Abstract
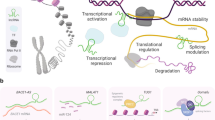
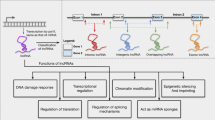
The human genome encodes tens of thousands of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), a novel and important class of genes. Our knowledge of lncRNAs has grown exponentially since their discovery within the last decade. lncRNAs are expressed in a highly cell- and tissue-specific manner, and are particularly abundant within the nervous system. lncRNAs are subject to post-transcriptional processing and inter- and intra-cellular transport. lncRNAs act via a spectrum of molecular mechanisms leveraging their ability to engage in both sequence-specific and conformational interactions with diverse partners (DNA, RNA, and proteins). Because of their size, lncRNAs act in a modular fashion, bringing different macromolecules together within the three-dimensional context of the cell. lncRNAs thus coordinate the execution of transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and epigenetic processes and critical biological programs (growth and development, establishment of cell identity, and deployment of stress responses). Emerging data reveal that lncRNAs play vital roles in mediating the developmental complexity, cellular diversity, and activity-dependent plasticity that are hallmarks of brain. Corresponding studies implicate these factors in brain aging and the pathophysiology of brain disorders, through evolving paradigms including the following: (i) genetic variation in lncRNA genes causes disease and influences susceptibility; (ii) epigenetic deregulation of lncRNAs genes is associated with disease; (iii) genomic context links lncRNA genes to disease genes and pathways; and (iv) lncRNAs are otherwise interconnected with known pathogenic mechanisms. Hence, lncRNAs represent prime targets that can be exploited for diagnosing and treating nervous system diseases. Such clinical applications are in the early stages of development but are rapidly advancing because of existing expertise and technology platforms that are readily adaptable for these purposes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein BE, Birney E, Dunham I, Green ED, Gunter C, Snyder M. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012;489:57-74.
Mercer TR, Neph S, Dinger ME, et al. The human mitochondrial transcriptome. Cell 2011;146:645-658.
Amaral PP, Dinger ME, Mercer TR, Mattick JS. The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. Science 2008;319:1787-1789.
Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT. Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics 2013;193:651-669.
Mercer TR, Mattick JS. Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2013;20:300-307.
Batista PJ, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013;152:1298-1307.
Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res 2012;22:1775-1789.
Volders PJ, Helsens K, Wang X, et al. LNCipedia: a database for annotated human lncRNA transcript sequences and structures. Nucleic Acids Res 2013;41:D246-251.
Managadze D, Lobkovsky AE, Wolf YI, Shabalina SA, Rogozin IB, Koonin EV. The vast, conserved mammalian lincRNome. PLoS Comput Biol 2013;9:e1002917.
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF. Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in brain evolution, development, plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012;13:528-541.
Lipovich L, Tarca AL, Cai J, et al. Developmental Changes in the transcriptome of human cerebral cortex tissue: long noncoding rna transcripts. Cereb Cortex 2013 Feb 1 [Epub ahead of print].
Ponjavic J, Oliver PL, Lunter G, Ponting CP. Genomic and transcriptional co-localization of protein-coding and long non-coding RNA pairs in the developing brain. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000617.
Chodroff RA, Goodstadt L, Sirey TM, et al. Long noncoding RNA genes: conservation of sequence and brain expression among diverse amniotes. Genome Biol 2010;11:R72.
Belgard TG, Marques AC, Oliver PL, et al. A transcriptomic atlas of mouse neocortical layers. Neuron 2011;71:605-616.
Qureshi IA, Mattick JS, Mehler MF. Long non-coding RNAs in nervous system function and disease. Brain Res 2010;1338:20-35.
Vallot C, Huret C, Lesecque Y, et al. XACT, a long noncoding transcript coating the active X chromosome in human pluripotent cells. Nat Genet 2013;45:239-241.
Latos PA, Pauler FM, Koerner MV, et al. Airn transcriptional overlap, but not its lncRNA products, induces imprinted Igf2r silencing. Science 2012;338:1469-1472.
Taguchi S, Iwami M, Kiya T. Identification and characterization of a novel nuclear noncoding RNA, Fben-1, which is preferentially expressed in the higher brain center of the female silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. Neurosci Lett 2011;496:176-180.
Reinius B, Shi C, Hengshuo L, et al. Female-biased expression of long non-coding RNAs in domains that escape X-inactivation in mouse. BMC Genomics 2010;11:614.
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF. Genetic and epigenetic underpinnings of sex differences in the brain and in neurological and psychiatric disease susceptibility. Prog Brain Res 2010;186:77-95.
Young RS, Marques AC, Tibbit C, et al. Identification and properties of 1,119 candidate lincRNA loci in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Biol Evol 2012;4:427-442.
Ulitsky I, Shkumatava A, Jan CH, Sive H, Bartel DP. Conserved function of lincRNAs in vertebrate embryonic development despite rapid sequence evolution. Cell 2011;147:1537-1550.
Pollard KS, Salama SR, Lambert N, et al. An RNA gene expressed during cortical development evolved rapidly in humans. Nature 2006;443:167-172.
Bond AM, Vangompel MJ, Sametsky EA, et al. Balanced gene regulation by an embryonic brain ncRNA is critical for adult hippocampal GABA circuitry. Nat Neurosci 2009;12:1020-1027.
Guttman M, Donaghey J, Carey BW, et al. lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation. Nature 2011;477:295-300.
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, et al. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 2011;147:358-369.
Klattenhoff CA, Scheuermann JC, Surface LE, et al. Braveheart, a long noncoding RNA required for cardiovascular lineage commitment. Cell 2013;152:570-583.
Moran I, Akerman I, van de Bunt M, et al. Human beta cell transcriptome analysis uncovers lncRNAs that are tissue-specific, dynamically regulated, and abnormally expressed in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab 2012;16:435-448.
Hu W, Yuan B, Flygare J, Lodish HF. Long noncoding RNA-mediated anti-apoptotic activity in murine erythroid terminal differentiation. Genes Dev 2011;25:2573-2578.
Sun L, Goff LA, Trapnell C, et al. Long noncoding RNAs regulate adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:3387-3392.
Kretz M, Siprashvili Z, Chu C, et al. Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding RNA TINCR. Nature 2013;493:231-235.
Mercer TR, Qureshi IA, Gokhan S, et al. Long noncoding RNAs in neuronal-glial fate specification and oligodendrocyte lineage maturation. BMC Neurosci 2010;11:14.
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009;458:223-227.
Lin M, Pedrosa E, Shah A, et al. RNA-Seq of human neurons derived from iPS cells reveals candidate long non-coding RNAs involved in neurogenesis and neuropsychiatric disorders. PLoS ONE 2011;6:e23356.
Rapicavoli NA, Poth EM, Blackshaw S. The long noncoding RNA RNCR2 directs mouse retinal cell specification. BMC Dev Biol 2010;10:49.
Rapicavoli NA, Poth EM, Zhu H, Blackshaw S. The long noncoding RNA Six3OS acts in trans to regulate retinal development by modulating Six3 activity. Neural Dev 2011;6:32.
Ng SY, Johnson R, Stanton LW. Human long non-coding RNAs promote pluripotency and neuronal differentiation by association with chromatin modifiers and transcription factors. EMBO J 2012;31:522-533.
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:11667-11672.
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010;329:689-693.
Bernard D, Prasanth KV, Tripathi V, et al. A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. EMBO J 2010;29:3082-3093.
Lin D, Pestova TV, Hellen CU, Tiedge H. Translational control by a small RNA: dendritic BC1 RNA targets the eukaryotic initiation factor 4A helicase mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 2008;28:3008-3019.
Anguera MC, Ma W, Clift D, Namekawa S, Kelleher RJ, 3rd, Lee JT. Tsx produces a long noncoding RNA and has general functions in the germline, stem cells, and brain. PLoS Genet 2011;7:e1002248.
Ling KH, Hewitt CA, Beissbarth T, et al. Spatiotemporal regulation of multiple overlapping sense and novel natural antisense transcripts at the Nrgn and Camk2n1 gene loci during mouse cerebral corticogenesis. Cereb Cortex 2011;21:683-697.
Bu Q, Hu Z, Chen F, et al. Transcriptome analysis of long non-coding RNAs of the nucleus accumbens in cocaine-conditioned mice. J Neurochem 2012;123:790-799.
Michelhaugh SK, Lipovich L, Blythe J, Jia H, Kapatos G, Bannon MJ. Mining Affymetrix microarray data for long non-coding RNAs: altered expression in the nucleus accumbens of heroin abusers. J Neurochem 2011;116:459-466.
Kryger R, Fan L, Wilce PA, Jaquet V. MALAT-1, a non protein-coding RNA is upregulated in the cerebellum, hippocampus and brain stem of human alcoholics. Alcohol 2012;46:629-634.
Ziats MN, Rennert OM. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in autistic brain. J Mol Neurosci 2013;49:589-593.
Lipovich L, Dachet F, Cai J, et al. Activity-dependent human brain coding/noncoding gene regulatory networks. Genetics 2012;192:1133-1148.
Kim TK, Hemberg M, Gray JM, et al. Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature 2010;465:182-187.
St Laurent G, 3rd, Faghihi MA, Wahlestedt C. Non-coding RNA transcripts: sensors of neuronal stress, modulators of synaptic plasticity, and agents of change in the onset of Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 2009;466:81-88.
Lakhotia SC. Long non-coding RNAs coordinate cellular responses to stress. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2012;3:779-796.
Hung T, Wang Y, Lin MF, et al. Extensive and coordinated transcription of noncoding RNAs within cell-cycle promoters. Nat Genet 2011;43:621-629.
Huarte M, Guttman M, Feldser D, et al. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 2010;142:409-419.
Wan G, Mathur R, Hu X, et al. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL (CDKN2B-AS) is induced by the ATM-E2F1 signaling pathway. Cell Signal 2013;25:1086-1095.
Wang X, Arai S, Song X, et al. Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription. Nature 2008;454:126-130.
Mariner PD, Walters RD, Espinoza CA, et al. Human Alu RNA is a modular transacting repressor of mRNA transcription during heat shock. Mol Cell 2008;29:499-509.
Yakovchuk P, Goodrich JA, Kugel JF. B2 RNA and Alu RNA repress transcription by disrupting contacts between RNA polymerase II and promoter DNA within assembled complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:5569-5574.
Valgardsdottir R, Chiodi I, Giordano M, Cobianchi F, Riva S, Biamonti G. Structural and functional characterization of noncoding repetitive RNAs transcribed in stressed human cells. Mol Biol Cell 2005;16:2597-2604.
Biamonti G, Vourc'h C. Nuclear stress bodies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a000695.
Shamovsky I, Ivannikov M, Kandel ES, Gershon D, Nudler E. RNA-mediated response to heat shock in mammalian cells. Nature 2006;440:556-560.
Shamovsky I, Nudler E. Isolation and characterization of the heat shock RNA 1. Methods Mol Biol 2009;540:265-279.
Carrieri C, Cimatti L, Biagioli M, et al. Long non-coding antisense RNA controls Uchl1 translation through an embedded SINEB2 repeat. Nature 2012;491:454-457.
Royo H, Basyuk E, Marty V, Marques M, Bertrand E, Cavaille J. Bsr, a nuclear-retained RNA with monoallelic expression. Mol Biol Cell 2007;18:2817-2827.
Bishop NA, Lu T, Yankner BA. Neural mechanisms of ageing and cognitive decline. Nature 2010;464:529-535.
Kang HJ, Kawasawa YI, Cheng F, et al. Spatio-temporal transcriptome of the human brain. Nature 2011;478:483-489.
Colantuoni C, Lipska BK, Ye T, et al. Temporal dynamics and genetic control of transcription in the human prefrontal cortex. Nature 2011;478:519-523.
Wood SH, Craig T, Li Y, Merry B, de Magalhaes JP. Whole transcriptome sequencing of the aging rat brain reveals dynamic RNA changes in the dark matter of the genome. Age (Dordr) 2013;35:763-776.
Mus E, Hof PR, Tiedge H. Dendritic BC200 RNA in aging and in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:10679-10684.
Liu N, Landreh M, Cao K, et al. The microRNA miR-34 modulates ageing and neurodegeneration in Drosophila. Nature 2012;482:519-523.
Jones DL, Rando TA. Emerging models and paradigms for stem cell ageing. Nat Cell Biol 2011;13:506-512.
Kim WY, Sharpless NE. The regulation of INK4/ARF in cancer and aging. Cell 2006;127:265-275.
Ratajczak MZ. Igf2-H19, an imprinted tandem gene, is an important regulator of embryonic development, a guardian of proliferation of adult pluripotent stem cells, a regulator of longevity, and a 'passkey' to cancerogenesis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2012;50:171-179.
Wang J, Geesman GJ, Hostikka SL, et al. Inhibition of activated pericentromeric SINE/Alu repeat transcription in senescent human adult stem cells reinstates self-renewal. Cell Cycle 2011;10:3016-3030.
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF. Alu transcription: A rheostat for stem cell aging? Cell Cycle 2011;10:3820-3821.
Chen G, Wang Z, Wang D, et al. LncRNADisease: a database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 2013;41:D983-986.
Talkowski ME, Maussion G, Crapper L, et al. Disruption of a large intergenic noncoding RNA in subjects with neurodevelopmental disabilities. Am J Hum Genet 2012;91:1128-1134.
Cartault F, Munier P, Benko E, et al. Mutation in a primate-conserved retrotransposon reveals a noncoding RNA as a mediator of infantile encephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:4980-4985.
Pasmant E, Sabbagh A, Vidaud M, Bieche I. ANRIL, a long, noncoding RNA, is an unexpected major hotspot in GWAS. FASEB J 2011;25:444-448.
Ning S, Wang P, Ye J, et al. A global map for dissecting phenotypic variants in human lincRNAs. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Mar 6 [Epub ahead of print].
Chen G, Qiu C, Zhang Q, Liu B, Cui Q. Genome-wide analysis of human SNPs at long intergenic noncoding RNAs. Hum Mutat 2013;34:338-344.
Cabianca DS, Casa V, Bodega B, et al. A long ncRNA links copy number variation to a polycomb/trithorax epigenetic switch in FSHD muscular dystrophy. Cell 2012;149:819-831.
Faghihi MA, Zhang M, Huang J, et al. Evidence for natural antisense transcript-mediated inhibition of microRNA function. Genome Biol 2010;11:R56.
Saitsu H, Osaka H, Sasaki M, et al. Mutations in POLR3A and POLR3B encoding RNA polymerase III subunits cause an autosomal-recessive hypomyelinating leukoencephalopathy. Am J Hum Genet 2011;89:644-651.
Tollervey JR, Curk T, Rogelj B, et al. Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43. Nat Neurosci 2011;14:452-458.
Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Hutt KR, et al. Divergent roles of ALS-linked proteins FUS/TLS and TDP-43 intersect in processing long pre-mRNAs. Nat Neurosci 2012;15:1488-1497.
Massone S, Vassallo I, Fiorino G, et al. 17A, a novel non-coding RNA, regulates GABA B alternative splicing and signaling in response to inflammatory stimuli and in Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Dis 2011;41:308-317.
Han L, Zhang K, Shi Z, et al. LncRNA pro fi le of glioblastoma reveals the potential role of lncRNAs in contributing to glioblastoma pathogenesis. Int J Oncol 2012;40:2004-2012.
Zhang X, Sun S, Pu JK, et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes in glioma. Neurobiol Dis 2012;48:1-8.
Johnson R. Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington's disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 2012;46:245-254.
Mezzomo LC, Gonzales PH, Pesce FG, et al. Expression of cell growth negative regulators MEG3 and GADD45gamma is lost in most sporadic human pituitary adenomas. Pituitary 2012;15:420-427.
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 2008;10:1470-1476.
Balaj L, Lessard R, Dai L, et al. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat Commun 2011;2:180.
Chiba M, Kimura M, Asari S. Exosomes secreted from human colorectal cancer cell lines contain mRNAs, microRNAs and natural antisense RNAs, that can transfer into the human hepatoma HepG2 and lung cancer A549 cell lines. Oncol Rep 2012;28:1551-1558.
Sanchez Y, Huarte M. Long non-coding RNAs: challenges for diagnosis and therapies. Nucleic Acid Ther 2013;23:15-20.
Weinberg MS, Morris KV. Long non-coding RNA targeting and transcriptional de-repression. Nucleic Acid Ther 2013;23:9-14.
Bhartiya D, Kapoor S, Jalali S, et al. Conceptual approaches for lncRNA drug discovery and future strategies. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2012;7:503-513.
Qi P, Du X. The long non-coding RNAs, a new cancer diagnostic and therapeutic gold mine. Mod Pathol 2013;26:155-165.
Shao H, Chung J, Balaj L, et al. Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat Med 2012;18:1835-1840.
Kam Y, Rubinstein A, Naik S, et al. Detection of a long non-coding RNA (CCAT1) in living cells and human adenocarcinoma of colon tissues using FIT-PNA molecular beacons. Cancer Lett 2013 Feb 14 [Epub ahead of print].
Gutschner T, Baas M, Diederichs S. Noncoding RNA gene silencing through genomic integration of RNA destabilizing elements using zinc finger nucleases. Genome Res 2011;21:1944-1954.
Yang F, Huo XS, Yuan SX, et al. Repression of the long noncoding RNA-LET by histone deacetylase 3 contributes to hypoxia-mediated metastasis. Mol Cell 2013;49:1083-1096.
Modarresi F, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA, et al. Inhibition of natural antisense transcripts in vivo results in gene-specific transcriptional upregulation. Nat Biotechnol 2012;30:453-459.
Gutschner T, Hammerle M, Eissmann M, et al. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2013;73:1180-1189.
Sarma K, Levasseur P, Aristarkhov A, Lee JT. Locked nucleic acids (LNAs) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of Xist RNA localization to the X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:22196-22201.
Lakhal S, Wood MJ. Exosome nanotechnology: an emerging paradigm shift in drug delivery: exploitation of exosome nanovesicles for systemic in vivo delivery of RNAi heralds new horizons for drug delivery across biological barriers. Bioessays 2011;33:737-741.
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol 2011;29:341-345.
Katakowski M, Buller B, Zheng X, et al. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett 2013;335:201-204.
Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu P, et al. Variants on chromosome 9p21.3 correlated with ANRIL expression contribute to stroke risk and recurrence in a large prospective stroke population. Stroke 2012;43:14-21.
Pasmant E, Sabbagh A, Masliah-Planchon J, et al. Role of noncoding RNA ANRIL in genesis of plexiform neurofibromas in neurofibromatosis type 1. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011;103:1713-1722.
Burd CE, Jeck WR, Liu Y, Sanoff HK, Wang Z, Sharpless NE. Expression of linear and novel circular forms of an INK4/ARF-associated non-coding RNA correlates with atherosclerosis risk. PLoS Genet 2010;6:e1001233.
Cunnington MS, Santibanez Koref M, Mayosi BM, Burn J, Keavney B. Chromosome 9p21 SNPs associated with multiple disease phenotypes correlate with ANRIL expression. PLoS Genet 2010;6:e1000899.
Zuchner S, Gilbert JR, Martin ER, et al. Linkage and association study of late-onset Alzheimer disease families linked to 9p21.3. Ann Hum Genet 2008;72:725-731.
Wevrick R, Kerns JA, Francke U. Identification of a novel paternally expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome region. Hum Mol Genet 1994;3:1877-1882.
Maina EN, Webb T, Soni S, et al. Analysis of candidate imprinted genes in PWS subjects with atypical genetics: a possible inactivating mutation in the SNURF/SNRPN minimal promoter. J Hum Genet 2007;52:297-307.
Moseley ML, Zu T, Ikeda Y, et al. Bidirectional expression of CUG and CAG expansion transcripts and intranuclear polyglutamine inclusions in spinocerebellar ataxia type 8. Nat Genet 2006;38:758-769.
Daughters RS, Tuttle DL, Gao W, et al. RNA gain-of-function in spinocerebellar ataxia type 8. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000600.
Vandeweyer G, Van der Aa N, Ceulemans B, van Bon BW, Rooms L, Kooy RF. A de novo balanced t(2;6)(p15;p22.3) in a patient with West Syndrome disrupts a lnc-RNA. Epilepsy Res 2012;99:346-349.
Higashimoto K, Urano T, Sugiura K, et al. Loss of CpG methylation is strongly correlated with loss of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation at DMR-LIT1 in patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2003;73:948-956.
Albrecht S, Waha A, Koch A, Kraus JA, Goodyer CG, Pietsch T. Variable imprinting of H19 and IGF2 in fetal cerebellum and medulloblastoma. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1996;55:1270-1276.
Muller S, Zirkel D, Westphal M, Zumkeller W. Genomic imprinting of IGF2 and H19 in human meningiomas. Eur J Cancer 2000;36:651-655.
Balik V, Srovnal J, Sulla I, et al. MEG3: a novel long noncoding potentially tumour-suppressing RNA in meningiomas. J Neurooncol 2013;112:1-8.
Wang P, Ren Z, Sun P. Overexpression of the long non-coding RNA MEG3 impairs in vitro glioma cell proliferation. J Cell Biochem 2012;113:1868-1874.
Cheunsuchon P, Zhou Y, Zhang X, et al. Silencing of the imprinted DLK1-MEG3 locus in human clinically nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. Am J Pathol 2011;179:2120-2130.
Zhou Y, Zhang X, Klibanski A. MEG3 noncoding RNA: a tumor suppressor. J Mol Endocrinol 2012;48:R45-53.
Jong MT, Gray TA, Ji Y, et al. A novel imprinted gene, encoding a RING zinc-finger protein, and overlapping antisense transcript in the Prader-Willi syndrome critical region. Hum Mol Genet 1999;8:783-793.
Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Khalil AM, et al. Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer's disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase. Nat Med 2008;14:723-730.
Nogalska A, Engel WK, Askanas V. Increased BACE1 mRNA and noncoding BACE1-antisense transcript in sporadic inclusion-body myositis muscle fibers—possibly caused by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurosci Lett 2010;474:140-143.
Le Meur E, Watrin F, Landers M, Sturny R, Lalande M, Muscatelli F. Dynamic developmental regulation of the large non-coding RNA associated with the mouse 7C imprinted chromosomal region. Dev Biol 2005;286:587-600.
Brandon NJ, Sawa A. Linking neurodevelopmental and synaptic theories of mental illness through DISC1. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011;12:707-722.
Khalil AM, Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Brothers SP, Wahlestedt C. A novel RNA transcript with antiapoptotic function is silenced in fragile X syndrome. PLoS ONE 2008;3:e1486.
Ladd PD, Smith LE, Rabaia NA, et al. An antisense transcript spanning the CGG repeat region of FMR1 is upregulated in premutation carriers but silenced in full mutation individuals. Hum Mol Genet 2007;16:3174-3187.
Amaral PP, Neyt C, Wilkins SJ, et al. Complex architecture and regulated expression of the Sox2ot locus during vertebrate development. RNA 2009;15:2013-2027.
Sopher BL, Ladd PD, Pineda VV, et al. CTCF regulates ataxin-7 expression through promotion of a convergently transcribed, antisense noncoding RNA. Neuron 2011;70:1071-1084.
Johnson R, Richter N, Jauch R, et al. The Human Accelerated Region 1 noncoding RNA is repressed by REST in Huntington's disease. Physiol Genomics 2010 Feb 23 [Epub ahead of print].
Kaneko H, Dridi S, Tarallo V, et al. DICER1 deficit induces Alu RNA toxicity in age-related macular degeneration. Nature 2011;471:325-330.
Acknowledgments
We regret that space constraints have prevented the citation of many relevant and important references. M.F.M. is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NS071571, HD071593, MH66290), as well as by the F.M. Kirby, Alpern Family, Mildred and Bernard H. Kayden, and Roslyn and Leslie Goldstein Foundations.
Required Author Forms
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the online version of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 315 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qureshi, I.A., Mehler, M.F. Long Non-coding RNAs: Novel Targets for Nervous System Disease Diagnosis and Therapy. Neurotherapeutics 10, 632–646 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-013-0199-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-013-0199-0