Abstract
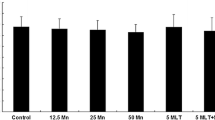
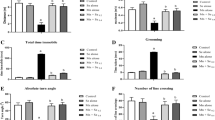
Excessive manganese (Mn) induces oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. However, the relationship between them during Mn neurotoxicity has not been clarified. The purpose of this study was to investigate the probable role of melatonin (MLT) against Mn-induced motor dysfunction and neuronal loss as a result of antagonizing oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Mice were randomly divided into five groups as follows: control, MnCl2, low MLT + MnCl2, median MLT + MnCl2, and high MLT + MnCl2. Administration of MnCl2 (50 mg/kg) for 2 weeks significantly induced hypokinesis, dopaminergic neurons degeneration and loss, neuronal ultrastructural damage, and apoptosis in the substantia nigra and the striatum. These conditions were caused in part by the overproduction of reactive oxygen species, malondialdehyde accumulation, and dysfunction of the nonenzymatic (GSH) and enzymatic (GSH-Px, superoxide dismutase, quinone oxidoreductase 1, glutathione S-transferase, and glutathione reductase) antioxidative defense systems. Mn-induced neuron degeneration, astrocytes, and microglia activation contribute to the changes of oxidative stress markers. Dopamine (DA) depletion and downregulation of DA transporter and receptors were also found after Mn administration, this might also trigger motor dysfunction and neurons loss. Pretreatment with MLT prevented Mn-induced oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurodegeneration and inhibited the interaction between them. As a result, pretreatment with MLT significantly alleviated Mn-induced motor dysfunction and neuronal loss. In conclusion, Mn treatment resulted in motor dysfunction and neuronal loss, possibly involving an interaction between oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Pretreatment with MLT attenuated Mn-induced neurotoxicity by means of its antioxidant properties and promotion of the DA system.












Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Aschner J, Aschner M (2005) Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol Aspects Med 26:353–362. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2005.07.003
Flynn MR, Susi P (2009) Neurological risks associated with manganese exposure from welding operations—a literature review. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212(5):459–469. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.12.003
Furbee B (2011) Welding and parkinsonism. Neurol Clin 29(3):623–640. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2011.05.007
Olanow CW (2004) Manganese-induced parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:209–223. doi:10.1196/annals.1306.018
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). Toxicological profile for manganese. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service. Available at http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp151.html, September 2000.
Boudia N, Halley R, Kennedy G, Lambert J, Gareau L, Zayed J (2006) Manganese concentrations in the air of the Montreal (Canada) subway in relation to surface automobile traffic density. Sci Total Environ 366(1):143–147. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.09.094
Cersosimo MG, Koller WC (2006) The diagnosis of manganese-induced parkinsonism. Neurotoxicol 27(3):340–346. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2005.10.006
Montes S, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Muriel P, Ríos C (2001) Striatal manganese accumulation induces changes in dopamine metabolism in the cirrhotic. Brain Res 891:123–129. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)03208-X
HaMai D, Bondy SC (2004) Oxidative basis of manganese neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:129–141. doi:10.1196/annals.1306.010
Martinez-Finley EJ, Gavin CE, Aschner M, Gunter TE (2013) Manganese neurotoxicity and the role of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 62:65–75. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.032
Daubner SC, Le T, Wang S (2011) Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 508:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2010.12.017
Defazio G, Soleo L, Zefferino R, Livrea P (1996) Manganese toxicity in serumless dissociated mesencephalic and striatal primary culture. Brain Res Bull 40(4):257–262. doi:10.1016/0361-9230(96)00041-X
Schmitt KC, Rothman RB, Reith ME (2013) Nonclassical pharmacology of the dopamine transporter: atypical inhibitors, allosteric modulators, and partial substrates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 346(1):2–10. doi:10.1124/jpet.111.191056
Ares-Santos S, Granado N, Moratalla R (2013) The role of dopamine receptors in the neurotoxicity of methamphetamine. J Intern Med 273(5):437–453. doi:10.1111/joim.12049
Hwang O (2013) Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 22(1):11–17. doi:10.5607/en.2013.22.1.11
Benot S, Goberna R, Reiter RJ, Garcia-Mauriño S, Osuna C, Guerrero JM (1999) Physiological levels of melatonin contribute to the antioxidant capacity of human serum. J Pineal Res 27(1):59–64. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.1999.tb00597.x
Reiter RJ, Tan D, Kim SJ, Manchester LC, Qi W, Garcia JJ, Cabrera JC, El-Sokkary G, Rouvier-Garay V (1999) Augmentation of indices of oxidative damage in life-long melatonin-deficient rats. Mech Ageing Dev 110(3):157–173. doi:10.1016/S0047-6374(99)00058-5
Poeggeler B, Saarela S, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Chen LD, Manchester LC, Barlow-Walden LR (1994) Melatonin-a highly potent endogenous radical scavenger and electron donor: new aspects of the oxidation chemistry of this indole accessed in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci 738:419–420. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb21831.x
Lincoln GA, Tortonese DJ (1995) Does melatonin act on dopaminergic pathways in the mediobasal hypothalamus to mediate effects of photoperiod on prolactin secretion in the ram? Neuroendocrinology 62(5):425–433. doi:10.1159/000127049
Sae-Ung K, Uéda K, Govitrapong P, Phansuwan-Pujito P (2012) Melatonin reduces the expression of alpha-synuclein in the dopamine containing neuronal regions of amphetamine-treated postnatal rats. J Pineal Res 52(1):128–137. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00927.x
Villalba M, Martínez-Serrano A, Börner C, Blanco P, Satrústegui J (1992) NMDA-induced increase in [Ca2+]i and 45Ca2+ uptake in acutely dissociated brain cells derived from adult rats. Brain Res 570(1–2):347–353. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(92)90600-E
Xiong N, Xiong J, Khare G, Chen C, Huang J, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Qiao X, Feng Y, Reesaul H, Zhang Y, Sun S, Lin Z, Wang T (2011) Edaravone guards dopamine neurons in a rotenone model for Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 6(6):e20677. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020677
Milatovic D, Yin Z, Gupta RC, Sidoryk M, Albrecht J, Aschner JL, Aschner M (2007) Manganese induces oxidative impairment in cultured rat astrocytes. Toxicol Sci 98(1):198–205. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm095
Zhang J, Cao R, Cai T, Aschner M, Zhao F, Yao T, Chen Y, Cao Z, Luo W, Chen J (2013) The role of autophagy dysregulation in manganese-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neurotox Res 24(4):478–490. doi:10.1007/s12640-013-9392-5
Sanchez-Betancourt J, Anaya-Martínez V, Gutierrez-Valdez AL, Ordoñez-Librado JL, Montiel-Flores E, Espinosa-Villanueva J, Reynoso-Erazo L, Avila-Costa MR (2012) Manganese mixture inhalation is a reliable Parkinson disease model in rats. Neurotoxicology 33(5):1346–1355. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2012.08.012
Cordova FM, Aguiar AS Jr, Peres TV, Lopes MW, Gonçalves FM, Pedro DZ, Lopes SC, Pilati C, Prediger RD, Farina M, Erikson KM, Aschner M, Leal RB (2013) Manganese-exposed developing rats display motor deficits and striatal oxidative stress that are reversed by Trolox. Arch Toxicol 87(7):1231–1244. doi:10.1007/s00204-013-1017-5
Lucchini RG, Martin CJ, Doney BC (2009) From manganism to manganese-induced parkinsonism: a conceptual model based on the evolution of exposure. Neuromolecular Med 11(4):311–321. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8108-8
Guilarte TR, Chen MK, McGlothan JL, Verina T, Wong DF, Zhou Y, Alexander M, Rohde CA, Syversen T, Decamp E, Koser AJ, Fritz S, Gonczi H, Anderson DW, Schneider JS (2006) Nigrostriatal dopamine system dysfunction and subtle motor deficits in manganese-exposed non-human primates. Exp Neurol 202(2):381–390. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.06.015
Erikson KM, Dorman DC, Lash LH, Aschner M (2007) Manganese inhalation by rhesus monkeys is associated with brain regional changes in biomarkers of neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 97(2):459–466. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm044
Sloot WN, Gramsbergen JB (1994) Axonal transport of manganese and its relevance to selective neurotoxicity in the rat basal ganglia. Brain Res 657(1–2):124–132. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)90959-8
Sloot WN, van der Sluijs-Gelling AJ, Gramsbergen JB (1994) Selective lesions by manganese and extensive damage by iron after injection into rat striatum or hippocampus. J Neurochem 62(1):205–216. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62010205.x
Dimova R, Vuillet J, Nieoullon A, Kerkerian-Le Goff L (1993) Ultrastructural features of the choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons and relationships with nigral dopaminergic and cortical afferent pathways in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 53(4):1059–1071. doi:10.1002/cne.902500108
Saka E, Iadarola M, Fitzgerald DJ, Graybiel AM (2002) Local circuit neurons in the striatum regulate neural and behavioral responses to dopaminergic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(13):9004–9009. doi:10.1073/pnas.132212499
HaMai D, Campbell A, Bondy SC (2001) Modulation of oxidative events by multivalent manganese complexes in brain tissue. Free Radic Biol Med 31(6):763–768. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00639-6
Oubrahim H, Stadtman ER, Chock PB (2001) Mitochondria play no roles in Mn(II)-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(17):9505–9510. doi:10.1073/pnas.181319898
Niki E, Yoshida Y, Saito Y, Noguchi N (2005) Lipid peroxidation: mechanisms, inhibition, and biological effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338(1):668–676. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.072
Zhang F, Xu Z, Gao J, Xu B, Deng Y (2008) In vitro effect of manganese chloride exposure on energy metabolism and oxidative damage of mitochondria isolated from rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26(2):232–236. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2008.04.003
Hussain T, Ali MM, Chandra SV (1987) The combined effect of Pb2+ and Mn2+ on monoamine uptake and Na+, K + -ATPase in striatal synaptosomes. J Appl Toxicol 7(4):277–280. doi:10.1002/jat.2550070409
Li GJ, Zhang LL, Lu L, Wu P, Zheng W (2004) Occupational exposure to welding fume among welders: alterations of manganese, iron, zinc, copper, and lead in body fluids and the oxidative stress status. J Occup Environ Med 46(3):241–248. doi:10.1097/01.jom.0000116900.49159.03
Zheng W, Fu SX, Dydak U, Cowan DM (2011) Biomarkers of manganese intoxication. Neurotoxicology 32(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2010.10.002
Franco R, Cidlowski JA (2012) Glutathione efflux and cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 17(12):1694–1713. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4553
Desole MS, Esposito G, Migheli R, Sircana S, Delogu MR, Fresu L, Miele M, de Natale G, Miele E (1997) Glutathione deficiency potentiates manganese toxicity in rat striatum and brainstem and in PC12 cells. Pharmacol Res 36(4):285–292. doi:10.1006/phrs.1997.0197
Sian J, Dexter DT, Lees AJ, Daniel S, Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994) Alterations in glutathione levels in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders affecting basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 36(3):348–355. doi:10.1002/ana.410360305
Shi GF, Wang GY, Chen XF (2013) Screening of radical-scavenging natural neuroprotective antioxidants from Swertia chirayita. Acta Biol Hung 64(3):267–278. doi:10.1556/ABiol.64.2013.3.1
Freedman JE, Frei B, Welch GN, Loscalzo J (1995) Glutathione peroxidase potentiates the inhibition of platelet function by S-nitrosothiols. J Clin Invest 96(1):394–400. doi:10.1172/JCI118047
Brad AP, Amitava DAS, Anil KJ (2012) NAD(P)H:Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) protects bladder epithelium against painful bladder syndrome in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 53(10):1886–1893. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.584
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Talalay P (2010) NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), a multifunctional antioxidant enzyme and exceptionally versatile cytoprotector. Arch Biochem Biophys 501(1):116–123. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.584
Settivari R, VanDuyn N, LeVora J, Nass R (2013) The Nrf2/SKN-1-dependent glutathione S-transferase π homologue GST-1 inhibits dopamine neuron degeneration in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of manganism. Neurotoxicology 38:51–60. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2013.05.014
Stanwood GD, Leitch DB, Savchenko V, Wu J, Fitsanakis VA, Anderson DJ, Stankowski JN, Aschner M, McLaughlin B (2009) Manganese exposure is cytotoxic and alters dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons within the basal ganglia. J Neurochem 110(1):378–389. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06145.x
Barhoumi R, Faske J, Liu X, Tjalkens RB (2004) Manganese potentiates lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of NOS2 in C6 glioma cells through mitochondrial-dependent activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 122(2):167–179. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.12.009
Kern CH, Smith DR (2011) Preweaning Mn exposure leads to prolonged astrocyte activation and lasting effects on the dopaminergic system in adult male rats. Synapse 65(6):532–544. doi:10.1002/syn.20873
Autissier N, Rochette L, Dumas P, Beley A, Loireau A, Bralet J (1982) Dopamine and norepinephrine turnover in various regions of the rat brain after chronic manganese chloride administration. Toxicology 24(2):175–182
Vidal L, Alfonso M, Campos F, Faro LR, Cervantes RC, Durán R (2005) Effects of manganese on extracellular levels of dopamine in rat striatum: an analysis in vivo by brain microdialysis. Neurochem Res 30(9):1147–1154. doi:10.1007/s11064-005-7775-6
Khalid M, Aoun RA, Mathews TA (2011) Altered striatal dopamine release following a sub-acute exposure to manganese. J Neurosci Methods 202(2):182–191. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.06.019
Varrone A, Halldin C (2010) Molecular imaging of the dopamine transporter. J Nucl Med 51(9):1331–1334. doi:10.2967/jnumed.109.065656
Zhu J, Reith ME (2008) Role of the dopamine transporter in the action of psychostimulants, nicotine, and other drugs of abuse. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 7(5):393–409. doi:10.2174/187152708786927877
McDougall SA, Reichel CM, Farley CM, Flesher MM, Der-Ghazarian T, Cortez AM, Wacan JJ, Martinez CE, Varela FA, Butt AE, Crawford CA (2008) Postnatal manganese exposure alters dopamine transporter function in adult rats: Potential impact on nonassociative and associative processes. Neuroscience 154(2):848–860. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.070
Reichel CM, Wacan JJ, Farley CM, Stanley BJ, Crawford CA, McDougall SA (2006) Postnatal manganese exposure attenuates cocaine-induced locomotor activity and reduces dopamine transporters in adult male rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28(3):323–332. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2006.02.002
Baik JH (2013) Dopamine signaling in reward-related behaviors. Front Neural Circuits 7:152. doi:10.3389/fncir.2013.00152
Eriksson H, Gillberg PG, Aquilonius SM, Hedström KG, Heilbronn E (1992) Receptor alterations in manganese intoxicated monkeys. Arch Toxicol 66(5):359–364. doi:10.1007/BF01973632
Emilien G, Maloteaux JM, Geurts M, Hoogenberg K, Cragg S (1999) Dopamine receptors–physiological understanding to therapeutic intervention potential. Pharmacol Ther 84(2):133–156. doi:10.1016/S0163-7258(99)00029-7
Kessler KR, Wunderlich G, Hefter H, Seitz RJ (2003) Secondary progressive chronic manganism associated with markedly decreased striatal D2 receptor density. Mov Disord 18(2):217–218. doi:10.1002/mds.10325
Calabresi P, Ammassari-Teule M, Gubellini P, Sancesario G, Morello M, Centonze D, Marfia GA, Saulle E, Passino E, Picconi B, Bernardi G (2001) A synaptic mechanism underlying the behavioral abnormalities induced by manganese intoxication. Neurobiol Dis 8(3):419–432. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2000.0379
Lee DW, Opanashuk LA (2004) Polychlorinated biphenyl mixture aroclor 1254-induced oxidative stress plays a role in dopaminergic cell injury. Neurotoxicology 25(6):925–939. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2004.05.005
Sharma R, McMillan CR, Tenn CC, Niles LP (2006) Physiological neuroprotection by melatonin in a 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 1068:230–236. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.10.084
Ma J, Shaw VE, Mitrofanis J (2009) Does melatonin help save dopaminergic cells in MPTP-treated mice? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15:307–314. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.07.008
Saravanan KS, Sindhu KM, Mohanakumar KP (2007) Melatonin protects against rotenone-induced oxidative stress in a hemiparkinsonian rat model. J Pineal Res 42:247–253. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00412.x
Lin AM, Ho LT (2000) Melatonin suppresses iron-induced neurodegeneration in rat brain. Free Radic Biol Med 28(6):904–911. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00169-6
Chen ST, Chuang JI, Hong MH, Li EI (2002) Melatonin attenuates MPP + -induced neurodegeneration and glutathione impairment in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. J Pineal Res 32(4):262–269. doi:10.1034/j.1600-079X.2002.01871.x
Patki G, Lau YS (2011) Melatonin protects against neurobehavioral and mitochondrial deficits in a chronic mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99(4):704–711. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2011.06.026
Tapias V, Escames G, López LC, López A, Camacho E, Carrión MD, Entrena A, Gallo MA, Espinosa A, Acuña-Castroviejo D (2009) Melatonin and its brain metabolite N(1)-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine prevent mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase induction in parkinsonian mice. J Neurosci Res 87(13):3002–3010. doi:10.1002/jnr.22123
Itzhak Y, Martin JL, Black MD, Ali SF (1998) Effect of melatonin on methamphetamine-and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity and methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization. Neuropharmacology 37(6):781–791. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(98)00067-7
Borah A, Mohanakumar KP (2009) Melatonin inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine production in the brain to protect against experimental parkinsonism in rodents. J Pineal Res 47(4):293–300. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00713.x
Lin CH, Huang JY, Ching CH, Chuang JI (2008) Melatonin reduces the neuronal loss, downregulation of dopamine transporter, and upregulation of D2 receptor in rotenone-induced parkinsonian rats. J Pineal Res 44(2):205–213. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00510.x
Sumaya IC, Byers DM, Irwin LN, Del Val S, Moss DE (2004) Circadian-dependent effect of melatonin on dopaminergic D2 antagonist-induced hypokinesia and agonist-induced stereotypies in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78(4):727–733. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2004.05.014
Willis GL, Robertson AD (2005) Recovery from experimental Parkinson's disease in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride treated marmoset with the melatonin analogue ML-23. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80(1):9–26. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2004.10.022
Golombek DA, Pévet P, Cardinali DP (1996) Melatonin effects on behavior: possible mediation by the central GABAergic system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 20(3):403–412. doi:10.1016/0149-7634(95)00052-6
Cheng S, Ma C, Qu H, Fan W, Pang J, He H (2008) Differential effects of melatonin on hippocampal neurodegeneration in different aged accelerated senescence prone mouse-8. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 29(1):91–99
Dong W, Huang F, Fan W, Cheng S, Chen Y, Zhang W, Shi H, He H (2010) Differential effects of melatonin on amyloid-beta peptide 25-35-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in hippocampal neurons at different stages of culture. J Pineal Res 48(2):117–125. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00734.x
Acknowledgments
The grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81302406) and the Specialized Research Fund of New Teachers for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20112104120017) supported this work financially.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Jiao, C., Mi, C. et al. Melatonin Inhibits Manganese-Induced Motor Dysfunction and Neuronal Loss in Mice: Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol 51, 68–88 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8789-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8789-3