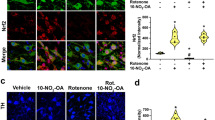
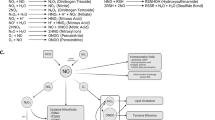
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) is an important inorganic molecule of the biological system owing to diverse physiological implications. NO is synthesised from a semi-essential amino acid l-arginine. NO biosynthesis is catalysed by a family of enzymes referred to as nitric oxide synthases (NOSs). NO is accused in many acute and chronic illnesses, which include central nervous system disorders, inflammatory diseases, reproductive impairments, cancer and cardiovascular anomalies. Owing to very unstable nature, NO gets converted into nitrite, peroxynitrite and other reactive nitrogen species that could lead to nitrosative stress in the nigrostriatal system. Nitrosative stress is widely implicated in Parkinson's disease (PD), and its beneficial and harmful effects are demonstrated in in vitro, rodent and primate models of toxins-induced parkinsonism and in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid and nigrostriatal tissues of sporadic PD patients. The current article updates the roles of NO and NOSs in sporadic PD and toxins-induced parkinsonism in rodents along with the scrutiny of how inhibitors of NOSs could open a new line of approach to moderately rescue from PD pathogenesis based on the existing literature. The article also provides a perspective concerning the lack of ample admiration to such an approach and how to minimise the underlying lacunae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh MP, Patel S, Dikshit M, Gupta YK (2006) Contribution of genomics and proteomics in understanding the role of modifying factors in Parkinson's disease. Indian J Biochem Biophys 43:69–81
Yadav S, Dixit A, Agrawal S, Singh A, Srivastava G, Singh AK, Srivastava PK, Prakash O, Singh MP (2012) Rodent models and contemporary molecular techniques: notable feats yet incomplete explanations of Parkinson's disease pathogenesis. Mol Neurobiol 46:495–512
Dixit A, Srivastava G, Verma D, Mishra M, Singh PK, Prakash O, Singh MP (2013) Minocycline, levodopa and MnTMPyP induced changes in the mitochondrial proteome profile of MPTP and maneb and paraquat mice models of Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:1227–1240
Moncada S, Higgs EA (2006) The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology. Br J Pharmacol 147:S193–S201
Jachymova M, Masters BS, Horky K, Zima T, Martasek P (2006) Nitric oxide synthase, typical flavohemoproteins and their complicated enzymology. Cas Lek Cesk 145:526–531
Zhou L, Zhu DY (2009) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase: structure, subcellular localization, regulation, and clinical implications. Nitric Oxide 20:223–230
Culotta E, Koshland DE Jr (1992) NO news is good news. (nitric oxide; includes information about other significant advances & discoveries of 1992) (Molecule of the Year). Science 258(5090):1862–1864
Kavya R, Saluja R, Singh S, Dikshit M (2006) Nitric oxide synthase regulation and diversity: implications in Parkinson's disease. Nitric Oxide 15:280–294
Chinje EC, Stratford IJ (1997) Role of nitric oxide in growth of solid tumours: a balancing act. Essays Biochem 32:61–72
Liu Q, Gross SS (1996) Binding sites of nitric oxide synthases. Methods Enzymol 268:311–324
Panda K, Rosenfeld RJ, Ghosh S, Meade AL, Getzoff ED, Stuehr DJ (2002) Distinct dimer interaction and regulation in nitric-oxide synthase types I, II, and III. J Biol Chem 277:31020–31030
Ponting CP, Phillips C (1995) DHR domains in syntrophins, neuronal NO synthases and other intracellular proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 20:102–103
Aquilano K, Baldelli S, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2008) Role of nitric oxide synthases in Parkinson's disease: a review on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of polyphenols. Neurochem Res 33:2416–2426
Knowles RG, Moncada S (1994) Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J 298:249–258
Duan W, Zhou J, Li W, Zhou T, Chen Q, Yang F, Wei T (2013) Plasma membrane calcium ATPase 4b inhibits nitric oxide generation through calcium-induced dynamic interaction with neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Protein Cell 4:286–298
Gupta SP, Patel S, Yadav S, Singh AK, Singh S, Singh MP (2010) Involvement of nitric oxide in maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson's disease phenotype in mouse: is there any link with lipid peroxidation? Neurochem Res 35:1206–1213
Singhal NK, Srivastava G, Patel DK, Jain SK, Singh MP (2011) Melatonin or silymarin reduces maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson's disease phenotype in the mouse. J Pineal Res 50:97–109
Kavya R, Dikshit M (2005) Role of nitric oxide/nitric oxide synthase in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurosci 12:1–5
Nelson EJ, Connolly J, McArthur P (2003) Nitric oxide and S-nitrosylation: excitotoxic and cell signaling mechanism. Biol Cell 95:3–8
Madhusoodanan KS, Murad F (2007) NO-cGMP signaling and regenerative medicine involving stem cells. Neurochem Res 32:681–694
Hall ED, Wang JA, Miller DM (2012) Relationship of nitric oxide synthase induction to peroxynitrite-mediated oxidative damage during the first week after experimental traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 238:176–182
Chalimoniuk M, Langfort J, Lukacova N, Marsala J (2004) Upregulation of guanylyl cyclase expression and activity in striatum of MPTP-induced parkinsonism in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:118–126
Kanao T, Sawada T, Davies SA, Ichinose H, Hasegawa K, Takahashi R, Hattori N, Imai Y (2012) The nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway regulates FoxO and alters dopaminergic neuron survival in Drosophila. PLoS One 7(2):e30958
Cooke RM, Mistry R, Challiss RA, Straub VA (2013) Nitric oxide synthesis and cGMP production is important for neurite growth and synapse remodeling after axotomy. J Neurosci 33:5626–5637
Chalimoniuk M, Stolecka A, Ziemińska E, Stepień A, Langfort J, Strosznajder JB (2009) Involvement of multiple protein kinases in cPLA2 phosphorylation, arachidonic acid release, and cell death in in vivo and in vitro models of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced parkinsonism—the possible key role of PKG. J Neurochem 110:307–317
Moncada S, Erusalimsky JD (2002) Does nitric oxide modulate mitochondrial energy generation and apoptosis? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:214–220
Singh S, Zhuo M, Gorgun M, Englander EW (2013) Overexpressed neuroglobin raises threshold for nitric oxide-induced impairment of mitochondrial respiratory activities and stress signaling in primary cortical neurons. Nitric Oxide 32:21–28
Erusalimsky JD, Moncada S (2007) Nitric oxide and mitochondrial signaling: from physiology to pathophysiology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2524–2531
Hwang O (2013) Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurobiol 22:11–17
Akhtar MW, Sunico CR, Nakamura T, Lipton SA (2012) Redox regulation of protein function via cysteine S-nitrosylation and its relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Cell Biol 2012:463756
Shergill JK, Cammack R, Cooper CE, Cooper JM, Mann VM, Schapira AH (1996) Detection of nitrosyl complexes in human substantia nigra, in relation to Parkinson's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 12:298–305
Zhang W, Phillips K, Wielgus AR, Liu J, Albertini A, Zucca FA, Faust R, Qian SY, Miller DS, Chignell CF, Wilson B, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S, Joset D, Loike J, Hong JS, Sulzer D, Zecca L (2011) Neuromelanin activates microglia and induces degeneration of dopaminergic neurons: implications for progression of Parkinson's disease. Neurotox Res 19:63–72
Ghosh A, Kanthasamy A, Joseph J, Anantharam V, Srivastava P, Dranka BP, Kalyanaraman B, Kanthasamy AG (2012) Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of an orally active apocynin derivative in pre-clinical models of Parkinson's disease. J Neuroinflammation 9:241
Sung YH, Kim SC, Hong HP, Park CY, Shin MS, Kim CJ, Seo JH, Kim DY, Kim DJ, Cho HJ (2012) Treadmill exercise ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal loss through suppressing microglial activation in Parkinson's disease mice. Life Sci 91:1309–1316
Matsui T, Motoki Y, Yoshida Y (2013) Hypothermia reduces toll-like receptor 3-activated microglial interferon-β and nitric oxide production. Mediat Inflamm 2013:436263
Colombo E, Cordiglieri C, Melli G, Newcombe J, Krumbholz M, Parada LF, Medico E, Hohlfeld R, Meinl E, Farina C (2012) Stimulation of the neurotrophin receptor TrkB on astrocytes drives nitric oxide production and neurodegeneration. J Exp Med 209:521–535
Kim SU, Park YH, Min JS, Sun HN, Han YH, Hua JM, Lee TH, Lee SR, Chang KT, Kang SW, Kim JM, Yu DY, Lee SH, Lee DS (2013) Peroxiredoxin I is a ROS/p38 MAPK-dependent inducible antioxidant that regulates NF-κB-mediated iNOS induction and microglial activation. J Neuroimmunol 259:26–36
Hoang T, Choi DK, Nagai M, Wu DC, Nagata T, Prou D, Wilson GL, Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Chesselet MF, Przedborski S (2009) Neuronal NOS and cyclooxygenase-2 contribute to DNA damage in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. Free Radic Biol Med 47:1049–1056
Boyd CS, Cadenas E (2002) Nitric oxide and cell signaling pathways in mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Biol Chem 383:411–423
Perier C, Tieu K, Guegan C, Caspersen C, Jakson-Lewis V, Carelli V, Martinuzzi A, Hirano M, Przedborski S, Vila M (2005) Complex I deficiency primes Bax-dependent neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial oxidative damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:19126–19131
Guo S, Yan J, Yang T, Yang X, Bezard E, Zhao B (2007) Protective effects of green tea polyphenols in the 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson's disease through inhibition of ROS-NO pathway. Biol Psychiatry 62:1353–1362
Hancock DB, Martin ER, Vance JM, Scott WK (2008) Nitric oxide synthase genes and their interactions with environmental factors in Parkinson's disease. Neurogenetics 9:249–262
Montesanto A, Crocco P, Tallaro F, Pisani F, Mazzei B, Mari V, Corsonello A, Lattanzio F, Passarino G, Rose G (2013) Common polymorphisms in nitric oxide synthase (NOS) genes influence quality of aging and longevity in humans. Biogerontology 14:177–186
Schulte C, Sharma M, Mueller JC, Lichtner P, Prestel J, Berg D, Gasser T (2006) Comprehensive association analysis of the NOS2A gene with Parkinson disease. Neurology 67:2080–2082
Huerta C, Sánchez-Ferrero E, Coto E, Blázquez M, Ribacoba R, Guisasola LM, Salvador C, Alvarez V (2007) No association between Parkinson's disease and three polymorphisms in the eNOS, nNOS, and iNOS genes. Neurosci Lett 413:202–205
Rife T, Rasoul B, Pullen N, Mitchell D, Grathwol K, Kurth J (2009) The effect of a promoter polymorphism on the transcription of nitric oxide synthase 1 and its relevance to Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res 87:2319–2325
Lo HS, Hogan EL, Soong BW (2002) 5′-Flanking region polymorphism of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene with Parkinson's disease in Taiwan. J Neurol Sci 194:11–13
Hancock DB, Martin ER, Fujiwara K, Stacy MA, Scott BL, Stajich JM, Jewett R, Li YJ, Hauser MA, Vance JM, Scott WK (2006) NOS2A and the modulating effect of cigarette smoking in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 60:366–373
Levecque C, Elbaz A, Clavel J, Richard F, Vidal JS, Amouyel P, Tzourio C, Alpérovitch A, Chartier-Harlin MC (2003) Association between Parkinson's disease and polymorphisms in the nNOS and iNOS genes in a community-based case–control study. Hum Mol Genet 12:79–86
Sinha A, Srivastava N, Singh S, Singh AK, Bhushan S, Shukla R, Singh MP (2009) Identification of differentially displayed proteins in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson's disease patients: a proteomic approach. Clin Chim Acta 400:14–20
Beyer K (2007) Mechanistic aspects of Parkinson's disease: alpha-synuclein and the biomembrane. Cell Biochem Biophys 47:285–299
Reif DW, Simmons RD (1990) Nitric oxide mediates iron release from ferritin. Arch Biochem Biophys 283:537–541
Luong KV, Nguyen LT (2012) Thiamine and Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci 316:1–8
Gu Z, Nakamura T, Lipton SA (2010) Redox reactions induced by nitrosative stress mediate protein misfolding and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 41:55–72
Chung KK, Thomas B, Li X, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Marsh L, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2004) S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates ubiquitination and compromises parkin's protective function. Science 304:1328–1331
Yao D, Gu Z, Nakamura T, Shi ZQ, Ma Y, Gaston B, Palmer LA, Rockenstein EM, Zhang Z, Masliah E, Uehara T, Lipton SA (2004) Nitrosative stress linked to sporadic Parkinson's disease: S-nitrosylation of parkin regulates its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10810–10814
Fang J, Nakamura T, Cho DH, Gu Z, Lipton SA (2007) S-nitrosylation of peroxiredoxin 2 promotes oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell death in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18742–1847
Betarbet R, Sherer TB, Greenamyre JT (2002) Animal models of Parkinson's disease. Bioessays 24:308–318
Choi HJ, Lee SY, Cho Y, Hwang O (2004) JNK activation by tetrahydrobiopterin: implication for Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res 75:715–721
Joniec I, Ciesielska A, Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, Przybylkowski A, Czlonkowska A, Czlonkowski A (2009) Age and sex-differences in the nitric oxide synthase expression and dopamine concentration in the murine model of Parkinson's disease induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Brain Res 1261:7–19
Nakamura T, Lipton SA (2011) S-nitrosylation of critical protein thiols mediates protein misfolding and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:1479–1492
Hara MR, Thomas B, Cascio MB, Bae BI, Hester LD, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Sawa A, Snyder SH (2006) Neuroprotection by pharmacologic blockade of the GAPDH death cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:3887–3889
Kim HG, Ju MS, Ha SK, Lee H, Lee H, Kim SY, Oh MS (2012) Acacetin protects dopaminergic cells against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1287–1294
Roy A, Ghosh A, Jana A, Liu X, Brahmachari S, Gendelman HE, Pahan K (2012) Sodium phenylbutyrate controls neuroinflammatory and antioxidant activities and protects dopaminergic neurons in mouse models of Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 7:e38113
Di Matteo V, Pierucci M, Benigno A, Crescimanno G, Esposito E, Di Giovanni G (2009) Involvement of nitric oxide in nigrostriatal dopaminergic system degeneration: a neurochemical study. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1155:309–315
Yuste JE, Echeverry MB, Ros-Bernal F, Gomez A, Ros CM, Campuzano CM, Fernandez-Villalba E, Herrero MT (2012) 7-Nitroindazole down-regulates dopamine/DARPP-32 signaling in neostriatal neurons in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology 63:1258–1267
Singh S, Kumar S, Dikshit M (2010) Involvement of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and nitric oxide synthase in dopaminergic neuronal death induced by 6-hydroxydopamine and lipopolysaccharide. Redox Rep 15:115–122
Singh S, Das T, Ravindran A, Chaturvedi RK, Shukla Y, Agarwal AK, Dikshit M (2005) Involvement of nitric oxide in neurodegeneration: a study on the experimental models of Parkinson's disease. Redox Rep 10:103–109
Li M, Dai FR, Du XP, Yang QD, Chen Y (2012) Neuroprotection by silencing iNOS expression in a 6-OHDA model of Parkinson's disease. J Mol Neurosci 48:225–233
Broom L, Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Sadeghian M, Davis JB, Medhurst AD, Dexter DT (2011) Neuroprotection by the selective iNOS inhibitor GW274150 in a model of Parkinson disease. Free Radic Biol Med 50:633–640
Miller RL, James-Kracke M, Sun GY, Sun AY (2009) Oxidative and inflammatory pathways in Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Res 34:55–65
Gomez C, Bandez MJ, Navarro A (2007) Pesticides and impairment of mitochondrial function in relation with the parkinsonian syndrome. Front Biosci 12:1079–1093
Xiong N, Long X, Xiong J, Jia M, Chen C, Huang J, Ghoorah D, Kong X, Lin Z, Wang T (2012) Mitochondrial complex I inhibitor rotenone-induced toxicity and its potential mechanisms in Parkinson's disease models. Crit Rev Toxicol 42:613–632
Abdin AA, Sarhan NI (2011) Intervention of mitochondrial dysfunction-oxidative stress-dependent apoptosis as a possible neuroprotective mechanism of α-lipoic acid against rotenone-induced parkinsonism and l-dopa toxicity. Neurosci Res 71:387–395
Tada-Oikawa S, Hiraku Y, Kawanishi M, Kawanishi S (2003) Mechanism for generation of hydrogen peroxide and change of mitochondrial membrane potential during rotenone-induced apoptosis. Life Sci 73:3277–3288
He Y, Imam SZ, Dong Z, Jankovic J, Ali SF, Appel SH, Le W (2003) Role of nitric oxide in rotenone-induced nigro-striatal injury. J Neurochem 86:1338–1345
Bashkatova V, Alam M, Vanin A, Schmidt WJ (2004) Chronic administration of rotenone increases levels of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation products in rat brain. Exp Neurol 186:235–241
Pal R, Miranda M, Narayan M (2011) Nitrosative stress-induced Parkinsonian Lewy-like aggregates prevented through polyphenolic phytochemical analog intervention. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:324–329
Cannon JR, Tapias V, Na HM, Honick AS, Drolet RE, Greenamyre JT (2009) A highly reproducible rotenone model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 34:279–290
Hu LF, Lu M, Tiong CX, Dawe GS, Hu G, Bian JS (2010) Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide on Parkinson's disease rat models. Aging Cell 9:135–146
Verma R, Nehru B (2009) Effect of centrophenoxine against rotenone-induced oxidative stress in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int 55:369–375
Bi J, Jiang B, Hao S, Zhang A, Dong Y, Jiang T, An L (2009) Catalpol attenuates nitric oxide increase via ERK signaling pathways induced by rotenone in mesencephalic neurons. Neurochem Int 54:264–270
Yadav S, Gupta SP, Srivastava G, Srivastava PK, Singh MP (2012) Role of secondary mediators in caffeine-mediated neuroprotection in maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinson's disease phenotype in the mouse. Neurochem Res 37:875–884
Costello S, Cockburn M, Bronstein J, Zhang X, Ritz B (2009) Parkinson's disease and residential exposure to maneb and paraquat from agricultural applications in the central valley of California. Am J Epidemiol 169:919–926
Mangano EN, Litteljohn D, So R, Nelson E, Peters S, Bethune C, Bobyn J, Hayley S (2012) Interferon-γ plays a role in paraquat-induced neurodegeneration involving oxidative and proinflammatory pathways. Neurobiol Aging 33:1411–1426
Wang C, Ko HS, Thomas B, Tsang F, Chew KC, Tay SP, Ho MW, Lim TM, Soong TW, Pletnikova O, Troncoso J, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Lim KL (2005) Stress-induced alterations in parkin solubility promote parkin aggregation and compromise parkin's protective function. Hum Mol Genet 14:3885–3897
Shimizu K, Matsubara K, Ohtaki K, Shiono H (2003) Paraquat leads to dopaminergic neural vulnerability in organotypic midbrain culture. Neurosci Res 46:523–532
Shimizu K, Matsubara K, Ohtaki K, Fujimaru S, Saito O, Shiono H (2003) Paraquat induces long-lasting dopamine overflow through the excitotoxic pathway in the striatum of freely moving rats. Brain Res 976:243–252
Ahmad I, Kumar A, Shukla S, Prasad Pandey H, Singh C (2008) The involvement of nitric oxide in maneb- and paraquat-induced oxidative stress in rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Free Radic Res 42:849–862
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20:6309–6316
Lee YY, Park JS, Jung JS, Kim DH, Kim HS (2013) Anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside Rg5 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Sci 14:9820–9833
Arimoto T, Bing G (2003) Up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the substantia nigra by lipopolysaccharide causes microglial activation and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 12:35–45
Di Girolamo G, Farina M, Riberio ML, Ogando D, Aisemberg J, De los Santos AR, Martí ML, Franchi AM (2003) Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitor pretreatment on nitric oxide production, nNOS and iNOS expression in rat cerebellum. Br J Pharmacol 139:1164–1170
Choi DY, Liu M, Hunter RL, Cass WA, Pandya JD, Sullivan PG, Shin EJ, Kim HC, Gash DM, Bing G (2009) Striatal neuroinflammation promotes parkinsonism in rats. PLoS One 4:e5482
Tieu K (2011) A guide to neurotoxic animal models of Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1:a009316
Pubill D, Chipana C, Camins A, Pallàs M, Camarasa J, Escubedo E (2005) Free radical production induced by methamphetamine in rat striatal synaptosomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:57–68
Rajakumar B, Flumerfelt BA, Hrycyshyn AW, Rajakumar N (2007) Nitric oxide-containing neurons in long-term grafts in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Cell Transplant 16:449–459
Ali SF, Itzhak Y (1998) Effects of 7-nitroindazole, an NOS inhibitor on methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotoxicity in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci 844:122–130
Salum C, Issy AC, Brandão ML, Guimarães FS, Bel EA (2011) Nitric oxide modulates dopaminergic regulation of prepulse inhibition in the basolateral amygdala. J Psychopharmacol 25:1639–1648
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci 20:415–455
Bilska A, Dubiel M, Sokołowska-Jezewicz M, Lorenc-Koci E, Włodek L (2007) Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 146:1758–1771
Tadaiesky MT, Andreatini R, Vital MA (2006) Different effects of 7-nitroindazole in reserpine-induced hypolocomotion in two strains of mice. Eur J Pharmacol 535:199–207
Chalimoniuk M, Lukacova N, Marsala J, Langfort J (2006) Alterations of the expression and activity of midbrain nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylyl cyclase in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in mice. Neuroscience 141:1033–1046
Hantraye P, Brouillet E, Ferrante R, Palfi S, Dolan R, Matthews RT, Beal MF (1996) Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in baboons. Nat Med 2:1017–1021
Liberatore GT, Jackson-Lewis V, Vukosavic S, Mandir AS, Vila M, McAuliffe WG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Przedborski S (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease. Nat Med 5(12):1403–1409
Dehmer T, Lindenau J, Haid S, Dichgans J, Schulz JB (2000) Deficiency of inducible nitric oxide synthase protects against MPTP toxicity in vivo. J Neurochem 74(5):2213–2216
Tsang AH, Lee YI, Ko HS, Savitt JM, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Chung KK (2009) S-nitrosylation of XIAP compromises neuronal survival in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4900–4905
Stone DK, Kiyota T, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE (2012) A model of nitric oxide induced α-synuclein misfolding in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 523:167–173
Rojanathammanee L, Murphy EJ, Combs CK (2011) Expression of mutant alpha-synuclein modulates microglial phenotype in vitro. J Neuroinflammation 8:44
Gao HM, Zhang F, Zhou H, Kam W, Wilson B, Hong JS (2011) Neuroinflammation and α-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Environ Health Perspect 119:807–814
Phillips RJ, Walter GC, Wilder SL, Baronowsky EA, Powley TL (2008) Alpha-synuclein-immunopositive myenteric neurons and vagal preganglionic terminals: autonomic pathway implicated in Parkinson's disease? Neuroscience 153:733–750
Manzoni C (2012) LRRK2 and autophagy: a common pathway for disease. Biochem Soc Trans 40:1147–1151
Gillardon F, Schmid R, Draheim H (2012) Parkinson's disease-linked leucine-rich repeat kinase 2(R1441G) mutation increases proinflammatory cytokine release from activated primary microglial cells and resultant neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 208:41–48
Cherra SJ 3rd, Steer E, Gusdon AM, Kiselyov K, Chu CT (2013) Mutant LRRK2 elicits calcium imbalance and depletion of dendritic mitochondria in neurons. Am J Pathol 182:474–484
Hoepken HH, Gispert S, Morales B, Wingerter O, Del Turco D, Mülsch A, Nussbaum RL, Müller K, Dröse S, Brandt U, Deller T, Wirth B, Kudin AP, Kunz WS, Auburger G (2007) Mitochondrial dysfunction, peroxidation damage and changes in glutathione metabolism in PARK6. Neurobiol Dis 25:401–411
Brzozowski MJ, Alcantara SL, Iravani MM, Rose S, Jenner P (2011) The effect of nNOS inhibitors on toxin-induced cell death in dopaminergic cell lines depends on the extent of enzyme expression. Brain Res 1404:21–30
Zorzi G, Thony B, Blau N (2002) Reduced nitric oxide metabolites in CSF of patients with tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency. J Neurochem 80:362–644
Gomes MZ, Raisman-Vozari R, Del Bel EA (2008) A nitric oxide synthase inhibitor decreases 6-hydroxydopamine effects on tyrosine hydroxylase and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the rat nigrostriatal pathway. Brain Res 1203:160–169
Shi C, Zhang YX, Zhang ZF (2009) Effect of phosphorylated-ERK1/2 on inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the substantia nigra of mice with MPTP-induced Parkinson disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 29:60–63
Del-Bel E, Padovan-Neto FE, Raisman-Vozari R, Lazzarini M (2011) Role of nitric oxide in motor control: implications for Parkinson's disease pathophysiology and treatment. Curr Pharm Des 17:471–488
Padovan-Neto FE, Ferreira NR, Tavares D, de Aguiar D, Silva CA, Raisman-Vozari R, Del Bel E (2013) Anti-dyskinetic effect of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor is linked to decrease of FosB/DeltaFosB expression. Neurosci Lett 541:126–131
Takuma K, Tanaka T, Takahashi T, Hiramatsu N, Ota Y, Ago Y, Matsuda T (2012) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition attenuates the development of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemi-parkinsonian rats. Eur J Pharmacol 683:166–173
Camacho ME, Carrion MD, Lopez-Cara LC, Entrena A, Gallo MA, Espinosa A, Escames G, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2012) Melatonin synthetic analogs as nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Mini-Rev Med Chem 12:600–617
Van Dijk KD, Teunissen CE, Drukarch B, Jimenez CR, Groenewegen HJ, Berendse HW, van de Berg WD (2010) Diagnostic cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson's disease: a pathogenetically based approach. Neurobiol Dis 39:229–241
Antony PM, Diederich NJ, Balling R (2011) Parkinson's disease mouse models in translational research. Mamm Genome 22:401–419
Potashkin JA, Blume SR, Runkle NK (2010) Limitations of animal models of Parkinson's disease. Park Dis 2011:658083
Luo Z, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Yang X, Zhao B (2012) Protective effect of theaflavins on neuron against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. J Clin Biochem Nutr 50:133–138
Ojha RP, Rastogi M, Devi BP, Agrawal A, Dubey GP (2012) Neuroprotective effect of curcuminoids against inflammation-mediated dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7:609–618
Kilbourn RG, Szabó C, Traber DL (1997) Beneficial versus detrimental effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in circulatory shock: lessons learned from experimental and clinical studies. Shock 7:235–246
Acknowledgments
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, is gratefully acknowledged for supporting the study (Networked Project: miND/BSC0115) financially as well as for providing research fellowships to Satya Prakash Gupta, Sharawan Yadav and Manindra Nath Tiwari. The University Grants Commission, New Delhi, is acknowledged for providing fellowship to Naveen Kumar Singhal. The correspondence reference number of this article is 3135.
Conflict of Interest
There are no actual/potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Satya Prakash Gupta and Sharawan Yadav contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S.P., Yadav, S., Singhal, N.K. et al. Does Restraining Nitric Oxide Biosynthesis Rescue from Toxins-Induced Parkinsonism and Sporadic Parkinson's Disease?. Mol Neurobiol 49, 262–275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8517-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8517-4