Abstract
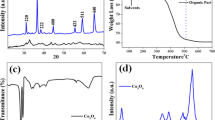
Purification efficiency of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) by the method of chemical oxidation was considered as a function of position and size of catalyst remains and consequently of the tubes morphology. Oxidation of CNTs by means of both HNO3 and NaOH treatment efficiently removes small catalyst particles embedded in the tubes top, following “tip-mode” CNTs growth mechanism. Destructive character of the purification can be assumed due to the resulting tiniest tube population increase as a consequence of their body tearing. However, limited purification efficiency was observed in the case of bigger metal particles with variable size and position in CNTs. Bigger particles occur on account of catalyst instability portrayed as small metal particles of active phase migration and merging. The formed agglomerates are not stable in the tubes hollow, but disintegrate leading to different sizes and position of metal particles in the tubes body. Consequently, CNT may be obtained with non-uniform thickness and morphology. The phenomenon is due to liquid-like behaviour of the active phase at reaction temperature (700 °C) which is higher than both Huttig and Tamman temperatures of applied metals. A mechanism is proposed assuming that an isolated bigger part of the mother particle stayed encapsulated inside the tube body inactive for further tube growth, while a smaller fragment of the collapsed particle resided at the tube top acting as a new-born active site. Owing to “replica effect” the tube further grows thinner following the size of the new active site. Consequently CNTs of irregular morphology occur as they resemble metal particles of various sizes following their disintegration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett E P, Joyner L G and Halenda P P 1951 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73 373
Boskovic G and Baerns M 2004 Catalyst deactivation in basic principles of applied catalysis (ed) M Baerns (Berlin: Springer) p. 479
Chen M, Yu H W, Chen J H and Koo H S 2007 Diamond Relat. Mater. 16 1110
Chen X, Wang R, Xu J and Yu D 2004 Micron 35 455
Ermakova M A and Ermakov D Y 2002 Catal. Today 77 225
Ermakova M A, Ermakov D Y, Chuvilin A L and Kuvshinov G G 2001 J. Catal. 201 183
Gohier A, Ewels C P, Minea T M and Djouadi M A 2008 Carbon 46 1331
Gulino G, Vieira R, Amadou J, Nguyen P, Ledoux M J, Galvagno S, Centi G and Pham-Huu C 2005 Appl. Catal. A 279 89
Hernadi K, Fonseca A, Nagy J B, Bernaerts D and Lucas A A 1996 Carbon 34 1249
Iijima S 1991 Nature 354 56
Louis B et al 2005 Catal. Today 102 23
Lowell S, Shields J E, Thomas M A and Thommes M 2004 Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size and density (Dordrecht/Boston/London: Kluwer Academic Publishers)
Monchelaho M A M, Xiong H, Moyo M, Jewell L L and Coville N J 2011 J. Mol. Catal. A 335 189
Montoro L A and Rosolen J M 2006 Carbon 44 3293
Moulijn J A, van Diepen A E and Kapteijn F 2001 Appl. Catal. A 212 3
Qian W, Liu T, Wang Z, Yu H, Li Z, Wei F and Luo G 2003 Carbon 41 2487
Ratkovic S, Vujicic Dj, Kiss E, Boskovic G and Geszti O 2011 Mater. Chem. Phys. 129 398
Son S Y, Lee Y, Won S and Lee D H 2008 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 47 2166
Teo K B K, Singh C, Chowalla M and Milne W I 2001 Encyclopedia of nanoscience and nanotechnology (USA: American Scientific Publishers)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technological Development of Serbia (project 172059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BOSKOVIC, G., RATKOVIC, S., KISS, E. et al. Carbon nanotubes purification constrains due to large Fe–Ni/Al 2 O 3 catalyst particles encapsulation. Bull Mater Sci 36, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-013-0435-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-013-0435-6