Abstract
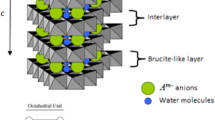
The layered double hydroxide (LDH) of Co with Al decomposes to yield an oxide residue with the spinel structure below 250°C. The decomposition reaction is preceded by the formation of an intermediate hydroxide in which the metal hydroxide layers are regularly stacked about the c-crystallographic axis, but the layers themselves are aperiodic. Aperiodicity is modeled by locating randomly chosen Co2+ ions in tetrahedral sites in the interlayer region. This phase is characterized by a single strong basal reflection in its powder diffraction pattern. All other reflections are extinguished on account of (i) turbostratic disorder which destroys all hkl reflections and (ii) layer aperiodicity, which destroys all two dimensional hk reflections. Given its topochemical relationship with the spinel structure, such an intermediate is a necessary precursor to spinel formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costantino U, Marmottini F, Nocchetti M and Vivani R 1998 Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1439
Duan X and Evans D G (ed.) 2006 Layered double hydroxides, structure and bonding (Berlin: Springer) 119
Figlarz M, Gerand B, Delahaye-Vidal A, Dumont B, Harb F, Coucou A and Fievet F 1990 Solid State Ionics 43 143
Hines D R, Seidler G T, Treacy M M J and Solin S A 1997 Solid State Commun. 101 835
Kannan S and Swamy C S 1999 Catal. Today 53 725
Ma R, Liu Z, Takada K, Fukuda K, Ebina Y, Bando Y and Sasaki T 2006 Inorg. Chem. 45 3964
Perez-Ramirez J, Mul G, Kapteijn F and Moulijn J A 2001 J. Mater. Chem. 11 821
Radha A V, Shivakumara C and Kamath P V 2005 Clays Clay Miner. 53 521
Radha A V, Kamath P V and Shivakumara C 2007a J. Phys. Chem. B111 3411
Radha A V, Kamath P V and Shivakumara C 2007b Acta Crystallogr. B63 243
Rey F, Fornes V and Rojo J M 1992 J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 88 2233
Sato T, Kato K, Endo T and Shimada M 1986 React. Solids 2 253
Thomas G S and Kamath P V 2006 J. Chem. Sci. 118 127
Thomas G S, Rajamathi M and Kamath P V 2004 Clays Clay Miner. 52 693
Thomas G S, Radha A V, Kamath P V and Kannan S 2006 J. Phys. Chem. B 110 12365
Treacy M M J, Newsam J M and Deem M W 1991 Proc. R. Soc., London A433 499
Verma A R and Krishna P 1966 Polymorphism and polytypism in crystals (NY: John Wiley & Sons)
Warren B E and Bodenstein P 1966 Acta Crystallogr. 20 602
Williams G R and O’Hare D 2006 J. Mater. Chem. 16 3065
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radha, A.V., Thomas, G.S., Vishnu Kamath, P. et al. Thermal decomposition of Co-Al layered double hydroxide: Identification of precursor to oxide with spinel structure. Bull Mater Sci 33, 319–324 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0049-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0049-1