Abstract
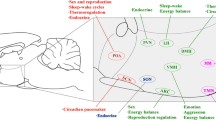
The hypothalamus has been particularly difficult to study at the molecular level because of the inherent cellular heterogeneity and complexity of neuronal circuits within. We have generated a large number of immortalized, clonal cell lines through retroviral gene transfer of the oncogene SV40 T-Ag into primary murine hypothalamic neuronal cell cultures. A number of these neuronal cell lines express neuropeptides linked to the control of feeding behavior and reproduction, including neuropeptide Y (NPY) and neurotensin (NT). We review recent studies on the direct regulation of NPY gene expression by estrogen, and the leptin-mediated control of signal transduction pathways and NT transcription. These studies provide new insights into the direct control of neuropeptide synthesis by hormones and nutrients at a mechanistic level in the individual neuron, not yet possible in the whole brain. Using these novel cell models, we expect to contribute substantially to the understanding of how individual neuronal cell types control overall endocrine function, especially with regard to two of the most well-known roles of distinct peptidergic neurons; these being the control of reproduction and energy homeostasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SV40 T-Ag:
-
simian virus large T antigen
- GnRH:
-
gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- NPY:
-
neuropeptide Y
- NT:
-
neurotensin
- AgRP:
-
agouti-related peptide
- MCH:
-
melanin-concentrating hormone
- GHRH:
-
growth hormone-releasing hormone
- POMC:
-
proopiomelanocortin
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
References
Everitt BJ, Hokfelt T (1990) Neuroendocrine anatomy of the hypothalamus. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 47:1–15
Kopelman PG (2000) Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404:635–643
Marx J (2003) Cellular warriors at the battle of the bulge. Science 299:846–849
Friedman JM (2003) A war on obesity, not the obese. Science 299:856–858
Wade GN, Gray JM, Bartness TJ (1985) Gonadal influences on adiposity. Int J Obes 9(Suppl 1):83–92
Cooke PS, Naaz A (2004) Role of estrogens in adipocyte development and function. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 229:1127–1135
Hoffman GE, Smith MS, Verbalis JG (1993) c-Fos and related immediate early gene products as markers of activity in neuroendocrine systems. Front Neuroendocrinol 14:173–213
Dufourny L, Warembourg M, Jolivet A (1999) Quantitative studies of progesterone receptor and nitric oxide synthase colocalization with somatostatin, or neurotensin, or substance P in neurons of the guinea pig ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus: an immunocytochemical triple-label analysis. J Chem Neuroanat 17:33–43
Elmquist JK, Elias CF, Saper CB (1999) From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 22:221–232
Smith MS, Grove KL (2002) Integration of the regulation of reproductive function and energy balance: lactation as a model. Front Neuroendocrinol 23:225–256
Cepko CL (1989) Immortalization of neural cells via retrovirus-mediated oncogene transduction. Annu Rev Neurosci 12:47–65
Augusti-Tocco G, Sato G (1969) Establishment of functional clonal lines of neurons from mouse neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 64:311–315
De Vitry F, Camier M, Czernichow P, Benda P, Cohen P, Tixier-Vidal A (1974) Establishment of a clone of mouse hypothalamic neurosecretory cells synthesizing neurophysin and vasopressin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 71:3575–3579
Mellon PL, Windle JJ, Goldsmith PC, Padula CA, Roberts JL, Weiner RI (1990) Immortalization of hypothalamic GnRH neurons by genetically targeted tumorigenesis. Neuron 5:1–10
Zakaria M, Dunn IC, Zhen S, Su E, Smith E, Patriquin E, Radovick S (1996) Phorbol ester regulation of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) gene in GnRH-secreting cell lines: a molecular basis for species differences. Mol Endocrinol 10:1282–1291
Earnest DJ, Liang FQ, DiGiorgio S, Gallagher M, Harvey B, Earnest B, Seigel GM (1999) Establishment and characterization of adenoviral E1A immortalized cell lines derived from the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. J Neurobiol 39:1–13
Radovick S, Wray S, Lee E, Nicols DK, Nakayama Y, Weintraub BD, Westphal H, Cutler GB Jr, Wondisford FE (1991) Migratory arrest of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:3402–3406
Wetsel WC (1995) Immortalized hypothalamic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) neurons: a new tool for dissecting the molecular and cellular basis of LHRH physiology. Cell Mol Neurobiol 15:43–78
Mahachoklertwattana P, Sanchez J, Kaplan SL, Grumbach MM (1994) N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors mediate the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by NMDA in a hypothalamic GnRH neuronal cell line (GT1-1). Endocrinology 134:1023–1030
Spergel DJ, Krsmanovic LZ, Stojilkovic SS, Catt KJ (1994) Glutamate modulates [Ca2+]i and gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion in immortalized hypothalamic GT1-7 neurons. Neuroendocrinology 59:309–317
Belsham DD, Wetsel WC, Mellon PL (1996) NMDA and nitric oxide act through the cGMP signal transduction pathway to repress hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. EMBO J 15:538–547
Brann DW, Mahesh VB (1995) Glutamate: a major neuroendocrine excitatory signal mediating steroid effects on gonadotropin secretion. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 53:325–329
Brann DW, Zamorano PL, De Sevilla L, Mahesh VB (2005) Expression of glutamate receptor subunits in the hypothalamus of the female rat during the afternoon of the proestrous luteinizing hormone surge and effects of antiprogestin treatment and aging. Neuroendocrinology 81:120–128
Gyurko R, Leupen S, Huang PL (2002) Deletion of exon 6 of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene in mice results in hypogonadism and infertility. Endocrinology 143:2767–2774
Krsmanovic LZ, Stojilkovic SS, Balla T, al Damluji S, Weiner RI, Catt KJ (1991) Receptors and neurosecretory actions of endothelin in hypothalamic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:11124–11128
Martinez de la Escalera G, Choi AL, Weiner RI (1992) β1-adrenergic regulation of the GT1 gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal cell lines: stimulation of GnRH release via receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology 131:1397–1402
Martinez de la Escalera G, Gallo F, Choi AL, Weiner RI (1992) Dopaminergic regulation of the GT1 gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal cell lines: stimulation of GnRH release via D1-receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology 131:2965–2971
Moretto M, Lopez FJ, Negro-Vilar A (1993) Nitric oxide regulates luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone secretion. Endocrinology 133:2399–2402
Rettori V, Belova N, Dees WL, Nyberg CL, Gimeno M, McCann SM (1993) Role of nitric oxide in the control of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:10130–10134
Krsmanovic LZ, Stojilkovic SS, Mertz LM, Tomic M, Catt KJ (1993) Expression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors and autocrine regulation of neuropeptide release in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:3908–3912
Whyte DB, Lawson MA, Belsham DD, Eraly SA, Bond CT, Adelman JP, Mellon PL (1995) A neuron-specific enhancer targets expression of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene to hypothalamic neurosecretory neurons. Mol Endocrinol 9:467–477
Clark ME, Mellon PL (1995) The POU homeodomain transcription factor Oct-1 is essential for activity of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 15:6169–6177
Lawson MA, Whyte DB, Mellon PL (1996) GATA factors are essential for activity of the neuron-specific enhancer of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol 16:3596–3605
Lawson MA, Buhain AR, Jovenal JC, Mellon PL (1998) Multiple factors interacting at the GATA sites of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron-specific enhancer regulate gene expression. Mol Endocrinol 12:364–377
Belsham DD, Mellon PL (2000) Transcription factors Oct-1 and C/EBP b (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-b) are involved in the glutamate/nitric oxide/cyclic-guanosine 5′-monophosphate-mediated repression of mediated repression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. Mol Endocrinol 14:212–228
Belsham DD, Evangelou A, Roy D, Duc VL, Brown TJ (1998) Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by 5α-dihydrotestosterone in GnRH-secreting GT1-7 hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology 139:1108–1114
Wetsel WC, Eraly SA, Whyte DB, Mellon PL (1993) Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone by protein kinases A and C in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology 132:2360–2370
Yu KL, Yeo TT, Dong KW, Jakubowski M, Lackner-Arkin C, Blum M, Roberts JL (1994) Second messenger regulation of mouse gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in immortalized mouse hypothalamic GT1-3 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 102:85–92
Bruder JM, Drebs WD, Nett TM, Wierman ME (1992) Phorbol ester activation of the protein kinase C pathway inhibits gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. Endocrinology 131:2552–2558
Eraly SA, Mellon PL (1995) Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone transcription by protein kinase C is mediated by evolutionarily conserved, promoter-proximal elements. Mol Endocrinol 9:848–859
Eraly S, Nelson S, Huang K, Mellon P (1998) Oct-1 binds promoter elements required for transcription of the GnRH gene. Mol Endocrinol 12:469–481
Roy D, Angelini N, Belsham DD (1999) Estrogen directly represses gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) mRNA synthesis in GT1-7 GnRH-secreting hypothalamic neurons expressing estrogen receptor (ER) a and ERb. Endocrinology 140:5045–5053
Roy D, Angelini N, Frieda H, Brown GM, Belsham DD (2001) Cyclical regulation of GnRH gene expression in GT1-7 GnRH-secreting neurons by melatonin. Endocrinology 142:4711–4720
Roy D, Belsham DD (2002) Melatonin receptor activation regulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) gene expression and secretion in GT1-7 GnRH neurons: signal transduction mechanisms. J Biol Chem 277:251–258
Shakil T, Hoque ANE, Husain M, Belsham DD (2002) Differential regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion and gene expression by androgen: membrane versus nuclear receptor activation. Mol Endocrinol 16:2592–2602
Gillespie JM, Chan BP, Roy D, Cai F, Belsham DD (2003) Expression of circadian rhythm genes in GnRH-secreting GT1-7 neurons. Endocrinology 144:5285–5292
Chappell PE, White RS, Mellon PL (2003) Circadian gene expression regulates pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretory patterns in the hypothalamic GnRH-secreting GT1-7 cell line. J Neurosci 23:11202–11213
Rave-Harel N, Givens ML, Nelson SB, Duong HA, Coss D, Clark ME, Hall SB, Kamps MP, Mellon PL (2004) TALE homeodomain proteins regulate gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression independently and via interactions with Oct-1. J Biol Chem 279:30287–30297
Rave-Harel N, Miller NL, Givens ML, Mellon PL (2005) The Groucho-related gene family regulates the gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene through interaction with the homeodomain proteins MSX1 and OCT1. J Biol Chem 280:30975–30983
Tang Q, Mazur M, Mellon PL (2005) The protein kinase C pathway acts through multiple transcription factors to repress gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in hypothalamic GT1-7 neuronal cells. Mol Endocrinol 19:2769–2779
Givens ML, Rave-Harel N, Goonewardena VD, Kurotani R, Berdy SE, Swan CH, Rubenstein JL, Robert B, Mellon PL (2005) Developmental regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by the MSX and DLX homeodomain protein families. J Biol Chem 280:19156–19165
Allen MP, Zeng C, Schneider K, Xiong X, Meintzer MK, Bellosta P, Basilico C, Varnum B, Heidenreich KA, Wierman ME (1999) Growth arrest-specific gene 6 (Gas6)/adhesion related kinase (Ark) signaling promotes gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal survival via extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt. Mol Endocrinol 13:191–201
Wierman ME, Pawlowski JE, Allen MP, Xu M, Linseman DA, Nielson-Priess S (2004) Molecular mechanisms of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal migration. Trends Endocrinol Metab 15:96–102
Clark ME, Lawson MA, Belsham DD, Eraly SA, Mellon PL (1997) Molecular aspects of GnRH gene expression. JAI Press, Greenwich, CT
Gore AC, Roberts JL (1997) Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in vivo and in vitro. Front Neuroendocrinol 18:209–245
Belsham DD, Lovejoy DA (2005) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: gene evolution, expression, and regulation. Vitam Horm 71:59–94
Belsham DD, Cai F, Cui H, Smukler SR, Salapatek AM, Shkreta L (2004) Generation of a phenotypic array of hypothalamic neuronal cell models to study complex neuroendocrine disorders. Endocrinology 145:393–400
Sawchenko PE, Imaki T, Vale W (1992) Co-localization of neuroactive substances in the endocrine hypothalamus. Ciba Found Symp 168:16–30
Broberger C, De Lecea L, Sutcliffe JG, Hokfelt T (1998) Hypocretin/orexin- and melanin-concentrating hormone-expressing cells form distinct populations in the rodent lateral hypothalamus: relationship to the neuropeptide Y and agouti gene-related protein systems. J Comp Neurol 402:460–474
Hahn TM, Breininger JF, Baskin DG, Schwartz MW (1998) Coexpression of Agrp and NPY in fasting-activated hypothalamic neurons. Nat Neurosci 1:271–272
Bjorbaek C, El-Haschimi K, Frantz JD, Flier JS (1999) The role of SOCS-3 in leptin signaling and leptin resistance. J Biol Chem 274:30059–30065
Bai F, Rankinen T, Charbonneau C, Belsham DD, Rao DC, Bouchard C, Argyropoulos G (2004) Functional dimorphism of two hAgRP promoter SNPs in linkage disequilibrium. J Med Genet 41:350–353
Cui H, Cai F, Belsham DD (2005) Anorexigenic hormones leptin, insulin, and a-melanocyte stimulating hormone directly induce neurotensin (NT) gene expression in novel NT-expressing cell models. J Neurosci 25:9497–9506
Wang L, Rotzinger S, Al Chawaf A, Elias CF, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Qian X, Wang NC, De Cristofaro A, Belsham D, Bittencourt JC, Vaccarino F, Lovejoy DA (2005) Teneurin proteins possess a carboxy terminal sequence with neuromodulatory activity. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 133:253–265
Titolo D, Cai F, Belsham DD (2006) Coordinate regulation of neuropeptide Y and agouti-related peptide gene expression by estrogen depends on the ratio of estrogen receptor (ER) alpha to ERbeta in clonal hypothalamic neurons. Mol Endocrinol 20:2080–2092
Cui H, Cai F, Belsham DD (2006) Leptin signaling in neurotensin neurons involves STAT, MAP kinases ERK1/2 and p38, through c-Fos and ATF1. FASEB J 20:2654–2656
Ning K, Miller LC, Laidlaw HA, Burgess LA, Perera NM, Downes CP, Leslie NR, Ashford ML (2006) A novel leptin signalling pathway via PTEN inhibition in hypothalamic cell lines and pancreatic beta-cells. EMBO J 25:2377–2387
Sagrillo CA, Grattan DR, McCarthy MM, Selmanoff M (1996) Hormonal and neurotransmitter regulation of GnRH gene expression and related reproductive behaviors. Behav Genet 26:241–277
Schwanzel-Fukuda M, Jorgenson KL, Bergen HT, Weesner GD, Pfaff DW (1992) Biology of normal luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone neurons during and after their migration from olfactory placode. Endocr Rev 13:623–634
Caraty A, Locatelli A, Martin GB (1989) Biphasic response in the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in ovariectomized ewes injected with oestradiol. J Endocrinol 123:375–382
Skynner M, Sim J, Herbison A (1999) Detection of estrogen receptor a and b messenger ribonucleic acids in adult gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Endocrinology 140:5195–5201
Butler J, Sjoberg M, Coen C (1999) Evidence for oestrogen receptor alpha-immunoreactivity in gonadotrophin-releasing hormone-expressing neurones. J Neuroendocrinol 11:331–335
Hrabovszky E, Shughrue P, Merchenthaler I, Hajszán T, Carpenter C, Liposits Z, Petersen S (2000) Detection of estrogen receptor-b messenger RNA and 125I-estrogen binding sites in LHR-releasing hormone neurons of the rat brain. Endocrinology 141:3506–3509
Wierman ME, Kepa JK, Sun W, Gordon DF, Wood WM (1992) Estrogen negatively regulates rat gonadotropin releasing hormone (rGnRH) promoter activity in transfected placental cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 86:1–10
Radovick S, Wray S, Muglia L, Westphal H, Olsen B, Smith E, Patriquin E, Wondisford FE (1994) Steroid hormone regulation and tissue-specific expression of the human GnRH gene in cell culture and transgenic animals. Horm Behav 28:520–529
Bowe J, Li XF, Sugden D, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS, O’Byrne KT (2003) The effects of the phytoestrogen, coumestrol, on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) mRNA expression in GT1-7 GnRH neurones. J Neuroendocrinol 15:105–108
Dorling AA, Todman MG, Korach KS, Herbison AE (2003) Critical role for estrogen receptor alpha in negative feedback regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone mRNA expression in the female mouse. Neuroendocrinology 78:204–209
Ordog T, Goldsmith JR, Chen MD, Connaughton MA, Hotchkiss J, Knobil E (1998) On the mechanism of the positive feedback action of estradiol on luteinizing hormone secretion in the rhesus monkey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:4047–4053
Herbison AE (1998) Multimodal influence of estrogen upon gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Endocr Rev 19:302–330
Kalra SP (1993) Mandatory neuropeptide-steroid signaling for the preovulatory luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone discharge. Endocr Rev 14:507–538
Smith MJ, Jennes L (2001) Neural signals that regulate GnRH neurones directly during the oestrous cycle. Reproduction 122:1–10
Wahlestedt C, Heilig M (1994) Neuropeptide Y and related peptides. In: Bloom F (ed) Psychopharmacology—the fourth generation of progress, on-line edition. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
Stanley BG, Kyrkouli S, Lampert S, Leibowitz S (1986) Neuropeptide Y chronically injected into the hypothalamus: a powerful neurochemical inducer of hyperphagia and obesity. Peptides 7:1189–1192
Sahu A, Crowley WR, Kalra SP (1995) Evidence that hypothalamic neuropeptide Y gene expression increases before the onset of the preovulatory LH surge. J Neuroendocrinol 7:291–296
Kalra PS, Bonavera JJ, Kalra SP (1995) Central administration of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA reveals the critical role of newly synthesized NPY in regulation of LHRH release. Regulatory Pept 59:215–220
Kalra PS, Kalra SP (2000) Use of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to study the physiological functions of neuropeptide Y. Methods 22:249–254
Kasuya E, Mizuno M, Watanabe G, Terasawa E (1998) Effects of an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide for neuropeptide Y mRNA on in vivo luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release in ovariectomized female rhesus monkeys. Regulatory Pept 75–76:319–325
Xu M, Hill JW, Levine JE (2000) Attenuation of luteinizing hormone surges in neuropeptide Y knockout mice. Neuroendocrinology 72:263–271
Li C, Chen P, Smith MS (1999) Morphological evidence for direct interaction between arcuate nucleus neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons and gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons and the possible involvement of NPY Y1 receptors. Endocrinology 140:5382–5390
Dudas B, Mihaly A, Merchenthaler I (2000) Topography and associations of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neuronal systems in the human diencephalon. J Comp Neurol 427:593–603
Simonian SX, Herbison AE (1997) Differential expression of estrogen receptor and neuropeptide Y by brainstem A1 and A2 noradrenaline neurons. Neuroscience 76:517–529
Ahima RS, Osei SY (2001) Molecular regulation of eating behavior: new insights and prospects for therapeutic strategies. Trends Mol Med 7:205–213
Spiegelman BM, Flier JS (2001) Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 104:531–543
Palmiter RD, Erickson JC, Hollopeter G, Baraban SC, Schwartz MW (1998) Life without neuropeptide Y. Recent Prog Horm Res 53:163–199
Morton GJ, Schwartz MW (2001) The NPY/AgRP neuron and energy homeostasis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25:S56–S62
Cone RD (1999) The central melanocortin system and energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10:211–216
Shimada M, Tritos NA, Lowell BB, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (1998) Mice lacking melanin-concentrating hormone are hypophagic and lean. Nature 396:670–674
Ludwig DS, Tritos NA, Mastaitis JW, Kulkarni R, Kokkotou E, Elmquist J, Lowell B, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (2001) Melanin-concentrating hormone overexpression in transgenic mice leads to obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 107:379–386
Tritos NA, Maratos-Flier E (1999) Two important systems in energy homeostasis: melanocortins and melanin-concentrating hormone. Neuropeptides 33:339–349
Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, Dunmore JH, Fang Q, Berkemeier LR, Gu W, Kesterson RA, Boston BA, Cone RD, Smith FJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Lee F (1997) Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 88:131–141
Cowley MA, Pronchuk N, Fan W, Dinulescu DM, Colmers WF, Cone RD (1999) Integration of NPY, AGRP, and melanocortin signals in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: evidence of a cellular basis for the adipostat. Neuron 24:155–163
Sahu A (1998) Evidence suggesting that galanin (GAL), melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), neurotensin (NT), proopiomelanocortin (POMC) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) are targets of leptin signaling in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 139:795–798
Ahima RS, Flier JS (2000) Leptin. Annu Rev Physiol 62:413–437
Hakansson ML, Brown H, Ghilardi N, Skoda RC, Meister B (1998) Leptin receptor immunoreactivity in chemically defined target neurons of the hypothalamus. J Neurosci 18:559–572
Baskin DG, Hahn TM, Schwartz MW (1999) Leptin sensitive neurons in the hypothalamus. Horm Metab Res 31:345–350
Iqbal J, Pompolo S, Murakami T, Grouzmann E, Sakurai T, Meister B, Clarke IJ (2001) Immunohistochemical characterization of localization of long-form leptin receptor (OB-Rb) in neurochemically defined cells in the ovine hypothalamus. Brain Res 920:55–64
Bates SH, Stearns WH, Dundon TA, Schubert M, Tso AW, Wang Y, Banks AS, Lavery HJ, Haq AK, Maratos-Flier E, Neel BG, Schwartz MW, Myers MG (2003) STAT3 signalling is required for leptin regulation of energy balance but not reproduction. Nature 421:856–859
Kim MS, Pak YK, Jang PG, Namkoong C, Choi YS, Won JC, Kim KS, Kim SW, Kim HS, Park JY, Kim YB, Lee KU (2006) Role of hypothalamic Foxo1 in the regulation of food intake and energy homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 9:901–906
Zhang EE, Chapeau E, Hagihara K, Feng GS (2004) Neuronal Shp2 tyrosine phosphatase controls energy balance and metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:16064–16069
Cohen P, Zhao C, Cai X, Montez JM, Rohani SC, Feinstein P, Mombaerts P, Friedman JM (2001) Selective deletion of leptin receptor in neurons leads to obesity. J Clin Invest 108:1113–1121
de Luca C, Kowalski TJ, Zhang Y, Elmquist JK, Lee C, Kilimann MW, Ludwig T, Liu SM, Chua SC Jr (2005) Complete rescue of obesity, diabetes, and infertility in db/db mice by neuron-specific LEPR-B transgenes. J Clin Invest 115:3484–3493
Elias CF, Aschkenasi C, Lee C, Kelly J, Ahima RS, Bjorbaek C, Flier JS, Saper CB, Elmquist JK (1999) Leptin differentially regulates NPY and POMC neurons projecting to the lateral hypothalamic area. Neuron 23:775–786
Watanobe H, Habu S (2002) Leptin regulates growth hormone-releasing factor, somatostatin, and alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone but not neuropeptide Y release in rat hypothalamus in vivo: relation with growth hormone secretion. J Neurosci 22:6265–6271
Sahu A, Carraway RE, Wang YP (2001) Evidence that neurotensin mediates the central effect of leptin on food intake in rat. Brain Res 888:343–347
Richy S, Burlet A, Max J, Burlet C, Beck B (2000) Effect of chronic intraperitoneal injections of leptin on hypothalamic neurotensin content and food intake. Brain Res 862:276–279
Carraway R, Leeman SE (1973) The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem 248:6854–6861
Carraway R, Leeman SE (1975) The amino acid sequence of a hypothalamic peptide, neurotensin. J Biol Chem 250:1907–1911
Remaury A, Vita N, Gendreau S, Jung M, Arnone M, Poncelet M, Culouscou JM, Le Fur G, Soubrie P, Caput D, Shire D, Kopf M, Ferrara P (2002) Targeted inactivation of the neurotensin type 1 receptor reveals its role in body temperature control and feeding behavior but not in analgesia. Brain Res 953:63–72
Meyer-Spasche A, Reed HE, Piggins HD (2002) Neurotensin phase-shifts the firing rate rhythm of neurons in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 16:339–344
Dobner PR, Fadel J, Deitemeyer N, Carraway RE, Deutch AY (2001) Neurotensin-deficient mice show altered responses to antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:8048–8053
Rostene WH, Alexander MJ (1997) Neurotensin and neuroendocrine regulation. Front Neuroendocrinol 18:115–173
Harris M, Aschkenasi C, Elias CF, Chandrankunnel A, Nillni EA, Bjoorbaek C, Elmquist JK, Flier JS, Hollenberg AN (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene by leptin and melanocortin signaling. J Clin Invest 107:111–120
Elias CF, Kelly JF, Lee CE, Ahima RS, Drucker DJ, Saper CB, Elmquist JK (2000) Chemical characterization of leptin-activated neurons in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 423:261–281
Beck B, Stricker-Krongrad A, Richy S, Burlet C (1998) Evidence that hypothalamic neurotensin signals leptin effects on feeding behavior in normal and fat-preferring rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:634–638
Wilding JP, Gilbey SG, Bailey CJ, Batt RA, Williams G, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1993) Increased neuropeptide-Y messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and decreased neurotensin mRNA in the hypothalamus of the obese (ob/ob) mouse. Endocrinology 132:1939–1944
Stanley BG, Hoebel BG, Leibowitz SF (1983) Neurotensin: effects of hypothalamic and intravenous injections on eating and drinking in rats. Peptides 4:493–500
Harrison RJ, McNeil GP, Dobner PR (1995) Synergistic activation of neurotensin/neuromedin N gene expression by c-Jun and glucocorticoids: novel effects of Fos family proteins. Mol Endocrinol 9:981–993
Watters JJ, Dorsa DM (1998) Transcriptional effects of estrogen on neuronal neurotensin gene expression involve cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent signaling mechanisms. J Neurosci 18:6672–6680
Kaszubska W, Falls HD, Schaefer VG, Haasch D, Frost L, Hessler P, Kroeger PE, White DW, Jirousek MR, Trevillyan JM (2002). Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B negatively regulates leptin signaling in a hypothalamic cell line. Mol Cell Endocrinol 195:109–118
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the members of the Belsham Lab, past and present, for the contributions presented herein, particularly Fang Cai, Hong Cui, and Danny Titolo. This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, Canada Foundation for Innovation, and a Premier’s Research Excellence Award. DDB holds a Canada Research Chair in Neuroendocrinology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belsham, D.D. Hormonal Regulation of Clonal, Immortalized Hypothalamic Neurons Expressing Neuropeptides Involved in Reproduction and Feeding. Mol Neurobiol 35, 182–194 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0010-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0010-5