Abstract
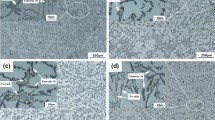
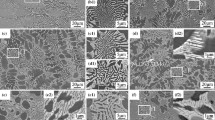
Effects of elements rhenium and chromium additions on properties and microstructure of 93W-4·9Ni-2·1Fe alloys were investigated. Optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and EDAX energy spectrometer were used to characterize the microstructure and compositions of the alloys, respectively. The tensile strength and elongation of alloys were evaluated using the quasi-static tensile testing machine, and the relative densities of the alloys were evaluated using the Archimedes water immersion method. The experimental results indicated that when elements Re and Cr were in the range of 0–1·0 wt.%, relative density, elongation, tensile strength of 93W-4·9Ni-2·1Fe alloys varied from 99·4%, 26·4%, 997·2 MPa without Re additions to 99·5%, 8·6%, 1161·2 MPa with 1·0 wt.% Re addition, respectively. Rhenium generated solid-solution strengthening, grain refinement, reducing ductile tearing and increasing transcrystalline fracture, which resulted in the ductility reduction and the strength increase of the heavy alloys. With the increase of Cr content from 0–1·0 wt.%, the tensile strength, relative density and elongation of 93W-Ni-Fe alloy reduced from 997·2 MPa, 99·3%, 15% to 844·4 MPa, 95·2%, 5·7%, respectively. Element Cr formed interphases with elements W, Ni, Fe and O and gathered along the interface of the alloys, which induced interfacial cohesion and resulted in lower mechanical properties of 93W-Ni-Fe alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose A and German R M 1988 Metall. Trans. A19 3100
Bose A and German R M 1990 Metall. Trans. A21 1325
Bose A, Sims D M and German R M 1988 Metal & Hard Mater. 98
Edmonds D V and Jones P N 1979 Metall. Trans. A10 289
German R M 1985 Liquid phase sintering (New York: Plenum Press) pp 2–19
German R M, Bose A, Kemp P B and Zhang H 1989 Additive effect on the microstructure and properties of tungsten heavy alloy composites, in Advances in powder metallurgy (eds) T G Basbarre and W F Jandeska (Princeton, NJ: Metal Powder Industries Federation) Vol. 2, pp 401–414
Hogwood M C and Bentley A R 1995 The development of high strength and toughness fibrous microstructures in tungsten-nickel-iron alloys for kinetic energy penetrator applications, in Proc. of the 1994 int. conf. on tungsten and refractory metals (eds) A Bose and R J Dowding (Princeton, NJ: Metal Powder Industries Federation) pp 37–45
Hong S H, Kang S J L, Yoon D N and Baek W H 1991 Matall. Trans. A22 2969
Kemp P B and German R M 1991 J. Less Common Metals 175 353
Kemp P B and German R M 1995 Metall. Mater. Trans. A26 2187
Muddle B C 1984 Metall. Trans. A15 1989
Park H D, Baik W H, Kang S J L and Yoon D Y 1996 Metall. Mater. Trans. A27 3120
Wu G C, You Q and Wang D 1999 Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 17 299
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Ma, Y. & Huang, B. Influence of minor elements additions on microstructure and properties of 93W-4·9Ni-2·1Fe alloys. Bull Mater Sci 31, 1–6 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0001-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0001-9