Abstract
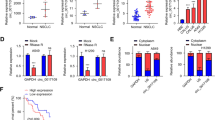
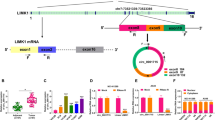
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been identified to be dysregulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and implicated in the progression of this cancer. Here, this work aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of circ_0082374 on NSCLC progression. Levels of circ_0082374, miR-491-5p, GPX4 (glutathione peroxidase 4) and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins were examined by quantitative real-time PCR or western blotting, respectively. Cell proliferation and metastasis were detected using cell counting kit-8, colony formation, EdU, transwell, and Scratch assays. Cell ferroptosis was evaluated by measuring cell survival after the treatment of different ferroptosis inducers or inhibitors, as well as the accumulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), ferrous iron (Fe2+) and malondialdehyde (MDA). The binding between miR-491-5p and circ_0082374 or GPX4 was confirmed using dual-luciferase reporter and RNA pull-down assays. In vivo experiments were conducted using murine xenograft assay and immunohistochemistry. Circ_0082374 was a stable circRNA with high expression in NSCLC tissues and cells. Functionally, circ_0082374 silencing suppressed NSCLC cell proliferation and metastasis. Moreover, its down-regulation enhanced ferroptosis by decreasing iron and lipid peroxidation accumulation. Mechanistically, circ_0082374 could indirectly up-regulate GPX4 expression via miR-491-5p, indicating the circ_0082374/miR-491-5p/GPX4 competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNA) network. Rescue experiments demonstrated that the miR-491-5p/GPX4 axis mediated the regulatory effects of circ_0082374 exerted on NSCLC cells. Moreover, knockdown of circ_0082374 impeded NSCLC growth and EMT via regulating miR-491-5p and GPX4. Circ_0082374 silencing could suppress NSCLC cell proliferation, metastasis and induce ferroptosis through miR-491-5p/GPX4 axis, suggesting a novel therapeutic approach for NSCLC patients.
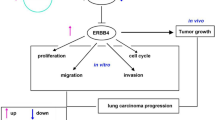
Graphical Abstract
Circ_0082374 acts as a sponge for miR-491-5p, and up-regulates GPX4 expression through sequestering miR-491-5p, thereby promoting NSCLC cell proliferation, metastasis and suppressing ferroptosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNAs
- GPX4:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 4
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxyen species
- miRNA/miR:
-
MicroRNA
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNA
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
- EdU:
-
5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- NC:
-
Negative control
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- Fe2+:
-
Ferrous iron
- ShRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- Fer-1:
-
Ferrostatin-1
References
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., & Jemal, A. (2019). Cancer statistics, 2019. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 69(1), 7–34.
Gridelli, C., Rossi, A., Carbone, D. P., Guarize, J., Karachaliou, N., Mok, T., Petrella, F., Spaggiari, L., & Rosell, R. (2015). Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 1, 15009.
Torre, L. A., Siegel, R. L., & Jemal, A. (2016). Lung cancer statistics. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 893, 1–19.
Sun, H., & Sun, Y. (2019). Lidocaine inhibits proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cell via regulation of miR-539/EGFR axis. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology., 47(1), 2866–2874.
Zou, J., Wang, L., Tang, H., Liu, X., Peng, F., & Peng, C. (2021). Ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer: Progression and therapeutic potential on it. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(24), 13335.
Geng, Y., Jiang, J., & Wu, C. (2018). Function and clinical significance of circRNAs in solid tumors. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 11(1), 98.
Chen, L.-L., & Yang, L. (2015). Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biology, 12(4), 381–388.
Arnaiz, E., Sole, C., Manterola, L., Iparraguirre, L., Otaegui, D., & Lawrie, C. H. (2019). CircRNAs and cancer: Biomarkers and master regulators. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 58, 90–99.
Vo, J. N., Cieslik, M., Zhang, Y., Shukla, S., Xiao, L., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y. M., Dhanasekaran, S. M., Engelke, C. G., & Cao, X. (2019). The landscape of circular RNA in cancer. Cell, 176(4), 869-881.e813.
Huang, G., Liang, M., Liu, H., Huang, J., Li, P., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Lin, Y., & Jiang, X. (2020). CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death & Disease, 11(12), 1065.
Yang, H., Li, X., Meng, Q., Sun, H., Wu, S., Hu, W., Liu, G., Li, X., Yang, Y., & Chen, R. (2020). CircPTK2 (hsa_circ_0005273) as a novel therapeutic target for metastatic colorectal cancer. Molecular Cancer, 19(1), 13.
Chen, D., Ma, W., Ke, Z., & Xie, F. (2018). CircRNA hsa_circ_100395 regulates miR-1228/TCF21 pathway to inhibit lung cancer progression. Cell Cycle, 17(16), 2080–2090.
Wang, B., Li, B., & Si, T. (2020). Knockdown of circ0082374 inhibits cell viability, migration, invasion and glycolysis in glioma cells by miR-326/SIRT1. Brain Research, 1748, 147108.
Hong, W., Xue, M., Jiang, J., Zhang, Y., & Gao, X. (2020). Circular RNA circ-CPA4/ let-7 miRNA/PD-L1 axis regulates cell growth, stemness, drug resistance and immune evasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 39(1), 149.
Tao, W., Cao, C., Ren, G., & Zhou, D. (2021). Circular RNA circCPA4 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating miR-214-3p/TGIF2 in lung cancer. Thoracic Cancer, 12(24), 3356–3369.
Chen, Z., Wang, W., Abdul Razak, S. R., Han, T., Ahmad, N. H., & Li, X. (2023). Ferroptosis as a potential target for cancer therapy. Cell Death & Disease, 14(7), 460.
Kuche, K., Yadav, V., Patel, M., Chaudhari, D., Date, T., & Jain, S. (2023). Enhancing anti-cancer potential by delivering synergistic drug combinations via phenylboronic acid modified PLGA nanoparticles through ferroptosis-based therapy. Biomaterials Advances, 156, 213700.
Hansen, T. B., Jensen, T. I., Clausen, B. H., Bramsen, J. B., Finsen, B., Damgaard, C. K., & Kjems, J. (2013). Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature, 495(7441), 384–388.
Salmena, L., Poliseno, L., Tay, Y., Kats, L., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2011). A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell, 146(3), 353–358.
Chen, X., Li, J., Kang, R., Klionsky, D. J., & Tang, D. (2021). Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy, 17(9), 2054–2081.
Fedchenko, N., & Reifenrath, J. (2014). Different approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry analysis results in the bone tissue—A review. Diagnostic Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-014-0221-9
Yang, W. S., & Stockwell, B. R. (2016). Ferroptosis: Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends in Cell Biology, 26(3), 165–176.
Luo, M., Wu, L., Zhang, K., Wang, H., Zhang, T., Gutierrez, L., O’Connell, D., Zhang, P., Li, Y., & Gao, T. (2018). miR-137 regulates ferroptosis by targeting glutamine transporter SLC1A5 in melanoma. Cell Death and Differentiation, 25(8), 1457–1472.
Jeck, W. R., Sorrentino, J. A., Wang, K., Slevin, M. K., Burd, C. E., Liu, J., Marzluff, W. F., & Sharpless, N. E. (2013). Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA, 19(2), 141–157.
Zhang, Y., Cai, Z., Liang, J., Chai, E., Lu, A., & Shang, Y. (2020). CircCPA4 promotes the malignant phenotypes in glioma via miR-760/MEF2D axis. Neurochemical Research, 45(12), 2903–2913.
Yang, S., Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Liu, C., Lu, Y., Fang, Z., Shi, H., Zhang, W., & Wu, X. (2019). MicroRNA-4712-5p promotes proliferation of the vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cell line A431 by targeting PTEN through the AKT/cyclin D1 signaling pathways. Oncology Reports, 42(5), 1689–1698.
Hu, L., Wu, H., Wan, X., Liu, L., He, Y., Zhu, L., Liu, S., Yao, H., & Zhu, Z. (2018). MicroRNA-585 suppresses tumor proliferation and migration in gastric cancer by directly targeting MAPK1. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 499(1), 52–58.
Rupaimoole, R., Calin, G. A., Lopez-Berestein, G., & Sood, A. K. (2016). miRNA deregulation in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discovery., 6(3), 235–246.
Wu, F., Ji, A., Zhang, Z., Li, J., & Li, P. (2021). miR-491-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration of A549 cells by FOXP4. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine., 21(6), 622.
Gong, F., Ren, P., Zhang, Y., Jiang, J., & Zhang, H. (2016). MicroRNAs-491-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by inhibiting IGF2BP1 in non-small cell lung cancer. American Journal of Translational Research, 8(2), 485–495.
Ge, W., Chi, H., Tang, H., Xu, J., Wang, J., Cai, W., & Ma, H. (2021). Circular RNA CELF1 drives immunosuppression and anti-PD1 therapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via the miR-491-5p/EGFR axis. Aging, 13(22), 24560–24579.
Yang, W. S., SriRamaratnam, R., Welsch, M. E., Shimada, K., Skouta, R., Viswanathan, V. S., Cheah, J. H., Clemons, P. A., Shamji, A. F., & Clish, C. B. (2014). Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell, 156(1–2), 317–331.
Brigelius-Flohé, R., & Maiorino, M. (2013). Glutathione peroxidases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1830(5), 3289–3303.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mengdi Fan and Zhibo Zhou designed and performed the research; Xianyin Sang analyzed the data; Zongyu Li wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants and this study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Shuren University Shulan International Medical College. The animal study has obtained the assent of the Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Shuren University Shulan International Medical College Animal Care and Use Committee.
Research Involving Human and Animal Rights
Animal studies were performed in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines and the Basel Declaration. All animals received humane care according to the National Institutes of Health (USA) guidelines.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12033_2024_1059_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 (TIF 220 KB)—Circ_0082374/miR-491-5p axis can regulate GPX4 in NSCLC cells. (A, B) The effects of circ_0082374/miR-491-5p axis on GPX4 expression was evaluated by western blotting. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Fan, M., Zhou, Z. et al. Circ_0082374 Promotes the Tumorigenesis and Suppresses Ferroptosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Up-Regulating GPX4 Through Sequestering miR-491-5p. Mol Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01059-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01059-z