Abstract
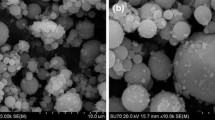
High performance and reactivity of ultra-fine aluminium is the present new area of interest in aerospace and defence applications. Ultra-fine aluminium is an important ingredient in propellant compositions and formulations, which significantly improves the performance parameters of rockets. This paper discusses the characterization of synthesized ultra-fine aluminium, such as active (metallic) aluminium content, bulk density, X-ray diffraction, surface area (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller), scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, thermal analysis and X-ray photo-electron spectroscopy. It is observed that the maximum metallic aluminium content of 85.93% was obtained by a gas volumetric method. The synthesized ultra-fine aluminium particles will greatly promote the application of these particles in composite propellants.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisenreich N, Juez-Lorenzo M, Kolarik V, Koleczko A, Weiser V and Fietzek H 2004 Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 29 137
Jayaraman K, Chakravarthy S R and Sarathi R 2010 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 46 21
DeLuca L T, Colombo G, Maggi F, Bandera A, Babuk V A, Galfetti L et al 2010 J. Propul. Power 26 724
Ivanov Y F, Sedoi V S, Arkhipov V A, Bondarchuk S S, Vorozhtsov A B, Korotkikhand A G et al 2003 Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 28 319
Jayaraman K, Chakravarthy S R, Anand K V and Sarathi R 2009 Combust. Flame 156 1662
Li F, Guo X, Liu L, Li M, Chen W, Jiang W et al 2011 Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propul. 10 67
Babuk V, Dolotkazin I, Conti A, Galfetti L, DeLuca L T, Glebov A et al 2009 Prog. Propuls. Phys. 1 3
Galfetti L, Severini F, Colombo G, Meda L, DeLuca L T and Marra G 2007 Eur. Conf. Aerosp. Sci. EUCASS 11 26
Jigatch A N, Kuskov M L, Stoenko N I, Storozhev V, Leipunsky I O and Pribory B 2002 Exp. Tech. Instrum. 6 122
Ya G M and Miller A V 1981 USSR inventor’s certificate no. 814 432 Byull. Izobret no. 11
Mazalov Y A, Bogdanova V V, Ivashkevich L S, Pavlovets G Y and Chinnov V V 1993 Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 29 198
Khan A S, Farrokh B and Takacs L 2008 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 489 77
Haber J A and Buhor W E 1998 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 10847
Gutmanas E Y, Trusov L I and Gotman I 1994 Nanostruct. Mater. 4 893
Sanchez-Lopez J C, Caballero A and Fernandez A 1998 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 18 1195
Sun X K, Sun M, Cong H T and Yang M C 1999 Nanostruct. Matter 11 917
Sedoi V S and Valveich V V 1999 J. Tech. Phys. 25 81
Girshick S L, Muno R, Wu C Y, Yang L, Singh S K, Chiu C P et al 1993 J. Aerosol. Sci. 24 367
Kobayashi N, Kawakami Y, Kamada K, Li J G, Watanabe R and Ishigaki T 2008 Thin Solid Films 516 4402
Mamak M, Stadler U, Dolbec R, Boulos M, Choi S Y and Petrov S 2010 J. Mater. Chem. 20 9855
Jung T, Kwon H, Park S, Ho J, Jung S, Baek J et al 2015 J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15 8424
Ananthapadmanabhan P V, Sreekumar K P, Thiyagarajan K and Venkatramani N 2004 Scr. Mater. 50 143
Ye R, Li J G and Ishigaki T 2007 Thin Solid Films 515 4251
Kim K I, Kim J H, Cho W S, Hwang K T, Choi S C and Han K S 2014 Ceram. Int. 40 8117
Dreizin E L 2009 Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 35 141
Maggi F, Paravan C, DeLuca L T, Dossi S and Liljedahl M 2015 Powder Technol. 270 46
Chen L, Song W, Lv J, Chen X and Xie C 2010 Mater. Chem. Phys. 120 670
Gromov A A, Strokova Y I and Ditts A A 2010 Russian J. Phys. Chem. 4 156
Wang F, Wu Z, Shangguan X, Sun Y, Feng J, Li Z et al 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 5228
Wang S 2005 Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 30 148
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Director ASL, for facilitating this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tejasvi, K., Venkateswara Rao, V. & Pydi Setty, Y. Characterization of ultra-fine aluminium particles with potential applications as composite propellants. Bull Mater Sci 42, 207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1895-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1895-0