Abstract
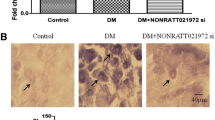
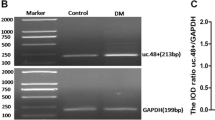
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in physiological and pathophysiological processes. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for more than 90 % of all cases of diabetes mellitus (DM). Diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP) is a common complication of T2DM. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of lncRNA NONRATT021972 small interference RNA (siRNA) on DNP mediated by the P2X3 receptor in dorsal root ganglia (DRG). These experiments showed that the expression levels of NONRATT021972 in DRG were increased in the T2DM rat model (intraperitoneal injection of STZ with 30 mg/kg). The concentration of NONRATT021972 in T2DM patient serum was higher compared to control healthy subjects. The mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) in T2DM rats were lower compared to control rats. MWT and TWL in T2DM rats treated with NONRATT021972 siRNA were higher compared with those in T2DM rats. The expression levels of the P2X3 protein and messenger RNA (mRNA) of T2DM rat DRG were higher compared to the control, while those in T2DM rats treated with NONRATT021972 siRNA were significantly lower compared to T2DM rats. The level of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the serum of T2DM rats treated with NONRATT021972 siRNA was significantly decreased compared with T2DM rats. NONRATT021972 siRNA inhibited the phosphorylation and activation of ERK1/2 in T2DM DRG. Thus, NONRATT021972 siRNA treatment may suppress the upregulated expression and activation of the P2X3 receptor and reduce the hyperalgesia potentiated by the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α in T2DM rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 June 2019
In the original version of this article ���lncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA Decreases Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by the P2X3 Receptor in Dorsal Root Ganglia���, which we have published in Mol Neurobiol (2017) 54:511���523.
26 June 2019
In the original version of this article ���lncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA Decreases Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by the P2X3 Receptor in Dorsal Root Ganglia���, which we have published in Mol Neurobiol (2017) 54:511���523.
References
Colvin LA, Dougherty PM (2015) Peripheral neuropathic pain: signs, symptoms, mechanisms, and causes: are they linked? Br J Anaesth 114(3):361–363. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu323
Pruimboom L, van Dam AC (2007) Chronic pain: a non-use disease. Med Hypotheses 68(3):506–511. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.08.036
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R et al (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70(18):1630–1635. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59
Schmader KE, Baron R, Haanpaa ML, Mayer J, O’Connor AB, Rice AS, Stacey B (2010) Treatment considerations for elderly and frail patients with neuropathic pain. Mayo Clin Proc 85(3Suppl):S26–S32. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0646
Ma RC, Chan JC (2013) Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1281:64–91. doi:10.1111/nyas.12098
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Jiang Y, Dai M et al (2013) Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 310(9):948–959. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.168118
Callaghan BC, Cheng HT, Stables CL, Smith AL, Feldman EL (2012) Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol 11(6):521–534. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70065-0
Obrosova IG (2009) Diabetes and the peripheral nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(10):931–940. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.11.005
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J (2011) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94(3):311–321. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.029
Schreiber AK, Nones CF, Reis RC, Chichorro JG, Cunha JM (2015) Diabetic neuropathic pain: physiopathology and treatment. World J Diabetes 6(3):432–444. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.432
Bansal V, Kalita J, Misra UK (2006) Diabetic neuropathy. Postgrad Med J 82(964):95–100. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2005.036137
Singh R, Kishore L, Kaur N (2014) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: current perspective and future directions. Pharmacol Res 80:21–35. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.12.005
Davies M, Brophy S, Williams R, Taylor A (2006) The prevalence, severity, and impact of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29(7):1518–1522. doi:10.2337/dc05-2228
Morales-Vidal S, Morgan C, McCoyd M, Hornik A (2012) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Postgrad Med 124(4):145–153. doi:10.3810/pgm.2012.07.2576
Tavakoli M, Malik RA (2008) Management of painful diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 9(17):2969–2978. doi:10.1517/14656560802498149
Tesfaye S, Selvarajah D (2012) Advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 28(Suppl 1):8–14. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2239
Costa FF (2010) Non-coding RNAs: meet thy masters. Bioessays 32(7):599–608
Ponting CP, Belgard TG (2010) Transcribed dark matter: meaning or myth? Hum Mol Genet 19(R2):R162–R168. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq362
Stein LD (2004) Human genome: end of the beginning. Nature 431(7011):915–916. doi:10.1038/431915a
Louro R, Smirnova AS, Verjovski-Almeida S (2009) Long intronic noncoding RNA transcription: expression noise or expression choice? Genomics 93(4):291–298. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.11.009
Ponjavic J, Ponting CP, Lunter G (2007) Functionality or transcriptional noise? Evidence for selection within long noncoding RNAs. Genome Res 17(5):556–565. doi:10.1101/gr.6036807
Batista PJ, Chang HY (2013) Long noncoding RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 152(6):1298–1307. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.012
Di Gesualdo F, Capaccioli S, Lulli M (2014) A pathophysiological view of the long non-coding RNA world. Oncotarget 5(22):10976–10996
Qureshi IA, Mattick JS, Mehler MF (2010) Long non-coding RNAs in nervous system function and disease. Brain Res 1338:20–35. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.110
Sauvageau M, Goff LA, Lodato S, Bonev B, Groff AF, Gerhardinger C, Sanchez-Gomez DB, Hacisuleyman E et al (2013) Multiple knockout mouse models reveal lincRNAs are required for life and brain development. Elife 2, e01749. doi:10.7554/eLife.01749
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O et al (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458(7235):223–227. doi:10.1038/nature07672
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, Garber M, Raj A, Rivea Morales D, Thomas K, Presser A et al (2009) Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(28):11667–11672. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904715106
Mercer TR DM, Mattick JS (2009) Long noncoding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10:155–159
Pastori C, Wahlestedt C (2012) Involvement of long noncoding RNAs in diseases affecting the central nervous system. RNA Biol 9(6):860–870. doi:10.4161/rna.20482
Wang X, Arai S, Song X, Reichart D, Du K, Pascual G, Tempst P, Rosenfeld MG et al (2008) Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription. Nature 454(7200):126–130. doi:10.1038/nature06992
Hu W, Alvarez-Dominguez JR, Lodish HF (2012) Regulation of mammalian cell differentiation by long non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep 13(11):971–983. doi:10.1038/embor.2012.145
Kaikkonen MU, Lam MT, Glass CK (2011) Non-coding RNAs as regulators of gene expression and epigenetics. Cardiovasc Res 90(3):430–440. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr097
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136(4):629–641. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006
Rapicavoli NA, Qu K, Zhang J, Mikhail M, Laberge RM, Chang HY (2013) A mammalian pseudogene lncRNA at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Elife 2, e00762. doi:10.7554/eLife.00762
Rinn JL, Chang HY (2012) Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 81:145–166. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-051410-092902
Burnstock G (2014) Purinergic signalling: from discovery to current developments. Exp Physiol 99(1):16–34. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2013.071951
Burnstock G (2007) Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev 87(2):659–797. doi:10.1152/physrev.00043.2006
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110(3):433–454. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.08.013
Burnstock G (2009) Purinergic receptors and pain. Curr Pharm Des 15(15):1717–1735
Gao Y, Xu C, Liang S, Zhang A, Mu S, Wang Y, Wan F (2008) Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on primary afferent transmission mediated by P2X3 receptor in neuropathic pain states. Brain Res Bull 77(1):27–32. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.02.026
Gao Y, Liu H, Deng L, Zhu G, Xu C, Li G, Liu S, Xie J et al (2011) Effect of emodin on neuropathic pain transmission mediated by P2X 2/3 receptor of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res Bull 84(6):406–413. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.01.017
Liang S, Xu C, Li G, Gao Y (2010) P2X receptors and modulation of pain transmission: focus on effects of drugs and compounds used in traditional Chinese medicine. Neurochem Int 57(7):705–712. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.09.004
Lin J, Li G, Den X, Xu C, Liu S, Gao Y, Liu H, Zhang J et al (2010) VEGF and its receptor-2 involved in neuropathic pain transmission mediated by P2X 2/3 receptor of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res Bull 83(5):284–291. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.08.002
Novakovic SD, Kassotakis LC, Oglesby IB, Smith JA, Eglen RM, Ford AP, Hunter JC (1999) Immunocytochemical localization of P 2X3 purinoceptors in sensory neurons in naive rats and following neuropathic injury. Pain 80(1–2):273–282
Zhang A, Gao Y, Zhong X, Xu C, Li G, Liu S, Lin J, Li X et al (2010) Effect of sodium ferulate on the hyperalgesia mediated by P2X 3 receptor in the neuropathic pain rats. Brain Res 1313:215–221. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.11.067
Burnstock G, Novak I (2013) Purinergic signalling and diabetes. Purinergic Signal 9(3):307–324. doi:10.1007/s11302-013-9359-2
Xu GY, Li G, Liu N, Huang LY (2011) Mechanisms underlying purinergic P2X3 receptor-mediated mechanical allodynia induced in diabetic rats. Mol Pain 7:60. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-7-60
Yu Y, Fuscoe JC, Zhao C, Guo C, Jia M, Qing T, Bannon DI, Lancashire L et al (2014) A rat RNA-Seq transcriptomic BodyMap across 11 organs and 4 developmental stages. Nat Commun 5:3230. doi:10.1038/ncomms4230
Islam MS (2013) Animal models of diabetic neuropathy: progress since 1960s. J Diabetes Res 2013:149452. doi:10.1155/2013/149452
Li G, Xu H, Zhu S, Xu W, Qin S, Liu S, Tu G, Peng H et al (2013) Effects of neferine on CCL5 and CCR5 expression in SCG of type 2 diabetic rats. Brain Res Bull 90:79–87. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.10.002
Srinivasan K, Ramarao P (2007) Animal models in type 2 diabetes research: an overview. Indian J Med Res 125(3):451–472
Messinger RB, Naik AK, Jagodic MM, Nelson MT, Lee WY, Choe WJ, Orestes P, Latham JR et al (2009) In vivo silencing of the Ca V 3.2 T-type calcium channels in sensory neurons alleviates hyperalgesia in rats with streptozocin-induced diabetic neuropathy. Pain 145(1–2):184–195. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2009.06.012
Liu J, Li G, Peng H, Tu G, Kong F, Liu S, Gao Y, Xu H et al (2013) Sensory-sympathetic coupling in superior cervical ganglia after myocardial ischemic injury facilitates sympathoexcitatory action via P2X7 receptor. Purinergic Signal 9(3):463–479. doi:10.1007/s11302-013-9367-2
Wang F, Zhang P, Ma Y, Yang J, Moyer MP, Shi C, Peng J, Qin H (2012) NIRF is frequently upregulated in colorectal cancer and its oncogenicity can be suppressed by let-7a microRNA. Cancer Lett 314(2):223–231. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.09.033
Gunduz O, Oltulu C, Buldum D, Guven R, Ulugol A (2011) Anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of ceftriaxone in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 491(1):23–25. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.12.063
Xu C, Xu W, Xu H, Xiong W, Gao Y, Li G, Liu S, Xie J et al (2012) Role of puerarin in the signalling of neuropathic pain mediated by P2X 3 receptor of dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res Bull 87(1):37–43. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.10.007
Li G, Liu S, Yang Y, Xie J, Liu J, Kong F, Tu G, Wu R et al (2011) Effects of oxymatrine on sympathoexcitatory reflex induced by myocardial ischemic signaling mediated by P2X(3) receptors in rat SCG and DRG. Brain Res Bull 84(6):419–424. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.01.011
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF (2013) Long non-coding RNAs: novel targets for nervous system disease diagnosis and therapy. Neurotherapeutics 10(4):632–646. doi:10.1007/s13311-013-0199-0
Wapinski O, Chang HY (2011) Long noncoding RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol 21(6):354–361. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2011.04.001
Chodroff RA, Goodstadt L, Sirey TM, Oliver PL, Davies KE, Green ED, Molnar Z, Ponting CP (2010) Long noncoding RNA genes: conservation of sequence and brain expression among diverse amniotes. Genome Biol 11(7):R72. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-7-r72
Guil S, Esteller M (2015) RNA-RNA interactions in gene regulation: the coding and noncoding players. Trends Biochem Sci 40(5):248–256. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2015.03.001
Barrett AM, Lucero MA, Le T, Robinson RL, Dworkin RH, Chappell AS (2007) Epidemiology, public health burden, and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a review. Pain Med 8(Suppl 2):S50–S62. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2006.00179.x
Galer BS, Gianas A, Jensen MP (2000) Painful diabetic polyneuropathy: epidemiology, pain description, and quality of life. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 47(2):123–128
Ziegler D (2009) Painful diabetic neuropathy: advantage of novel drugs over old drugs? Diabetes Care 32(Suppl 2):S414–S419. doi:10.2337/dc09-S350
Burnstock G, Krugel U, Abbracchio MP, Illes P (2011) Purinergic signalling: from normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog Neurobiol 95(2):229–274. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.006
Chizh BA, Illes P (2001) P2X receptors and nociception. Pharmacol Rev 53(4):553–568
Stein C, Clark JD, Oh U, Vasko MR, Wilcox GL, Overland AC, Vanderah TW, Spencer RH (2009) Peripheral mechanisms of pain and analgesia. Brain Res Rev 60(1):90–113. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.017
Obata K, Yamanaka H, Kobayashi K, Dai Y, Mizushima T, Katsura H, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A et al (2004) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in injured and intact primary afferent neurons for mechanical and heat hypersensitivity after spinal nerve ligation. J Neurosci 24(45):10211–10222. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3388-04.2004
Seino D, Tokunaga A, Tachibana T, Yoshiya S, Dai Y, Obata K, Yamanaka H, Kobayashi K et al (2006) The role of ERK signaling and the P2X receptor on mechanical pain evoked by movement of inflamed knee joint. Pain 123(1–2):193–203. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.02.032
Acknowledgments
These works were supported by the grant (nos. 81570735, 31560276, 81560219, 81560529, 81171184, 31060139, and 81200853) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the grant (no. 20151BBG70250) from the Technology Pedestal and Society Development Project of Jiangxi Province, the grant (no. 20142BAB205028) from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, and the grant (nos. GJJ13155 and GJJ14319) from the Educational Department of Jiangxi Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committees of Nanchang University Medical Schools. The IASP’s ethical guidelines for pain research in animals were followed. All animals were treated according to the ARVO Statement for the use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research in China.
Informed Consent
Following local ethics committee approval, written informed consent was obtained from each individual.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Haiying Peng, Lifang Zou, and Jinyan Xie are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Zou, L., Xie, J. et al. lncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA Decreases Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by the P2X3 Receptor in Dorsal Root Ganglia. Mol Neurobiol 54, 511–523 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9632-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9632-1