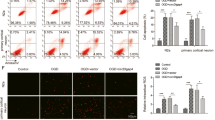
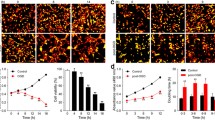
Abstract
Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) is a stress-induced transcription factor with diverse functions under disease states in multiple cell types. ATF3 has neuroprotective action against cerebral ischemia, which may involve caspase 3. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying ATF3 regulation of apoptosis are largely unknown. Here, we used gain- and loss-of-function and rescue approaches to demonstrate ATF3 attenuating hypoxic neuronal apoptosis. As well, the protective effect of ATF3 was mediated by downregulation of carboxyl-terminal modulator protein (CTMP), a pro-apoptotic factor that inhibits the anti-apoptotic Akt/PKB cascade. ATF3 (1) downregulated the mRNA and protein levels of CTMP; (2) its temporal expression pattern was reciprocal to that of CTMP; and (3) nuclear localization suggested that ATF3 may regulate CTMP transcription following hypoxic insult. Reporter assays demonstrated that ATF3 suppressed CTMP transcription, whereas ATF3 fusion with VP16, converting ATF3 to transcriptional activator, boosted CTMP transcription. By contrast, NF-κB increased CTMP transcription, and degradation-resistant IκBα decreased CTMP transcription. ChIP assays further confirmed that binding of ATF3 to the ATF/CREB site hindered NF-κB binding to the CTMP promoter, which repressed CTMP expression. Furthermore, CTMP siRNA treatment reduced hypoxic neuronal apoptosis by increasing p-Akt (Ser473) levels and leaving the upstream ATF3 level unchanged. We have identified an endogenous neuroprotective ATF3→CTMP signal cascade that may be a therapeutic target for reducing ischemic brain injury.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hai TW, Liu F, Coukos WJ, Green MR (1989) Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev 3(12B):2083–2090
Liang G, Wolfgang CD, Chen BP, Chen TH, Hai T (1996) ATF3 gene. Genomic organization, promoter, and regulation. J Biol Chem 271(3):1695–1701
Hai T, Hartman MG (2001) The molecular biology and nomenclature of the activating transcription factor/cAMP responsive element binding family of transcription factors: activating transcription factor proteins and homeostasis. Gene 273(1):1–11
Miyazaki K, Inoue S, Yamada K, Watanabe M, Liu Q, Watanabe T, Adachi MT, Tanaka Y, Kitajima S (2009) Differential usage of alternate promoters of the human stress response gene ATF3 in stress response and cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 37(5):1438–1451. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn1082
Hunt D, Raivich G, Anderson PN (2012) Activating transcription factor 3 and the nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci 5:7. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2012.00007
Hai T, Wolfgang CD, Marsee DK, Allen AE, Sivaprasad U (1999) ATF3 and stress responses. Gene Expr 7(4–6):321–335
Thompson MR, Xu D, Williams BR (2009) ATF3 transcription factor and its emerging roles in immunity and cancer. J Mol Med 87(11):1053–1060. doi:10.1007/s00109-009-0520-x
Hai T, Wolford CC, Chang YS (2010) ATF3, a hub of the cellular adaptive-response network, in the pathogenesis of diseases: is modulation of inflammation a unifying component? Gene Expr 15(1):1–11
Ohba N, Maeda M, Nakagomi S, Muraoka M, Kiyama H (2003) Biphasic expression of activating transcription factor-3 in neurons after cerebral infarction. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 115(2):147–156
Tang Y, Pacary E, Freret T, Divoux D, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P, Bernaudin M (2006) Effect of hypoxic preconditioning on brain genomic response before and following ischemia in the adult mouse: identification of potential neuroprotective candidates for stroke. Neurobiol Dis 21(1):18–28. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.06.002
Zhang SJ, Buchthal B, Lau D, Hayer S, Dick O, Schwaninger M, Veltkamp R, Zou M, Weiss U, Bading H (2011) A signaling cascade of nuclear calcium-CREB-ATF3 activated by synaptic NMDA receptors defines a gene repression module that protects against extrasynaptic NMDA receptor-induced neuronal cell death and ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci 31(13):4978–4990. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2672-10.2011
Wang L, Deng S, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Yang L, Guan Y, Jiang H, Li H (2012) Increased inflammation and brain injury after transient focal cerebral ischemia in activating transcription factor 3 knockout mice. Neuroscience 220:100–108. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.06.010
Wu F, Echeverry R, Wu J, An J, Haile WB, Cooper DS, Catano M, Yepes M (2013) Tissue-type plasminogen activator protects neurons from excitotoxin-induced cell death via activation of the ERK1/2-CREB-ATF3 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci 52:9–19. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2012.10.001
Song DY, Oh KM, Yu HN, Park CR, Woo RS, Jung SS, Baik TK (2011) Role of activating transcription factor 3 in ischemic penumbra region following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion injury. Neurosci Res 70(4):428–434. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2011.05.002
Hartman MG, Lu D, Kim ML, Kociba GJ, Shukri T, Buteau J, Wang X, Frankel WL, Guttridge D, Prentki M, Grey ST, Ron D, Hai T (2004) Role for activating transcription factor 3 in stress-induced beta-cell apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 24(13):5721–5732. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.13.5721-5732.2004
Lin TN, Cheung WM, Wu JS, Chen JJ, Lin H, Chen JJ, Liou JY, Shyue SK, Wu KK (2006) 15d-prostaglandin J2 protects brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26(3):481–487. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000201933.53964.5b
Goldberg MP, Choi DW (1993) Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurosci 13(8):3510–3524
Wu JS, Lin TN, Wu KK (2009) Rosiglitazone and PPAR-gamma overexpression protect mitochondrial membrane potential and prevent apoptosis by upregulating anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Physiol 220(1):58–71. doi:10.1002/jcp.21730
Wu JS, Cheung WM, Tsai YS, Chen YT, Fong WH, Tsai HD, Chen YC, Liou JY, Shyue SK, Chen JJ, Chen YE, Maeda N, Wu KK, Lin TN (2009) Ligand-activated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma protects against ischemic cerebral infarction and neuronal apoptosis by 14-3-3 epsilon upregulation. Circulation 119(8):1124–1134. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.108.812537
Wu JS, Tsai HD, Huang CY, Chen JJ, Lin TN (2013) 15-Deoxy–PGJ, by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, suppresses p22phox transcription to protect brain endothelial cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8600-x
Lin H, Lin TN, Cheung WM, Nian GM, Tseng PH, Chen SF, Chen JJ, Shyue SK, Liou JY, Wu CW, Wu KK (2002) Cyclooxygenase-1 and bicistronic cyclooxygenase-1/prostacyclin synthase gene transfer protect against ischemic cerebral infarction. Circulation 105(16):1962–1969
Li HF, Cheng CF, Liao WJ, Lin H, Yang RB (2010) ATF3-mediated epigenetic regulation protects against acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(6):1003–1013. doi:10.1681/asn.2009070690
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129(7):1261–1274. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009
Fong WH, Tsai HD, Chen YC, Wu JS, Lin TN (2010) Anti-apoptotic actions of PPAR-gamma against ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 41(2–3):180–186. doi:10.1007/s12035-010-8103-y
Saito A, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Nishi T, Song YS, Yu F, Liu J, Lee YS, Nito C, Kamada H, Dodd RL, Hsieh LB, Hassid B, Kim EE, Gonzalez M, Chan PH (2005) Oxidative stress and neuronal death/survival signaling in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 31(1–3):105–116. doi:10.1385/mn:31:1-3:105
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2006) Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt survival signal pathways are implicated in neuronal survival after stroke. Mol Neurobiol 34(3):249–270. doi:10.1385/mn:34:3:249
Nakagomi S, Suzuki Y, Namikawa K, Kiryu-Seo S, Kiyama H (2003) Expression of the activating transcription factor 3 prevents c-Jun N-terminal kinase-induced neuronal death by promoting heat shock protein 27 expression and Akt activation. J Neurosci 23(12):5187–5196
Parcellier A, Tintignac LA, Zhuravleva E, Cron P, Schenk S, Bozulic L, Hemmings BA (2009) Carboxy-terminal modulator protein (CTMP) is a mitochondrial protein that sensitizes cells to apoptosis. Cell Signal 21(4):639–650. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.01.016
Parcellier A, Tintignac LA, Zhuravleva E, Dummler B, Brazil DP, Hynx D, Cron P, Schenk S, Olivieri V, Hemmings BA (2009) The Carboxy-terminal modulator protein (CTMP) regulates mitochondrial dynamics. PLoS One 4(5):e5471. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005471
Simon PO Jr, McDunn JE, Kashiwagi H, Chang K, Goedegebuure PS, Hotchkiss RS, Hawkins WG (2009) Targeting AKT with the proapoptotic peptide, TAT-CTMP: a novel strategy for the treatment of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 125(4):942–951. doi:10.1002/ijc.24424
Maira SM, Galetic I, Brazil DP, Kaech S, Ingley E, Thelen M, Hemmings BA (2001) Carboxyl-terminal modulator protein (CTMP), a negative regulator of PKB/Akt and v-Akt at the plasma membrane. Science (New York, NY) 294(5541):374–380. doi:10.1126/science.1062030
Franke TF (2008) Intracellular signaling by Akt: bound to be specific. Sci Signal 1(24):pe29. doi:10.1126/scisignal.124pe29
Miyawaki T, Ofengeim D, Noh KM, Latuszek-Barrantes A, Hemmings BA, Follenzi A, Zukin RS (2009) The endogenous inhibitor of Akt, CTMP, is critical to ischemia-induced neuronal death. Nat Neurosci 12(5):618–626. doi:10.1038/nn.2299
Acknowledgments
We thank Yu-Chang Chen and Yen-Ling Chen for the technical support. We thank the Institute of Biomedical Sciences Instrumental Core Facility, Academia Sinica for confocal microscopy assistance. This work was supported by grants from the National Science Council and Academia Sinica, Taiwan. The authors had full access to and take full responsibility for the integrity of the data. All authors have read and agree to the manuscript as written.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CY., Chen, JJ., Wu, JS. et al. Novel Link of Anti-apoptotic ATF3 with Pro-apoptotic CTMP in the Ischemic Brain. Mol Neurobiol 51, 543–557 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8710-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8710-0