Abstract
During brain development, each neuron must find and synapse with the correct pre- and postsynaptic partners. The complexity of these connections and the relatively large distances some neurons must send their axons to find the correct partners makes studying brain development one of the most challenging, and yet fascinating disciplines in biology. Furthermore, once the initial connections have been made, the neurons constantly remodel their dendritic and axonal arbours in response to changing demands. Neurexin and neuroligin are two cell adhesion molecules identified as important regulators of this process. The importance of these genes in the development and modulation of synaptic connectivity is emphasised by the observation that mutations in these genes in humans have been associated with cognitive disorders such as Autism spectrum disorders, Tourette syndrome and Schizophrenia. The present review will discuss recent advances in our understanding of the role of these genes in synaptic development and modulation, and in particular, we will focus on recent work in invertebrate models, and how these results relate to studies in mammals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Proper brain function depends on the precise arrangement of trillions of individual synaptic connections. While neurobiologists have been fascinated by the stereotyped complexity of neuronal networks for over a century, it is only in the last few decades that we have begun to understand some of the molecular mechanisms that govern the formation and function of these networks. The development of specific patterns of connectivity requires axons and dendrites of synaptic partners to be targeted to defined regions of the CNS, correctly identify their synaptic targets within that region, and then form specialised synapses with their targets. Each of these steps is mediated by a host of interactions between individual neurons and their targets. A defect at any stage of this process leads to incorrect patterns of connectivity and impaired nervous system function.
One of the first tasks a newly differentiated neuron must complete is to extend an axon towards its synaptic target(s). Axon guidance is thought to be mediated by extracellular cues which are expressed in concentration gradients that may exert either attractive or repulsive effects on incoming axons. Axons are able to navigate to their correct position by means of receptors expressed in the growth cone capable of responding to the various guidance cues. Once the axons have reached the appropriate regions, they need to correctly identify their targets amongst a heterogeneous population of cells. Combined expression of both synaptogenic (attractive) molecules and antisynaptogenic (repulsive) molecules in both presynaptic and postsynaptic cells is necessary to form the correct pattern of innervation. The final step in the formation of functional synaptic networks is the formation and specialisation of synapses. Two key molecules that have been implicated in this process are Neurexin and Neuroligin.
Neurexin and neuroligin are trans-synaptic binding partners expressed in the presynaptic and postsynaptic compartments respectively. As detailed below, both neuroligin and neurexin exhibit synaptogenic activity in cell culture assays [1–4]. Knockout studies in mice however, show that synaptogenesis is not significantly affected by loss of either and suggest that neuroligin may be more important for activity dependent maturation of synapses [5–7]. Given the apparent discrepancy between cell culture and knockout studies, it is important to first clearly define what is meant by synapse formation and maturation. For the purpose of this review, we will define a synapse as the sum of all connections between a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic target. As such, each synapse may consist of multiple morphologically distinct connections (e.g., synaptic boutons in a neuromuscular junction (NMJ)). Based on this definition of a synapse, synapse formation can be defined as the transient establishment of the first functional contact between the presynaptic neuron and its postsynaptic partner. The stabilisation of that contact through pre- and postsynaptic signalling cascades, or the creation of additional contacts between the pre- and postsynaptic cell then falls under the broader definition of synapse maturation.
Since early studies of neuroligin and neurexin function in cell culture used changes in the total number of synaptic specialisations as a readout of synaptogenesis, the results reflect a combination of both synaptogenesis and synaptic maturation. Furthermore, the two processes may be difficult to separate under such experimental conditions. Upon closer inspection, it was noted that the “synaptogenic” activity of neuroligins 1 and 2 is suppressed when synaptic activity is blocked [5]. Based on these results, it was proposed that rather than mediating synaptogenesis, trans-synaptic interactions between neurexin and neuroligin may be more important for synapse maturation and specifically, activity dependent modification of synaptic strength [8]. In the present review, we will discuss some recent observations made in invertebrates that lend support to this hypothesis.
Neurexin
Neurexins were originally identified as presynaptic receptors for the black widow spider toxin α-latrotoxin [9]. Three neurexin homologues have been identified in mammals, each of which gives rise to an α-neurexin and a β-neurexin via independent promoters [10]. Homologues of α-neurexin have also been identified in several invertebrate species including Drosophila, Caenorhabditis elegans, honeybees and Aplysia [10–12]. Until recently, there was no evidence of β-neurexin isoforms in invertebrates suggesting that this may be a relatively recent evolution of the gene [10, 12]. However, a recent analysis of the neurexin superfamily of genes in C. elegans identified a β-neurexin splice form of the nrx-1 gene [13] suggesting that a closer analysis of other invertebrate neurexins may be required.
α-Neurexins and β-neurexins encode type I transmembrane proteins with identical intracellular domains but different extracellular domains [9]. The short intracellular domain of neurexins binds to a number of presynaptic proteins such as synaptotagmin [14], CASK [15] and Mint [16] via a postsynaptic density (PSD)-95/discs large/zona-occludens-1 (PDZ) binding motif at the C terminus. The extracellular domain of α-neurexin has a signal peptide at the N terminus, three epidermal growth factor like domains, each surrounded by two laminin/neurexin/sex hormone-binding globulin domains (LNS) and an O-linked carbohydrate-rich region proximal to the transmembrane domain [9]. The extracellular domain of β-neurexin has a single LNS domain in addition to the O-linked carbohydrate-rich stalk [9, 17]. All three mammalian neurexins are capable of generating both an α-neurexin and a β-neurexin isoform. Furthermore, each α-neurexin has five canonical splice sites, two of which are also present in the β-neurexin isoforms. Alternative splicing at these sites allows for the generation of hundreds of alternative neurexin isoforms, each of which has unique binding affinities for different substrates [18–22].
All neurexins show broad, yet heterogeneous expression throughout the nervous system by in situ hybridization [23, 24]. Based on immunoflourescence analysis and known interactions between the intracellular domain of neurexin and several presynaptic proteins, neurexins are thought to exist primarily at presynaptic membranes [12, 13, 25–27]. However, neurexins have also been observed at the postsynaptic membrane in some synapses and have been shown to exert cell autonomous effects on postsynaptic receptor function [12, 26, 28, 29] suggesting that both the expression pattern and function of neurexins may be broader than originally hypothesised.
Neuroligins
Neuroligins were first identified as synaptic binding partners for neurexins [30]. Four neuroligin homologues have been identified in mammals plus an additional neuroligin homologue on the Y chromosome in humans [30–33]. Homologues of neuroligin have also been identified in the nervous systems of many invertebrates including Drosophila (four homologues [34, 35]), Aplysia (single homologue [12]), honeybees (five homologues [11, 36]) and C. elegans (single homologue [37]). So far, only two of the four homologues in Drosophila have been functionally characterised [34, 35]. Neuroligins have been implicated in sensory modulation in both honeybees and C. elegans [36, 37], and in long-term synaptic modulation in Aplysia (discussed in more detail below [12]). Phylogenetic analysis of neuroligin sequences from multiple species suggests that neuroligins diversified independently during evolution in both vertebrates and insects. By contrast, neurexins have diversified in vertebrates, but not in insects (Fig. 1). In addition to gene duplications giving rise to three neurexin genes in vertebrates, vertebrate neurexins have also acquired an alternative promoter and multiple splice sites that significantly increase the potential diversity of neurexin transcripts in vertebrates. The diversity of neuroligin genes across a wider range of species suggests that neuroligin may be under stronger evolutionary selection than neurexin.
Neurexin and neuroligin structure, function and evolution. A Domain structure of Drosophila neuroligins and neurexin compared to human neuroligin 1 and neurexin 1-α. The conservation of individual protein domains between Drosophila homologues and the human gene are given as a % identity. The global conservation is listed to the right side of each homologue. B Phylogenetic tree of neuroligin sequences from multiple species. Red branches indicate neuroligin sequences in vertebrates, blue branches indicate neuroligin sequences in insects and green branches indicate neuroligin sequences in worms. This tree was adapted from tree TF326187 (available at http://www.treefam.org). As seen from this tree, neuroligin sequences diversified independently in insects and vertebrates from a common ancestral neuroligin sequence. Branches corresponding to the four neuroligin genes in vertebrates and the two characterised neuroligin genes in Drosophila are indicated. C Phylogenetic tree of neurexin sequences from multiple species. Red branches indicate neurexin sequences in vertebrates, blue branches indicate neurexin sequences in insects and green branches indicate neurexin sequences in worms. This tree was adapted from tree TF32103 (available at http://www.treefam.org). Neurexin sequences have shown less diversification in insects than vertebrates. Branches corresponding to the three neurexin genes in vertebrates and the Drosophila dnrx gene are indicated
Neuroligins encode type I transmembrane proteins composed of a long extracellular domain and a relatively short intracellular domain. The extracellular portion of neuroligin contains an O-linked carbohydrate-rich region near the transmembrane domain and a single globular domain with a high degree of sequence homology to acetylcholinesterases that lacks catalytic activity [30]. The intracellular portion of neuroligin contains a PDZ binding motif at the extreme C-terminal end of the protein that has been show to interact with the PDZ domain scaffolding proteins PSD-95, Shank and Gephryn [38–40]. Like neurexin, neuroligin also contains alternative splice variants and the binding affinity of neuroligin for either α-neurexin or β-neurexin is greatly affected by alternative splicing [20, 30, 33, 41, 42] suggesting that variable splicing of both neuroligin and neurexin may constitute a code governing the specificity of synaptic interactions.
While all neuroligins localise to postsynaptic densities, in mammals, different neuroligin homologues localise to different synapse classes. Neuroligins 1 and 2 localise exclusively to excitatory and inhibitory synapses respectively, while neuroligin 3 localises to both [43–45]. Neuroligin 4 has also recently been shown to localise to inhibitory synapses, preferentially with glycinergic synapses [46]. The synapse specific localization of different neuroligin homologues may be regulated by interactions with postsynaptic scaffolding proteins such as PSD-95 and gephyrin [47–49]. These results suggest that recruitment of specific neuroligin homologues may direct the development of individual synapses towards either an excitatory or inhibitory fate.
Neurexin/Neuroligin Function and Synaptic Maturation
Neurexin and neuroligin are primarily expressed on presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes respectively, and are thought to form a trans-synaptic complex. It should be noted however, that both neurexins and neuroligins have been shown to interact with other cell adhesion molecules [50–54], which may contribute to the functional and morphological defects observed in loss of function mutants. The first hints of the functional significance of complexes between neurexin and neuroligin came from a study showing that expression of neuroligin in non-neuronal cells was sufficient to induce presynaptic specialisations in co-cultured neurons [4]. The neuroligin induced clustering of vesicles could be blocked if cultures were incubated with a soluble β-neurexin suggesting that trans-synaptic interactions between neuroligin and β-neurexin were necessary for presynaptic specialisation [4]. In similar experiments, expression of neurexin in non-neuronal cells induced postsynaptic specialisations in co-cultured neurons [2, 3].
It should be noted that the synaptic specialisations observed in these studies consisted of clustering of synaptic vesicles or postsynaptic receptors. If we define a synapse as the sum of all synaptic connections between a pre- and postsynaptic cell, then this increase in the number of synaptic specialisations may not reflect an increase in the number of synapses, but rather an increase in the strength of pre-existing synapses, or perhaps an increase both in the number and strength of synapses. To address this issue, Chubykin et al. [5] asked whether neuroligins 1 and 2 functioned as synapse-inducing agents, independent of synaptic activity, or whether they acted downstream of synaptic signalling to modify the strength of existing synapses. They found that blocking synaptic activity reduced the “synaptogenic” activity of neuroligins 1 and 2, suggesting that they stabilise and/or strengthen existing synapses in an activity dependent manner.
Consistent with this, studies in knockout mice show that neurexins and neuroligins are important for synaptic function, but do not significantly affect the number of synapses. Deletion of all three α-neurexins in mice did not appreciably alter synaptic structure [6], however, synaptic function was significantly impaired. Moreover, both excitatory and inhibitory transmitter release in the CNS and acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction were reduced in α-neurexin knockout mice [6, 55–57]. These defects were attributed, in large part, to impaired function of N-type and P/Q-type voltage gated calcium channels in the neurexin knockout mice [6, 57]. A cell autonomous reduction in postsynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor but not α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxyzolepropionic acid receptor function was also observed in α-neurexin knockout mice [28]. Homeostatic regulation of transmitter release at neuromuscular junctions was also impaired in α-neurexin knockout mice [56], consistent with a role for α-neurexins in activity dependent growth of synapses. Interestingly, the consequences associated with a loss of β-neurexin have yet to be determined. Furthermore, it is unclear from these neurexin knockout studies what percentage of α-neurexin function is mediated via a trans-synaptic interaction with neuroligin.
Similar phenotypes were observed in neuroligin knockout mice. Loss of neuroligins 1–3 had no effect on brain architecture or synapse formation but significantly impaired both excitatory and inhibitory transmitter release [7]. Whereas individual α-neurexins appear to be partially redundant [6, 55–57], deletion of either neuroligins 1 and 2 specifically impaired excitatory or inhibitory transmitter release respectively [58–60]. For a list of synaptic, behavioural and morphological phenotypes observed in mice lacking either neurexin or neuroligin, see Table 1. Taken together, the studies in knockout mice showed that while neurexin and neuroligin are not essential for synapse formation they are required for proper synaptic function. Furthermore, these studies are consistent with a role for neurexin and neuroligin in synapse maturation or development.
Neurexin and Neuroligin Mediate Maturation of the NMJ in Drosophila
The highly stereotyped pattern of musculature and innervation in Drosophila embryos and larvae has made neuromuscular junction development in Drosophila an excellent model for studying all aspects of synapse formation. First, newly differentiated motorneurons send their axons into the periphery toward the target muscle fibres [65]. Once at the body wall, each axon then selects the correct muscle(s) with which to synapse [66, 67]. Finally, as the embryos hatch and progress through larval development, the muscles increase significantly in size requiring substantial remodelling of the synapse in order to maintain the necessary strength of synaptic input [68, 69]. By studying the role of neurexin and neuroligin in this process, it should be possible to more accurately dissect at exactly which stages of synapse formation/maturation they are required. An additional advantage of this system is that it is possible to analyse the role of specific genes in synapse formation/maturation with single cell resolution in an in vivo context, something that is difficult to achieve in the mammalian CNS.
Several studies have examined the role of both neurexin and neuroligin in NMJ development in Drosophila [26, 27, 34, 35, 70]. Drosophila has a single neurexin homologue and four neuroligin homologues. Recent studies have examined the role of Drosophila neurexin (dnrx) and two of the four Drosophila homologues of neuroligin (dnl1 and dnl2) in NMJ formation and maturation [26, 27, 34, 35, 70]. Interestingly, while there is some overlap in the mutant phenotypes of dnrx, dnl1 and dnl2, there are also phenotypic traits unique to each gene suggesting independent roles for each at the same synapse [26, 27, 34, 35, 70]. All three genes show strong expression at the NMJ, however, dnl1 appears to be a muscle specific homologue [34] while dnl2 and drnx show strong nervous system expression in addition to muscle expression [26, 27, 35, 70]. Deletion of dnl1, dnl2 or dnrx leads to a number of both presynaptic and postsynaptic defects.
Deletion of either dnl1 or dnl2 or deletion of dnrx leads to a reduction in the number of synaptic boutons at larval NMJs [26, 27, 34, 35, 70]. In the case of the dnl1 mutants, this reduction in bouton number results from a failure of the NMJ to expand during development since embryonic NMJs were not significantly different [34]. In wild-type animals, the number of synaptic boutons in larval NMJs increases in an activity dependent manner throughout larval development [71–73]. The reduced NMJ expansion in dnl1 mutants is consistent with a role for neuroligin in synapse maturation. In contrast however, embryonic and larval NMJs are smaller than the control in dnrx mutants [26, 27] suggesting that dnrx may be involved in NMJ development at a much earlier stage than dnl1. Both Drosophila neuroligin mutants and the dnrx mutant also showed a defect in the number of active zones. In dnl1 mutants, the total number of active zones was reduced, consistent with the decrease in synaptic boutons [34]. By contrast, both the number and density of active zones per synaptic bouton were increased in dnl2 and dnrx mutants ([27, 35], see Table 2 for a list of phenotypes observed in Drosophila neurexin and neuroligin mutants).
In addition to the morphological defects, dnl1, dnl2 and dnrx mutants also show defects in synaptic transmission at the NMJ [27, 34, 35]. As with the defects in morphology however, the defects in synaptic function also differed between the various mutants. Both dnl1 and dnrx mutants showed a reduction in evoked transmitter release [27, 34]. In the case of the dnl1 mutants, this reduction in transmitter release is consistent with the reduction in the number of synaptic boutons and active zones. As such, the functional defects are likely a consequence of changes in synaptic morphology at dnl1 mutant NMJs. By contrast, dnl2 mutants showed an increase in transmitter release relative to controls [35]. While dnl2 mutants showed fewer synaptic boutons than controls, the number of active zones per bouton was increased [35]. As such, changes in transmitter release in both dnl1 and dnl2 mutants are likely a reflection of changes in the number of active zones. In dnl1 mutants, fewer active zones leads to a reduction in transmitter release, while in dnl2 mutants, increased active zones translates to an increase in transmitter release.
The situation in dnrx mutants, however, is somewhat more complicated. dnrx mutants showed a reduction in the number of synaptic boutons, but an increase in the number of active zones per bouton, similar to that seen in dnl2 mutants [27, 35]. However, unlike dnl2 mutants, dnrx mutants showed a reduction in transmitter release. This discrepancy may be explained by an interaction between neurexin and voltage gated calcium channels. Neurexin knockout mice showed defects in synaptic transmission that were attributed, in large part, to impaired function of N-type and P/Q-type voltage gated calcium channels in the neurexin knockout mice [6, 57]. Given that dnrx mutant NMJs also showed defects in calcium sensitivity, which were not observed in dnl2 mutants [27, 35], it seems likely that the functional differences between dnl2 and dnrx mutant NMJs can be attributed to changes in calcium channel function.
The increase in the density of active zones observed in dnl2 and dnrx mutants is particularly interesting since it has been suggested that each active zone requires a fixed perisynaptic area for proper function such that the density of active zones within synaptic boutons is homeostatically maintained at a constant level [74]. However, an interesting exception to this rule was noted in animals that lack the Drosophila glutamate receptor (GluR) subunit GluR IIA [75, 76]. GluRs at the NMJ in Drosophila are formed by a heteromeric tetramer of five possible subunits. All GluRs contain the GluR IIE, GluR IID and GluR IIC (or GluR III) subunits [77–79]. In addition, each GluR also contains either a GluR IIA or GluR IIB subunit, and receptors containing these subunits are referred to as A-type or B-type, respectively [78, 80, 81]. Immature PSDs are composed primarily of A-type receptors, then during maturation, the ratio of A-type to B-type receptors becomes more balanced [82]. Interestingly, in both dnl2 mutants and embryonic dnrx mutants, PSDs show an increased abundance of A-type receptors indicating that the PSDs in these mutants are immature [26, 35]. It is unclear at present whether a similar shift in the ratio of A-type to B-type receptors also exists in dnl1 mutants.
Changes in the expression of the GluR IIA subunit (independently of changes in the other subunits) induce a retrograde signal that mediates changes in the number of presynaptic active zones [75, 76]. Over-expression of the GluR IIA subunit leads to an increase in the number of active zones but does not change the density of active zones within single synaptic boutons [76]. Reductions in the expression of the GluR IIA subunit leads to a reduction in the number of synaptic boutons, with a compensatory increase in the density of active zones within the boutons [75, 76]. In contrast to these observations, dnl2 and dnrx mutants show an increase in GluR IIA expression, yet the density of active zones is increased in these mutants [26, 35]. The mechanisms that link postsynaptic GluR IIA expression levels to presynaptic active zone numbers and/or density are unclear. The observations in dnl2 and dnrx mutant NMJs however [26, 35], suggest that an interaction between neurexin and neuroligin may be involved in the link between GluR IIA expression and presynaptic active zone regulation (see below for further discussion).
Further evidence that neuroligin and neurexin regulate the coordination of presynaptic and postsynaptic architecture can be seen in the ‘orphan’ boutons observed in dnl1 mutants [34]. In dnl1 mutants, a small percentage of synaptic boutons that contain the presynaptic release machinery, as visualised by the presence of synaptic vesicles, were observed to lack all postsynaptic markers, including GluR clusters [34]. Similarly, long stretches of axon, devoid of any synaptic boutons were often observed in dnrx mutants, although it is unclear whether postsynaptic densities still existed under these axon branches [27]. These misalignments between presynaptic and postsynaptic structures were also apparent at the ultrastructural level where the presynaptic membrane was sometimes observed to pull away from the postsynaptic membrane in both dnl1 and dnrx mutants [27, 34]. In dnl2 mutants however, no such misalignment between presynaptic and postsynaptic structures was observed.
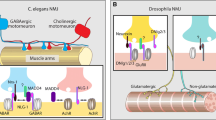
Another interesting ultrastructural observation in these mutants was the change in the architecture of the postsynaptic membrane in dnl1 and dnl2 mutants. In the postsynaptic muscle cells, both dnl1 and dnl2 mutants showed a reduction in the complexity of the subsynaptic reticulum (SSR) [34, 35]. The SSR is composed of several layers of convoluted folds in the postsynaptic membrane surrounding type I boutons. Embryonic NMJs lack a SSR, and instead, synaptic boutons are closely apposed to the muscle membrane. As the muscles grow, simple folds start to appear in the muscle membrane beneath synaptic boutons, which become both more extensive and convoluted throughout larval development [83]. The reduced complexity of the SSR in dnl1 and dnl2 mutants is indicative of an underdeveloped postsynaptic apparatus. Interestingly, mutations in discs large (dlg), the Drosophila homologue of PSD-95, also impairs the development of the SSR, similar to that seen in dnl1 and dnl2 mutants [83, 84]. Neuroligins are known to interact with PSD-95 in mammals through the C-terminal PDZ binding motif [39]. While a direct interaction between Drosophila neuroligins and dlg has yet to be demonstrated, over-expression of dnl1 in muscles leads to accumulation of dlg and a SSR under type II boutons, which normally lack these postsynaptic structures [34]. This accumulation was not observed when dnl1 constructs lacking the cytoplasmic domain (dnl1 ∆cyto) or the extracellular domain (dnl1 ∆extra) were expressed in muscles. Interestingly, the Dnl1∆cyto construct was localised at type II terminals but still failed to recruit Dlg or a SSR. The Dnl1∆extra construct did not localise to type II terminals, but rather, accumulated in granules that contained Dlg and GluRs [34]. These observations suggest that Dnl1 may interact directly with Dlg and contribute to the formation of the SSR (Fig. 2).
Model of known and potential interactions involving neurexin and neuroligin at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction. Dnl1 and Dnl2 are expressed in the postsynaptic muscle while Dnrx is expressed in the presynaptic neurons. Dnrx has also been shown to be present in the muscle during embyrogenisis. Based on their similarity to mammalian neuroligins, it seems likely that the Drosophila neuroligins form dimers, although this remains to be shown directly. Whether Drosophila neuroligins form exclusively as homodimers or as heterodimers (as shown for Dnl1/Dnl2) remains to be determined. Dnl2 forms a complex with Dnrx in vivo while the same has not been shown for Dnl1. Compelling evidence does exist however to suggest that dnrx complements dnl1 function (see text for details). In the presynaptic terminal, Dnrx has been shown to interact with Caki, a Drosophila homologue of mammalian CASK. Mammalian neuroligins have been shown to interact with PSD-95 at excitatory synapses. Based on their similarity to mammalian neuroligins, we would predict that the Drosophila neuroligins may also interact with discs large (Dlg), the Drosophila homologue of PSD-95, although this remains to be shown experimentally. Dlg is known to bind to the homophilic cell adhesion molecule Fascicilin II (FasII) and regulate both presynaptic morphology and postsynaptic membrane organisation. Dlg also regulates the size of postsynaptic glutamate receptor (GluR) patches and the subunit composition of GluRs. As is the case for mammalian neurexins and neuroligins, both Dnrx and the Drosophila neuroligins are likely involved in many other interactions at the NMJ, but further work will be required to elucidate these interactions
Invertebrate Neurexin and Neuroligin Interactions
The observation of fewer synaptic boutons and immature postsynaptic architectures in dnrx and dnl mutants supports a role for neuroligin and neurexin in synaptic maturation. But can analysis of the Drosophila NMJ also offer insight into how these cell adhesion molecules might accomplish that? The presynaptic and postsynaptic enrichment of neurexin and neuroligin respectively, combined with cell culture assays that indicate a functional co-dependence suggests that these proteins form a trans-synaptic complex [1–4, 40]. Indeed, structural analysis of neurexin–neuroligin interactions indicates that the extracellular domains of these proteins bind to each other in the presence of calcium [20, 22, 85–88]. Furthermore, the intracellular domains of both neurexin and neuroligin include PDZ binding motifs capable of binding to multiple PDZ domain proteins [14–16, 38–40]. Several interactions have been identified for both neurexin and neuroligin in mammals including synaptotagmin [14], CASK [15] and Mint [16] for neurexin and PSD-95, S-SCAM, Shank and Gephryn [38–40] for neuroligin.
At the Drosophila NMJ, neurexin has been shown to directly interact with Caki, the Drosophila homologue of CASK [70]. This interaction is mediated by the PDZ binding motif at the C-terminal end of neurexin. caki mutants show several defects in NMJ structure and function, similar to those observed in dnrx mutants. However, only some of the dnrx mutant phenotypes appear to be mediated via an interaction between caki and dnrx. For example, as discussed above, dnrx mutants have a reduced number of synaptic boutons [26, 27, 70]. caki mutants, on the other hand show a small increase in the number of boutons [70] suggesting that caki negatively regulates bouton numbers at the NMJ. Similar to dnrx mutants however, caki mutants show reduced transmitter release and vesicle recycling [70]. Interestingly, animals that are trans-heterozygous for caki and dnrx show much more severe defects in synaptic function than animals that are heterozygous for either caki or dnrx alone [70]. These results suggest that caki and dnrx act synergistically at the Drosophila NMJ to regulate synaptic function. In contrast, synaptic morphology was not affected in animals trans-heterozygous for caki and dnrx. This suggests that while synaptic function is regulated by an interaction between caki and dnrx, synaptic morphology is regulated independently by both genes. It is important to note that the enhancement of synaptic phenotypes observed in double heterozygous caki/dnrx mutants was not due to a change in the localization of either gene [70]. In fact, contradictory to work performed in cultured hippocampal neurons [89], synaptic localization of Dnrx does not require the PDZ binding motif at the C-terminal end [70].
The cytoplasmic domain of Dnl1 is also important for the regulation of synapse maturation. Expression of a dnl1 construct lacking the cytoplasmic domain (Dnl1∆cyto) in wild-type muscles produced NMJs that were even smaller than those observed in dnl1 null mutants [34]. Furthermore, in a dnl1 mutant background, the Dnl1∆cyto not only failed to rescue the NMJ mutant phenotype, but rather exacerbated it. In similar experiments, a dnl1 construct lacking the extracellular domain (Dnl1∆extra) had no effect on NMJ morphology when expressed in a wild-type background, but also failed to rescue the defect in NMJ morphology in a dnl1 mutant background [34]. Both the Dnl1∆extra and Dnl1∆cyto constructs were expressed at type I NMJs, similar to wild-type Dnl1, however, the Dnl1∆cyto construct was also apparent at type II terminals, whereas the Dnl1∆extra construct was absent from these terminals [34]. Rather, the Dnl1∆extra construct accumulated in vesicles that also stained for Dlg and GluRs. These observations suggest that Dnl1 can be targeted to the correct synapses by either the extracellular or intracellular portions of the protein. However, ectopic accumulation of Dnl1 at type II terminals specifically requires the extracellular portion of Dnl1 [34]. The localization of the truncated Dnl1 constructs at type I terminals may be facilitated by interactions with endogenous Dnl1 or Dnrx. At type II synapses however, where neither Dnl1 nor Dnrx are endogenously expressed at detectable levels, the extracellular domain Dnl1 appears to be required to facilitate the ectopic expression. Given that Dnrx has not been detected at type II terminals, this ectopic expression of Dnl1 may be mediated by trans-synaptic interactions with a different presynaptic protein, or alternatively, it may be mediated by an interaction with the extracellular domain of another postsynaptic protein (possibly one of the as yet uncharacterised Drosophila neuroligin genes).
The observation that expression of the Dnl1∆cyto construct in wild-type muscles can induce a presynaptic defect in synaptic bouton morphology is particularly interesting. These results were interpreted as a dominant negative effect caused by the truncated Dnl1 construct being incorporated into signalling complexes, which were unable to propagate that signal to the muscle [34]. Due to the postsynaptic localization of Dnl1, any effect of Dnl1 on presynaptic bouton morphology must involve a retrograde signal to the motorneuron. Assuming that the extracellular domain of the Dnl1∆cyto construct is capable of the same interactions as wild-type Dnl1, the results indicate that binding between the extracellular domains of Dnl1 and Dnrx is not sufficient to induce a retrograde signal. However, postsynaptic signalling mediated through the cytosolic domain of Dnl1 does appear to be required for the retrograde signal. It is possible that the interaction between the extracellular domains of neurexin and neuroligin merely serves to align pre- and postsynaptic specialisations mediated by the intracellular domains of these proteins. It should be noted however that over-expression of the dnl1 ∆cyto construct at NMJs may interfere with endogenous interactions between members of the cell adhesion machinery, thus preventing functional interactions. A recent study in cultured hippocampal neurons showed that the cytoplasmic region of neuroligin 3 is important in synapse maturation and that this effect is masked in the presence of endogenous neuroligin, presumably due to heterodimers formed between the truncated and endogenous proteins [90]. It will be interesting to see how loss of both dnl1 and dnl2 affects NMJ formation and maturation in Drosophila.
Clues from Neurexin/Neuroligin Double Mutants
As discussed above, both the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of neurexin and neuroligin play important roles in synapse maturation within the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells, respectively. One of the unique aspects of recent studies on neurexin and neuroligin function using the Drosophila NMJ as a model, is the in vivo examination of neurexin–neuroligin double mutants at the same synapse, which has not been examined in mammalian knockouts [34, 35]. Interestingly these studies suggest that the interaction between dnrx and either dnl1 or dnl2 are functionally different. The expression patterns of dnl2 and dnrx showed substantial overlap both in the CNS and at synaptic boutons in the NMJ [35]. By contrast, the expression of Dnl1 showed relatively little overlap with Dnrx, and appeared to concentrate in patches adjacent to Dnrx clusters [34]. Consistent with the co-localization data, Dnl2 was shown to form a complex with Dnrx in vivo [35] while the same could not be shown for Dnl1. It should be noted however, that Dnl1 may still functionally interact with Dnrx, and as detailed below, there are several lines of evidence to suggest a functional interaction between Dnl1 and Dnrx at the NMJ.
First, over-expression of untagged Dnl1 at high levels reduced the size of the NMJ, similar to that seen in dnl1 or dnrx single mutants. This dominant negative effect however, was not observed in a dnrx mutant background or with a Dnl1 construct that lacks a residue predicted to be necessary for Dnrx binding [34], suggesting that dnrx may contribute to the dominant negative effects of dnl1 over-expression. Furthermore, postsynaptic Dnl1 clusters were reduced in size in dnrx mutants [34] suggesting that Dnrx may facilitate the clustering of Dnl1. The morphological defects observed in dnl1 mutants were considerably worse than those observed in either dnrx or dnl2 mutants suggesting that dnl1 may have a more fundamental role in regulating NMJ development. Loss of dnrx function in the dnl1 mutant background did not significantly enhance the phenotype observed in dnl1 mutants suggesting that dnl1 may act through dnrx to regulate synaptic morphology. Interestingly however, the Dnl1mutant construct, which lacks a Dnrx binding site, was able to partially rescue synaptic morphology defects in dnl1 mutants suggesting that dnrx is not absolutely required for dnl1 function. Together, these data suggest that dnrx is not strictly necessary for dnl1 function, but likely promotes dnl1 function, possibly by concentrating Dnl1 at the NMJ [34].
In contrast to dnl1/dnrx double mutants, which were completely viable and no worse than dn1 mutants, dnl2/dnrx double mutants are lethal, (dnrx and dnl2 single mutants are both viable [35]). Furthermore, when NMJs from dnrx/dnl2 double mutants were examined at an earlier developmental stage, prior to lethality, synaptic morphology defects were exacerbated in double mutants, compared to either single mutant [35]. These results suggest that dnrx and dnl2 may act in parallel pathways to regulate NMJ development.
Unlike mammals, Drosophila has only a single neurexin homologue [27, 91]. As such, it is possible that Dnl1 and Dnl2 compete with each other for Dnrx binding. Alternatively, Dnl1 and Dnl2 may co-operatively bind to Dnrx. Analysis of the structure of neuroligin/neurexin complexes revealed that neuroligin forms a constitutive dimer via the AChE-like domain. A single neurexin then binds to each neuroligin molecule, thus forming a trans-synaptic tetramer or double dimer [85]. Furthermore, at synapses expressing multiple neuroligin homologues, neuroligin heterodimers can be formed between the different homologues [43, 90]. It is possible that Dnl1 and Dnl2 form a heterodimer, with Dnrx binding to both Dnl1 and Dnl2 (Fig. 2).
By comparing the synaptic phenotypes of dnrx, dnl1 and dnl2 mutants, it is apparent that all three genes play a role in maturation of the NMJ. However, despite the similarities in phenotypes, each mutant also shows some unique phenotypes suggesting that these genes may function independently of each other. So far, only two of the four neuroligin homologues in Drosophila have been characterised and it will be interesting to see what role (if any) the other homologues play at this synapse. Furthermore, it should also be noted that in mammals, both neurexin and neuroligin can mediate synaptic development via interactions with other cell adhesion molecules [50, 52, 54]. Whether similar interactions regulate synaptic development in Drosophila remains to be determined.
Neurexins and Neuroligins in Autism Spectrum Disorder
The studies detailed above demonstrate the importance of neurexin and neuroligin in activity dependent modulation of synapses. As such, it is not surprising that mutations in neurexin and neuroligin have been associated with developmental cognitive disorders such as autism spectrum disorders (ASD), Tourette syndrome and Schizophrenia [8, 92]. ASDs are characterised by behavioural abnormalities such as repetitive behaviours and/or restrictive interests and deficits in social interactions and communication [93, 94]. Genetic segregation studies in siblings and parents of children diagnosed with ASD combined with an approximately four fold higher prevalence in males suggests a strong genetic contribution to ASD [94–99]. Interestingly, many of the genes identified as potential risk factors for ASD are cell adhesion molecules including neurexin and neuroligin [92].
Several studies in mice have attempted to model ASD symptoms through genetic manipulation of neuroligin or neurexin expression [5, 6, 55–64, 100]. Consistent with the wide variation in symptoms and severity observed with ASD, the phenotypes in mice with different mutations are also quite varied. For example, mice lacking neuroligin 1 show impaired spatial memory and reduced LTP in the hippocampus [58]. Furthermore, neuroligin 1 null mice were observed to spend more time grooming, which might reflect the increased repetitive behaviours observed in some autistic children [58]. Interestingly, the abnormal grooming behaviour could be rescued by treating the mice with a NMDA receptor co-agonist suggesting that the behavioural defect was the result of reduced NMDA receptor activation. Mice lacking neuroligin 2 on the other hand show increased anxiety like behaviour and decreased pain sensitivity and motor coordination [59]. Mice bearing a gain-of-function arginine to cysteine substitution (R451C) in the esterase homology domain show decreased social interaction and increased spatial learning, but do not show any change in anxiety like behaviour, such as those seen in neuroligin 2 knockout mice [63]. Neurexin 1α knockout mice also show increased grooming behaviour, similar to that seen in neuroligin 2 knockouts [55]. The variation in behavioural phenotypes observed in these different mutants is likely a reflection of differences in the physiological consequences of these mutations, which in turn reflects varied spatial and temporal requirements for the different homologues of each gene (For a list of both behavioural and physiological consequences of different neuroligin and neurexin mutations in vivo, see Table 1).
Behavioural defects have also been observed in Drosophila neurexin and neuroligin mutants. Both dnrx and dnl2 mutants show a reduction in locomotion compared with controls [35]. While this defect may arise in part from the defects in NMJ structure and function described above, it is likely that defects in synaptic signalling within the CNS also contribute. Indeed, dnrx mutants showed a reduction in the number of synapses in the CNS [91]. Interestingly dnrx mutant larvae also showed a reduction in associative learning that cannot be accounted for by the reduced locomotion [91]. Studies in honey bees and C. elegans have suggested a link between neuroligin function and sensory processing [36, 37]. Neuroligin deficient C. elegans have defects in sensory processing [37]. Furthermore, sensory deprivation in honey bees resulted in reduced neuroligin 1 expression while associative scent training resulted in increased expression of neurexin and neuroligins 1 and 3 [36]. Unlike honeybees and worms however, the defect in olfactory associative learning in dnrx mutants was not due to changes in the olfactory preferences [91]. The defect in associative learning in dnrx mutants likely represents an inability to modulate synaptic strength following training. Interestingly, the changes in neuroligin expression in honeybees were also interpreted to be the result of changes in neuronal wiring triggered by the altered sensory environment [36].
Neurexin and neuroligin have also been implicated in the storage of long-term memory in Aplysia [12]. In Aplysia, a monosynaptic connection between a siphon sensory neuron and the gill motor neuron is a crucial part of the gill withdrawal reflex which constitutes a learned fear behaviour. Repeated application of serotonin increases synaptic strength at this synapse and leads to a sensitization of the gill withdrawal behaviour [101, 102]. Long-term increases in synaptic strength are dependent not only on RNA and protein synthesis, but also on kinesin heavy chain (KHC) regulated anterograde transport [103, 104]. Interestingly, both neurexin and neuroligin were shown to be carried as cargo by the KHC complex during serotonin induced synaptic facilitation [104]. It is not surprising then, that over-expression of both neurexin and neuroligin at this synapse leads to a long-term facilitation in the absence of serotonin treatment. Furthermore, depletion of either neuroligin in the motor neuron, or neurexin in the siphon sensory neuron decreased the long-term strengthening of this synapse following serotonin application [12]. These observations in Aplysia are consistent with a trans-synaptic interaction between neurexin and neuroligin being crucial for activity dependent modulation of synaptic strength. It will be interesting to see whether Drosophila neuroligin mutants have cognitive defects that may be used to model ASD. Associative learning assays have been well characterised in Drosophila [105] and learning defects have already been observed in dnrx mutants [91]. Whether neuroligin mutants also have defects in learning and/or memory remains to be determined. In addition to learning assays however, assays for social behaviours are also possible in Drosophila [106]. It will be interesting to see whether neuroligin or neurexin mutants in Drosophila display any defects in these social behaviours.
Conclusions
Our understanding of the roles of neurexin and neuroligin has evolved significantly over the last decade. From early hypotheses predicting a role in synapse formation, it is now generally accepted that a trans-synaptic interaction between these cell adhesion molecules is more important for activity dependent modulation of synaptic strength. There are however, many questions left to be answered regarding the roles of these proteins. For example, what role do β-neurexins play in synapse formation/maturation? Several studies have examined the role of α-neurexins [6, 55–57, 64], yet so far, there are no data on the role of β-neurexins. What are the functional consequences of the numerous splice forms of both neurexin and neuroligin? While the binding efficiency of different splice forms has been studied [18, 19, 41, 107], it is still unclear how the expression of different splice forms is regulated in vivo, and further, how interactions between specific splice forms affects downstream signalling. Another question that remains to be answered is what other binding partners are important for neuroligin and neurexin function? Recent work has indicated that both proteins can mediate trans-synaptic specialisation independently of each other [52, 54, 108, 109] and it has also been shown that neuroligin works co-operatively with the cell adhesion molecule N-cadherin [50, 110]. It is possible that neuroligin/neurexin may also work with or against other cell adhesion molecules to refine synaptic structure and function.
These are just some of the questions that remain to be answered in order to fully understand the complexity of synapse formation, maturation and modulation. The work reviewed here shows that the function of neuroligin and neurexin is evolutionarily conserved from Aplysia and C. elegans, all the way through to mammals. The ability to analyse synaptic development and modulation with single cell resolution in these model organisms will help in answering these and other questions in the future.
References
Chih B, Engelman H, Scheiffele P (2005) Control of excitatory and inhibitory synapse formation by neuroligins. Science 307:1324–1328
Graf ER, Zhang X, Jin SX, Linhoff MW, Craig AM (2004) Neurexins induce differentiation of GABA and glutamate postsynaptic specializations via neuroligins. Cell 119:1013–1026
Nam CI, Chen L (2005) Postsynaptic assembly induced by neurexin–neuroligin interaction and neurotransmitter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:6137–6142
Scheiffele P, Fan J, Choih J, Fetter R, Serafini T (2000) Neuroligin expressed in nonneuronal cells triggers presynaptic development in contacting axons. Cell 101:657–669
Chubykin AA, Atasoy D, Etherton MR, Brose N, Kavalali ET, Gibson JR, Sudhof TC (2007) Activity-dependent validation of excitatory versus inhibitory synapses by neuroligin-1 versus neuroligin-2. Neuron 54:919–931
Missler M, Zhang W, Rohlmann A, Kattenstroth G, Hammer RE, Gottmann K, Sudhof TC (2003) Alpha-neurexins couple Ca2+ channels to synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Nature 423:939–948
Varoqueaux F, Aramuni G, Rawson RL, Mohrmann R, Missler M, Gottmann K, Zhang W, Sudhof TC, Brose N (2006) Neuroligins determine synapse maturation and function. Neuron 51:741–754
Sudhof TC (2008) Neuroligins and neurexins link synaptic function to cognitive disease. Nature 455:903–911
Ushkaryov YA, Petrenko AG, Geppert M, Sudhof TC (1992) Neurexins: synaptic cell surface proteins related to the alpha-latrotoxin receptor and laminin. Science 257:50–56
Tabuchi K, Sudhof TC (2002) Structure and evolution of neurexin genes: insight into the mechanism of alternative splicing. Genomics 79:849–859
Biswas S, Russell RJ, Jackson CJ, Vidovic M, Ganeshina O, Oakeshott JG, Claudianos C (2008) Bridging the synaptic gap: neuroligins and neurexin I in Apis mellifera. PLoS One 3:e3542
Choi YB, Li HL et al (2011) Neurexin–neuroligin transsynaptic interaction mediates learning-related synaptic remodeling and long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Neuron 70:468–481
Haklai-Topper L, Soutschek J, Sabanay H, Scheel J, Hobert O, Peles E (2011) The neurexin superfamily of Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene Expr Patterns 11:144–150
Hata Y, Davletov B, Petrenko AG, Jahn R, Sudhof TC (1993) Interaction of synaptotagmin with the cytoplasmic domains of neurexins. Neuron 10:307–315
Hata Y, Butz S, Sudhof TC (1996) CASK: a novel dlg/PSD95 homolog with an N-terminal calmodulin-dependent protein kinase domain identified by interaction with neurexins. J Neurosci 16:2488–2494
Biederer T, Sudhof TC (2000) Mints as adaptors. Direct binding to neurexins and recruitment of munc18. J Biol Chem 275:39803–39806
Ushkaryov YA, Hata Y, Ichtchenko K, Moomaw C, Afendis S, Slaughter CA, Sudhof TC (1994) Conserved domain structure of beta-neurexins. Unusual cleaved signal sequences in receptor-like neuronal cell-surface proteins. J Biol Chem 269:11987–11992
Comoletti D, Flynn RE et al (2006) Gene selection, alternative splicing, and post-translational processing regulate neuroligin selectivity for beta-neurexins. Biochemistry 45:12816–12827
Graf ER, Kang Y, Hauner AM, Craig AM (2006) Structure function and splice site analysis of the synaptogenic activity of the neurexin-1 beta LNS domain. J Neurosci 26:4256–4265
Koehnke J, Katsamba PS, Ahlsen G, Bahna F, Vendome J, Honig B, Shapiro L, Jin X (2010) Splice form dependence of beta-neurexin/neuroligin binding interactions. Neuron 67:61–74
Missler M, Sudhof TC (1998) Neurexins: three genes and 1001 products. Trends Genet 14:20–26
Tanaka H, Nogi T, Yasui N, Iwasaki K, Takagi J (2011) Structural basis for variant-specific neuroligin-binding by alpha-neurexin. PLoS One 6:e19411
Puschel AW, Betz H (1995) Neurexins are differentially expressed in the embryonic nervous system of mice. J Neurosci 15:2849–2856
Ullrich B, Ushkaryov YA, Sudhof TC (1995) Cartography of neurexins: more than 1000 isoforms generated by alternative splicing and expressed in distinct subsets of neurons. Neuron 14:497–507
Berninghausen O, Rahman MA, Silva JP, Davletov B, Hopkins C, Ushkaryov YA (2007) Neurexin Ibeta and neuroligin are localized on opposite membranes in mature central synapses. J Neurochem 103:1855–1863
Chen K, Gracheva EO, Yu SC, Sheng Q, Richmond J, Featherstone DE (2010) Neurexin in embryonic Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. PLoS One 5:e11115
Li J, Ashley J, Budnik V, Bhat MA (2007) Crucial role of Drosophila neurexin in proper active zone apposition to postsynaptic densities, synaptic growth, and synaptic transmission. Neuron 55:741–755
Kattenstroth G, Tantalaki E, Sudhof TC, Gottmann K, Missler M (2004) Postsynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor function requires alpha-neurexins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:2607–2612
Taniguchi H, Gollan L, Scholl FG, Mahadomrongkul V, Dobler E, Limthong N, Peck M, Aoki C, Scheiffele P (2007) Silencing of neuroligin function by postsynaptic neurexins. J Neurosci 27:2815–2824
Ichtchenko K, Hata Y, Nguyen T, Ullrich B, Missler M, Moomaw C, Sudhof TC (1995) Neuroligin 1: a splice site-specific ligand for beta-neurexins. Cell 81:435–443
Bolliger MF, Frei K, Winterhalter KH, Gloor SM (2001) Identification of a novel neuroligin in humans which binds to PSD-95 and has a widespread expression. Biochem J 356:581–588
Bolliger MF, Pei J, Maxeiner S, Boucard AA, Grishin NV, Sudhof TC (2008) Unusually rapid evolution of neuroligin-4 in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6421–6426
Ichtchenko K, Nguyen T, Sudhof TC (1996) Structures, alternative splicing, and neurexin binding of multiple neuroligins. J Biol Chem 271:2676–2682
Banovic D, Khorramshahi O, Owald D, Wichmann C, Riedt T, Fouquet W, Tian R, Sigrist SJ, Aberle H (2010) Drosophila neuroligin 1 promotes growth and postsynaptic differentiation at glutamatergic neuromuscular junctions. Neuron 66:724–738
Sun M, Xing G et al (2011) Neuroligin 2 is required for synapse development and function at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction. J Neurosci 31:687–699
Biswas S, Reinhard J, Oakeshott J, Russell R, Srinivasan MV, Claudianos C (2010) Sensory regulation of neuroligins and neurexin I in the honeybee brain. PLoS One 5:e9133
Hunter JW, Mullen GP, McManus JR, Heatherly JM, Duke A, Rand JB (2010) Neuroligin-deficient mutants of C. elegans have sensory processing deficits and are hypersensitive to oxidative stress and mercury toxicity. Dis Model Mech 3:366–376
Iida J, Hirabayashi S, Sato Y, Hata Y (2004) Synaptic scaffolding molecule is involved in the synaptic clustering of neuroligin. Mol Cell Neurosci 27:497–508
Irie M, Hata Y, Takeuchi M, Ichtchenko K, Toyoda A, Hirao K, Takai Y, Rosahl TW, Sudhof TC (1997) Binding of neuroligins to PSD-95. Science 277:1511–1515
Meyer G, Varoqueaux F, Neeb A, Oschlies M, Brose N (2004) The complexity of PDZ domain-mediated interactions at glutamatergic synapses: a case study on neuroligin. Neuropharmacology 47:724–733
Boucard AA, Chubykin AA, Comoletti D, Taylor P, Sudhof TC (2005) A splice code for trans-synaptic cell adhesion mediated by binding of neuroligin 1 to alpha- and beta-neurexins. Neuron 48:229–236
Lee H, Dean C, Isacoff E (2010) Alternative splicing of neuroligin regulates the rate of presynaptic differentiation. J Neurosci 30:11435–11446
Budreck EC, Scheiffele P (2007) Neuroligin-3 is a neuronal adhesion protein at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Eur J Neurosci 26:1738–1748
Song JY, Ichtchenko K, Sudhof TC, Brose N (1999) Neuroligin 1 is a postsynaptic cell-adhesion molecule of excitatory synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:1100–1105
Varoqueaux F, Jamain S, Brose N (2004) Neuroligin 2 is exclusively localized to inhibitory synapses. Eur J Cell Biol 83:449–456
Hoon M, Soykan T et al (2011) Neuroligin-4 is localized to glycinergic postsynapses and regulates inhibition in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:3053–3058
Levinson JN, Chery N, Huang K, Wong TP, Gerrow K, Kang R, Prange O, Wang YT, El-Husseini A (2005) Neuroligins mediate excitatory and inhibitory synapse formation: involvement of PSD-95 and neurexin-1beta in neuroligin-induced synaptic specificity. J Biol Chem 280:17312–17319
Levinson JN, Li R, Kang R, Moukhles H, El-Husseini A, Bamji SX (2010) Postsynaptic scaffolding molecules modulate the localization of neuroligins. Neuroscience 165:782–793
Prange O, Wong TP, Gerrow K, Wang YT, El-Husseini A (2004) A balance between excitatory and inhibitory synapses is controlled by PSD-95 and neuroligin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13915–13920
Aiga M, Levinson JN, Bamji SX (2011) N-Cadherin and neuroligins cooperate to regulate synapse formation in hippocampal cultures. J Biol Chem 286:851–858
de Wit J, Sylwestrak E et al (2009) LRRTM2 interacts with Neurexin1 and regulates excitatory synapse formation. Neuron 64:799–806
Ko J, Fuccillo MV, Malenka RC, Sudhof TC (2009) LRRTM2 functions as a neurexin ligand in promoting excitatory synapse formation. Neuron 64:791–798
Ko J, Soler-Llavina GJ, Fuccillo MV, Malenka RC, Sudhof TC (2011) Neuroligins/LRRTMs prevent activity- and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent synapse elimination in cultured neurons. J Cell Biol 194:323–334
Ko J, Zhang C, Arac D, Boucard AA, Brunger AT, Sudhof TC (2009) Neuroligin-1 performs neurexin-dependent and neurexin-independent functions in synapse validation. EMBO J 28:3244–3255
Etherton MR, Blaiss CA, Powell CM, Sudhof TC (2009) Mouse neurexin-1alpha deletion causes correlated electrophysiological and behavioral changes consistent with cognitive impairments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:17998–18003
Sons MS, Busche N et al (2006) alpha-Neurexins are required for efficient transmitter release and synaptic homeostasis at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Neuroscience 138:433–446
Zhang W, Rohlmann A, Sargsyan V, Aramuni G, Hammer RE, Sudhof TC, Missler M (2005) Extracellular domains of alpha-neurexins participate in regulating synaptic transmission by selectively affecting N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. J Neurosci 25:4330–4342
Blundell J, Blaiss CA, Etherton MR, Espinosa F, Tabuchi K, Walz C, Bolliger MF, Sudhof TC, Powell CM (2010) Neuroligin-1 deletion results in impaired spatial memory and increased repetitive behavior. J Neurosci 30:2115–2129
Blundell J, Tabuchi K, Bolliger MF, Blaiss CA, Brose N, Liu X, Sudhof TC, Powell CM (2009) Increased anxiety-like behavior in mice lacking the inhibitory synapse cell adhesion molecule neuroligin 2. Genes Brain Behav 8:114–126
Jedlicka P, Hoon M et al (2011) Increased dentate gyrus excitability in neuroligin-2-deficient mice in vivo. Cereb Cortex 21:357–367
Kim J, Jung SY et al (2008) Neuroligin-1 is required for normal expression of LTP and associative fear memory in the amygdala of adult animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:9087–9092
Gibson JR, Huber KM, Sudhof TC (2009) Neuroligin-2 deletion selectively decreases inhibitory synaptic transmission originating from fast-spiking but not from somatostatin-positive interneurons. J Neurosci 29:13883–13897
Tabuchi K, Blundell J, Etherton MR, Hammer RE, Liu X, Powell CM, Sudhof TC (2007) A neuroligin-3 mutation implicated in autism increases inhibitory synaptic transmission in mice. Science 318:71–76
Dudanova I, Tabuchi K, Rohlmann A, Sudhof TC, Missler M (2007) Deletion of alpha-neurexins does not cause a major impairment of axonal pathfinding or synapse formation. J Comp Neurol 502:261–274
Kaprielian Z, Imondi R, Runko E (2000) Axon guidance at the midline of the developing CNS. Anat Rec 261:176–197
Keshishian H, Broadie K, Chiba A, Bate M (1996) The Drosophila neuromuscular junction: a model system for studying synaptic development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:545–575
Rose D, Chiba A (2000) Synaptic target recognition at Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. Microsc Res Tech 49:3–13
Budnik V (1996) Synapse maturation and structural plasticity at Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6:858–867
Ruiz-Canada C, Budnik V (2006) Introduction on the use of the Drosophila embryonic/larval neuromuscular junction as a model system to study synapse development and function, and a brief summary of pathfinding and target recognition. Int Rev Neurobiol 75:1–31
Sun M, Liu L, Zeng X, Xu M, Fang M, Xie W (2009) Genetic interaction between Neurexin and CAKI/CMG is important for synaptic function in Drosophila neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Res 64:362–371
Gorczyca M, Augart C, Budnik V (1993) Insulin-like receptor and insulin-like peptide are localized at neuromuscular junctions in Drosophila. J Neurosci 13:3692–3704
Keshishian H, Chiba A et al (1993) Cellular mechanisms governing synaptic development in Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurobiol 24:757–787
Schuster CM, Davis GW, Fetter RD, Goodman CS (1996) Genetic dissection of structural and functional components of synaptic plasticity. I. Fasciclin II controls synaptic stabilization and growth. Neuron 17:641–654
Meinertzhagen IA, Govind CK, Stewart BA, Carter JM, Atwood HL (1998) Regulated spacing of synapses and presynaptic active zones at larval neuromuscular junctions in different genotypes of the flies Drosophila and Sarcophaga. J Comp Neurol 393:482–492
Reiff DF, Thiel PR, Schuster CM (2002) Differential regulation of active zone density during long-term strengthening of Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. J Neurosci 22:9399–9409
Sigrist SJ, Thiel PR, Reiff DF, Schuster CM (2002) The postsynaptic glutamate receptor subunit DGluR-IIA mediates long-term plasticity in Drosophila. J Neurosci 22:7362–7372
Featherstone DE, Rushton E, Rohrbough J, Liebl F, Karr J, Sheng Q, Rodesch CK, Broadie K (2005) An essential Drosophila glutamate receptor subunit that functions in both central neuropil and neuromuscular junction. J Neurosci 25:3199–3208
Marrus SB, Portman SL, Allen MJ, Moffat KG, DiAntonio A (2004) Differential localization of glutamate receptor subunits at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction. J Neurosci 24:1406–1415
Qin G, Schwarz T, Kittel RJ, Schmid A, Rasse TM, Kappei D, Ponimaskin E, Heckmann M, Sigrist SJ (2005) Four different subunits are essential for expressing the synaptic glutamate receptor at neuromuscular junctions of Drosophila. J Neurosci 25:3209–3218
Petersen SA, Fetter RD, Noordermeer JN, Goodman CS, DiAntonio A (1997) Genetic analysis of glutamate receptors in Drosophila reveals a retrograde signal regulating presynaptic transmitter release. Neuron 19:1237–1248
Schuster CM, Ultsch A, Schloss P, Cox JA, Schmitt B, Betz H (1991) Molecular cloning of an invertebrate glutamate receptor subunit expressed in Drosophila muscle. Science 254:112–114
Schmid A, Hallermann S et al (2008) Activity-dependent site-specific changes of glutamate receptor composition in vivo. Nat Neurosci 11:659–666
Guan B, Hartmann B, Kho YH, Gorczyca M, Budnik V (1996) The Drosophila tumor suppressor gene, dlg, is involved in structural plasticity at a glutamatergic synapse. Curr Biol 6:695–706
Lahey T, Gorczyca M, Jia XX, Budnik V (1994) The Drosophila tumor suppressor gene dlg is required for normal synaptic bouton structure. Neuron 13:823–835
Arac D, Boucard AA, Ozkan E, Strop P, Newell E, Sudhof TC, Brunger AT (2007) Structures of neuroligin-1 and the neuroligin-1/neurexin-1 beta complex reveal specific protein–protein and protein-Ca2+ interactions. Neuron 56:992–1003
Fabrichny IP, Leone P, Sulzenbacher G, Comoletti D, Miller MT, Taylor P, Bourne Y, Marchot P (2007) Structural analysis of the synaptic protein neuroligin and its beta-neurexin complex: determinants for folding and cell adhesion. Neuron 56:979–991
Leone P, Comoletti D, Ferracci G, Conrod S, Garcia SU, Taylor P, Bourne Y, Marchot P (2010) Structural insights into the exquisite selectivity of neurexin/neuroligin synaptic interactions. EMBO J 29:2461–2471
Reissner C, Klose M, Fairless R, Missler M (2008) Mutational analysis of the neurexin/neuroligin complex reveals essential and regulatory components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:15124–15129
Fairless R, Masius H, Rohlmann A, Heupel K, Ahmad M, Reissner C, Dresbach T, Missler M (2008) Polarized targeting of neurexins to synapses is regulated by their C-terminal sequences. J Neurosci 28:12969–12981
Shipman SL, Schnell E, Hirai T, Chen BS, Roche KW, Nicoll RA (2011) Functional dependence of neuroligin on a new non-PDZ intracellular domain. Nat Neurosci 14:718–726
Zeng X, Sun M, Liu L, Chen F, Wei L, Xie W (2007) Neurexin-1 is required for synapse formation and larvae associative learning in Drosophila. FEBS Lett 581:2509–2516
Betancur C, Sakurai T, Buxbaum JD (2009) The emerging role of synaptic cell-adhesion pathways in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders. Trends Neurosci 32:402–412
Lord C, Cook EH, Leventhal BL, Amaral DG (2000) Autism spectrum disorders. Neuron 28:355–363
Pardo CA, Eberhart CG (2007) The neurobiology of autism. Brain Pathol 17:434–447
Abrahams BS, Geschwind DH (2008) Advances in autism genetics: on the threshold of a new neurobiology. Nat Rev Genet 9:341–355
Bishop DV, Maybery M, Maley A, Wong D, Hill W, Hallmayer J (2004) Using self-report to identify the broad phenotype in parents of children with autistic spectrum disorders: a study using the Autism-Spectrum Quotient. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45:1431–1436
Bolton P, Macdonald H, Pickles A, Rios P, Goode S, Crowson M, Bailey A, Rutter M (1994) A case-control family history study of autism. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 35:877–900
Jorde LB, Hasstedt SJ et al (1991) Complex segregation analysis of autism. Am J Hum Genet 49:932–938
Steffenburg S, Gillberg C, Hellgren L, Andersson L, Gillberg IC, Jakobsson G, Bohman M (1989) A twin study of autism in Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 30:405–416
Poulopoulos A, Aramuni G et al (2009) Neuroligin 2 drives postsynaptic assembly at perisomatic inhibitory synapses through gephyrin and collybistin. Neuron 63:628–642
Glanzman DL, Kandel ER, Schacher S (1990) Target-dependent structural changes accompanying long-term synaptic facilitation in Aplysia neurons. Science 249:799–802
Montarolo PG, Goelet P, Castellucci VF, Morgan J, Kandel ER, Schacher S (1986) A critical period for macromolecular synthesis in long-term heterosynaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Science 234:1249–1254
Bailey CH, Montarolo P, Chen M, Kandel ER, Schacher S (1992) Inhibitors of protein and RNA synthesis block structural changes that accompany long-term heterosynaptic plasticity in Aplysia. Neuron 9:749–758
Puthanveettil SV, Monje FJ, Miniaci MC, Choi YB, Karl KA, Khandros E, Gawinowicz MA, Sheetz MP, Kandel ER (2008) A new component in synaptic plasticity: upregulation of kinesin in the neurons of the gill-withdrawal reflex. Cell 135:960–973
Dubnau J, Tully T (1998) Gene discovery in Drosophila: new insights for learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 21:407–444
Iliadi KG (2009) The genetic basis of emotional behavior: has the time come for a Drosophila model? J Neurogenet 23:136–146
Chih B, Gollan L, Scheiffele P (2006) Alternative splicing controls selective trans-synaptic interactions of the neuroligin-neurexin complex. Neuron 51:171–178
Matsuda K, Yuzaki M (2011) Cbln family proteins promote synapse formation by regulating distinct neurexin signaling pathways in various brain regions. Eur J Neurosci 33:1447–1461
Siddiqui TJ, Pancaroglu R, Kang Y, Rooyakkers A, Craig AM (2010) LRRTMs and neuroligins bind neurexins with a differential code to cooperate in glutamate synapse development. J Neurosci 30:7495–7506
Stan A, Pielarski KN, Brigadski T, Wittenmayer N, Fedorchenko O, Gohla A, Lessmann V, Dresbach T, Gottmann K (2010) Essential cooperation of N-cadherin and neuroligin-1 in the transsynaptic control of vesicle accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:11116–11121
Acknowledgements
G.L.B. holds a Canadian Institute of Health Research grant (MOP 14143) and is the recipient of a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Molecular and Developmental Neurobiology. We would like to thank Dr. Tanya R Da Sylva for comments on the manuscript.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Knight, D., Xie, W. & Boulianne, G.L. Neurexins and Neuroligins: Recent Insights from Invertebrates. Mol Neurobiol 44, 426–440 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8213-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8213-1