Abstract
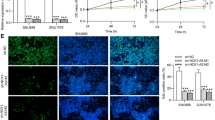
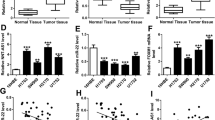
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) plays a key role in regulating cancer development. LncRNA deoxyguanosine kinase antisense RNA 1 (DGUOK-AS1) has been reported as a promoter in tumor. The work was designed to further investigate the mechanism of action of DGUOK-AS1 in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). DGUOK-AS1 level in LUSC cells was measured using RT-qPCR. Counting Kit-8 assays and colony forming assays were performed to evaluate LUSC cell viability and proliferation. Transwell assays were performed to detect cell migration and invasion. Luciferase reporter and RNA pulldown assays were used to verify the binding capacity of DGUOK-AS1 and miR-653-5p. RNA immunoprecipitation assays were performed to verify the relationship of DGUOK-AS1, miR-653-5p, and SLC6A15. DGUOK-AS1 was highly expressed in LUSC cells. DGUOK-AS1 knockdown suppressed LUSC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. SLC6A15 was demonstrated to be targeted by miR-653-5p, and DGUOK-AS1 interacted with miR-653-5p to modulate SLC6A15 level in LUSC cells. Overexpression of SLC6A15 reversed the suppressive effects of DGUOK-AS1 knockdown on LUSC cell processes. In conclusion, DGUOK-AS1 promotes malignant behaviors of LUSC cells by upregulating SLC6A15 level through interaction with miR-653-5p.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kim, Y., et al. (2014). Integrative and comparative genomic analysis of lung squamous cell carcinomas in East Asian patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 32(2), 121–128.
Nooreldeen, R., & Bach, H. (2021). Current and future development in lung cancer diagnosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(16), 8661.
Travis, W. D., et al. (2015). The 2015 world health organization classification of lung tumors: Impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 10(9), 1243–1260.
Chen, W. J., et al. (2017). Implication of downregulation and prospective pathway signaling of microRNA-375 in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Pathology - Research and Practice, 213(4), 364–372.
Li, Y., et al. (2018). Transcriptomic and functional network features of lung squamous cell carcinoma through integrative analysis of GEO and TCGA data. Science and Reports, 8(1), 15834.
Ning, P., et al. (2018). Integrated genomic analyses of lung squamous cell carcinoma for identification of a possible competitive endogenous RNA network by means of TCGA datasets. PeerJ, 6, e4254.
Li, J., et al. (2020). LncRNA-ATB promotes lung squamous carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting microRNA-590-5p/NF90 axis. DNA and Cell Biology, 39(3), 459–473.
Xu, Y., et al. (2019). LncRNA HULC promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating PTPRO via NF-κB. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120(12), 19415–19421.
Tang, Z., et al. (2017). GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(W1), W98-w102.
Liang, Y., et al. (2021). DGUOK-AS1 acts as a tumorpromoter through regulatingmiR-204-5p/IL-11 axis in breast cancer. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids, 26, 1079–1091.
Li, Y., et al. (2020). Identification of DGUOK-AS1 as a prognostic factor in breast cancer by bioinformatics analysis. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 1092.
Wu, N., et al. (2020). DGUOK-AS1 promotes cell proliferation in cervical cancer via acting as a ceRNA of miR-653-5p. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 38(7), 870–879.
Song, Y., et al. (2021). DGUOK-AS1 promotes cervical squamous cell carcinoma progression by suppressing miR-499a-5p that targets SPRR1B in vitro. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 585, 177–184.
Girodet, P. O., et al. (2016). Alternative macrophage activation is increased in asthma. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 55(4), 467–475.
Zhao, M., Feng, J., & Tang, L. (2021). Competing endogenous RNAs in lung cancer. Cancer Biology & Medicine, 18(1), 1–20.
Qi, X., et al. (2015). ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical implications. Journal of Medical Genetics, 52(10), 710–718.
Li, J. H., et al. (2014). starBase v20: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, D92–D97.
Lewis, B. P., Burge, C. B., & Bartel, D. P. (2005). Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell, 120(1), 15–20.
Rinn, J. L., et al. (2007). Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell, 129(7), 1311–1323.
Lee, N., et al. (2015). EBV noncoding RNA binds nascent RNA to drive host PAX5 to viral DNA. Cell, 160(4), 607–618.
Wutz, A., Rasmussen, T. P., & Jaenisch, R. (2002). Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nature Genetics, 30(2), 167–174.
Feng, Y., et al. (2023). LncRNA DGUOK-AS1 facilitates non-small cell lung cancer growth and metastasis through increasing TRPM7 stability via m6A modification. Transl Oncol, 32, 101661.
Correia de Sousa, M., et al. (2019). Deciphering miRNAs’ action through miRNA editing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(24), 6249.
Zhang, M., et al. (2021). miR-653-5p suppresses the growth and migration of breast cancer cells by targeting MAPK6. Molecular Medicine Reports. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.11839
Yu, Y. Z., et al. (2022). Hsa_circ_0003258 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by complexing with IGF2BP3 and sponging miR-653-5p. Molecular Cancer, 21(1), 12.
Li, Z., et al. (2021). MicroRNA-653-5p promotes gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting the SOCS6-STAT3 pathway. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 8, 655580.
Han, W., et al. (2019). Circular RNA circ-RAD23B promotes cell growth and invasion by miR-593-3p/CCND2 and miR-653-5p/TIAM1 pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 510(3), 462–466.
Bröer, A., et al. (2006). The orphan transporter v7–3 (slc6a15) is a Na+-dependent neutral amino acid transporter (B0AT2). The Biochemical Journal, 393(Pt 1), 421–430.
Wan, Q., & Tang, J. (2019). Exploration of potential key pathways and genes in multiple ocular cancers through bioinformatics analysis. Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 257(10), 2329–2341.
Chen, Y., et al. (2021). SLC6A15 acts as a tumor suppressor to inhibit migration and invasion in human papillary thyroid cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 122(8), 814–826.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate all the participants providing supports for this study.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YT was the main designer of this study. YT, SL, LW, CZ, LL, SW, JZ and JL performed the experiments and analyzed the data. YT, JH, HZ, NW and JL drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, Y., Li, S., Wei, L. et al. LncRNA DGUOK-AS1 Promotes Cell Progression in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulation of miR-653-5p/SLC6A15 Axis. Mol Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01088-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01088-8