sudhof TC (2017) ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4 differentially stimulate APP transcription and Abeta secretion. Cell 168(3):427–441 e421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.044
Hoe HS, Harris DC, Rebeck GW (2005) Multiple pathways of apolipoprotein E signaling in primary neurons. J Neurochem 93(1):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.03007.x
Sridharan S, Jain K, Basu A (2011) Regulation of autophagy by kinases. Cancers 3(2):2630–2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3022630
Itzhaki RF, Lin WR, Shang D, Wilcock GK, Faragher B, Jamieson GA (1997) Herpes simplex virus type 1 in brain and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 349(9047):241–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(96)10149-5
Piacentini R, De Chiara G, Li Puma DD, Ripoli C, Marcocci ME, Garaci E, Palamara AT, Grassi C (2014) HSV-1 and Alzheimer’s disease: more than a hypothesis. Front Pharmacol 5:97. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00097
DeKroon RM, Armati PJ (2001) The endosomal trafficking of apolipoprotein E3 and E4 in cultured human brain neurons and astrocytes. Neurobiol Dis 8(1):78–89. https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.2000.0362
Winkler K, Scharnagl H, Tisljar U, Hoschutzky H, Friedrich I, Hoffmann MM, Huttinger M, Wieland H et al (1999) Competition of Abeta amyloid peptide and apolipoprotein E for receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Lipid Res 40(3):447–455
Heeren J, Grewal T, Laatsch A, Becker N, Rinninger F, Rye KA, Beisiegel U (2004) Impaired recycling of apolipoprotein E4 is associated with intracellular cholesterol accumulation. J Biol Chem 279(53):55483–55492. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M409324200
Sandwall E, O'Callaghan P, Zhang X, Lindahl U, Lannfelt L, Li JP (2010) Heparan sulfate mediates amyloid-beta internalization and cytotoxicity. Glycobiology 20(5):533–541. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwp205
Wu D, Sharan C, Yang H, Goodwin JS, Zhou L, Grabowski GA, Du H, Guo Z (2007) Apolipoprotein E-deficient lipoproteins induce foam cell formation by downregulation of lysosomal hydrolases in macrophages. J Lipid Res 48(12):2571–2578. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M700217-JLR200
Lamb CA, Dooley HC, Tooze SA (2013) Endocytosis and autophagy: shared machinery for degradation. BioEssays: News Rev Mol, Cell Dev Biol 35(1):34–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201200130
Tooze SA, Abada A, Elazar Z (2014) Endocytosis and autophagy: exploitation or cooperation? Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6(5):a018358. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018358
Larsen KE, Sulzer D (2002) Autophagy in neurons: a review. Histol Histopathol 17(3):897–908. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-17.897
Acknowledgments
The Prajs-Drimmer Institute for degenerative diseases supported this work. We wish to thank Eya Wolfson and Shira Solomon for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• APOE4 is the most prevalent genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
• Impaired endocytosis, autophagy, and lysosomal activities are observed in AD and possibly contribute to disease progression.
• ApoE isoforms differentially affect endocytic, autophagic, and lysosomal activities.
• ApoE isoforms may affect Aβ production and clearance by mechanisms that involve the endocytic–autophagic–lysosomal axis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmukler, E., Michaelson, D.M. & Pinkas-Kramarski, R. The Interplay Between Apolipoprotein E4 and the Autophagic–Endocytic–Lysosomal Axis. Mol Neurobiol 55, 6863–6880 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0892-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0892-4