Abstract
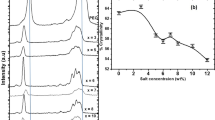
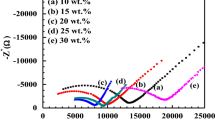
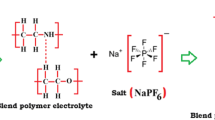
We have prepared, characterized and investigated a new PEG-2000 based solid polymer electrolyte (PEG) x : NH4NO3. Ionic conductivity measurements have been made as a function of salt concentration as well as temperature in the range 265–330 K. Selected compositions of the electrolyte are exposed to a beam of 8 MeV electrons and 60Co γ-rays to an accumulated dose of 10 kGy to study the effect on ionic conductivity. The electrolyte samples are also quenched at liquid nitrogen temperature and conductivity measurements are carried out. The ionic conductivity at room temperature exhibits a characteristic peak for the composition, x = 46. Electron beam irradiation results in an increase in conductivity for all compositions by a factor of 2–3. Exposure to γ-rays enhances the conductivity by one order of magnitude. Quenching at low temperature has resulted in an increase in conductivity by 1–2 orders of magnitude. The enhancement of conductivity upon irradiation and quenching is interpreted as due to an increase in amorphous region and decrease in crystallinity of the electrolyte. DSC and NMR measurements also support this conclusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand M B, Chabagno J M and Duclot M J 1979 Fast ion transport in solids (eds) P Vashista et al (New York: Elsevier North Holland)
Berthier C, Gorecki W, Minier M, Armand M B, Chabagno J M and Rigaud P 1983 Solid State Ionics 11 91
Binesh N and Bhat S V 1999 Solid State Ionics 122 291
Binesh N and Bhat S V 1998 J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 36 1201
Brinkmann D 1992 Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 24 527
Fulcher G H 1925 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 8 339
Gibbs J H and DiMarzio E A 1958 J. Chem. Phys. 28 373
Gray F M 1991 Solid polymer electrolyte—fundamentals and technological applications (New York: VCH Inc.)
Haig H I, Herema H R M and Baam B M 2004 J. Endo Chem.: Phys. Dut. Aspects 110
Hendrickson J R and Bray P J 1973 J. Magn. Res. 9 341
Hikichi K and Furuichi J 1965 J. Polym. Sci. A3 3003
Jenkins H D B and Morris D F C 1976 Mol. Phys. 32 231
Johansson A, Wendsjö A and Tegenfeldt J 1992 Electrochim. Acta 37 1487
Joykumar Singh T and Bhat S V 2003 Bull. Mater. Sci. 26 707
Le Nest J F, Gandini A and Cheradane H 1988 Br. Polym. J. 20 253
Li X and Hsu S L 1984 J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Phys. Ed. 22 1331
Nader Binesh and Bhat S V 1996 Solid State Ionics 92 261
Ratner M A 1987 in Polymer electrolyte reviews (eds) J R MacCallum and C A Vincent (Elsevier Applied Science) Vol. I, p. 185
Shi J and Vincent C A 1993 Solid State Ionics 60 11
Tamman V G and Hesse H Z 1926 Anorg. Allg. Chem. 19 245
Vincent C A 1987 Prog. Solid State Chem. 17 145
Vogel H 1922 Phys. Z. 22 645
Watanabe M, Togo M, Sanui K, Ogata N, Kobayashi T and Ohtaki Z 1984 Macromolecules 17 2908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damle, R., Kulkarni, P.N. & Bhat, S.V. Study of effect of composition, irradiation and quenching on ionic conductivity in (PEG) x : NH4NO3 solid polymer electrolyte. Bull Mater Sci 31, 869–876 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0139-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0139-5