Abstract
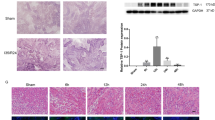
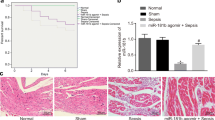
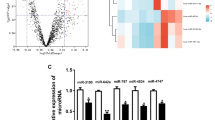
Hemorrhagic shock is a frequent threat to pregnant women, and blood transfusions can contribute to organ damage, including hepatic ischemia–reperfusion (HIR) injury. LncRNA SNHG7 (SNHG7) has been reported to exert an essential role in various diseases, while the effect of SNHG7 on HIR injury induced by hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion in pregnant rats is still unclear. In our study, we examined the function and mechanism of SNHG7 in the progression of HIR injury in pregnant rats. The results showed that SNHG7 expression was low in the hepatic tissues of pregnant rats after the hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion modeling. Knockdown of SNHG7 further aggravated hepatic injury, apoptosis, and oxidative stress induced by hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion during pregnancy. Additionally, SNHG7 was bound directly to miR-34a-5p, and miR-34a-5p inhibitors partially reversed the effect of SNHG7 silencing on models of hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion. Furthermore, YWHAG is a direct target of miR-34a-5p and is negatively regulated by miR-34a-5p mimics. Overexpression of YWHAG effectively eliminated the effect of SNHG7 knockdown on pregnant rats. In summary, this investigation proved that SNHG7 knockdown exacerbated HIR injury after hemorrhagic shock in pregnant rats, and reperfusion might by mediating miR-34a-5p/YWHAG axis, indicating that SNHG7 can serve as a target gene for the treatment of HIR injury caused by hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion during pregnancy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data underlying this article are available in the article. If needed, please contact the corresponding author. The email address is zhujiangang1@126.com.
References
Say, L., Chou, D., Gemmill, A., Tunçalp, Ö., Moller, A.-B., Daniels, J., Gülmezoglu, A. M., Temmerman, M., & Alkema, L. (2014). Global causes of maternal death: A who systematic analysis. The Lancet Global Health., 2(6), e323–e333. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(14)70227-x
Gravante, D. D., & Venditti, D. (2007). Post-endoscopic polypectomy delayed bleeding concomitant with an abdominoperineal resection: A case report. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences., 11(5), 355–357.
Qin, L.-B., Li, Z.-Y., Li, H., Fan, X.-Q., Liu, H.-G., Dong, X.-M., & Jia, W.-Y. (2018). Inhibitive effects of microrna-34a on protecting against ischemia-reperfusion injury of vital organs in hemorrhagic shock pregnant mice. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 22(6), 1812–1818.
Era, S., Matsunaga, S., Matsumura, H., Murayama, Y., Takai, Y., & Seki, H. (2015). Usefulness of shock indicators for determining the need for blood transfusion after massive obstetric hemorrhage. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research, 41(1), 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/jog.12480
Fontana, R. J., Hayashi, P. H., Gu, J., Reddy, K. R., Barnhart, H., Watkins, P. B., Serrano, J., Lee, W. M., Chalasani, N., Stolz, A., Davern, T., Talwakar, J. A., & Network, D. (2014). Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury is associated with substantial morbidity and mortality within 6 months from onset. Gastroenterology, 147(1), 96–108. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.03.045
Arguello, G., Balboa, E., Arrese, M., & Zanlungo, S. (2015). Recent insights on the role of cholesterol in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1852(9), 1765–1778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.05.015
Chen, R. J., Wu, H. H., & Wang, Y. J. (2015). Strategies to prevent and reverse liver fibrosis in humans and laboratory animals. Archives of Toxicology, 89(10), 1727–1750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1525-6
Gao, Q., Gu, Y., Jiang, Y., Fan, L., Wei, Z., Jin, H., Yang, X., Wang, L., Li, X., Tai, S., Yang, B., & Liu, Y. (2018). Long non-coding Rna Gm2199 rescues liver injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation through the upregulation of Erk1/2. Cell Death & Disease, 9(6), 602. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0595-9
Zhong, P., Xu, J., Yang, D., Shen, Y., Wang, L., Feng, Y., Du, C., Song, Y., Wu, C., Hu, X., & Sun, Y. (2020). Covid-19-associated gastrointestinal and liver injury: Clinical features and potential mechanisms. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 5(1), 256. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00373-7
Kong, X., Duan, Y., Sang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Liang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, N., & Yang, Q. (2019). Lncrna-Cdc6 promotes breast cancer progression and function as cerna to target cdc6 by sponging microrna-215. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(6), 9105–9117. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27587
Wang, L., Cho, K. B., Li, Y., Tao, G., Xie, Z., & Guo, B. (2019). Long noncoding Rna (Lncrna)-mediated competing endogenous Rna networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225758
Cao, H.-L., Li, Z.-J., Huang, P.-L., Yue, Y.-L., & Xi, J.-N. (2019). Lncrna-Rmrp promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer Via Mir-206. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences., 23(3), 1012–1021.
Tang, B., Bao, N., He, G., & Wang, J. (2019). Long noncoding Rna hotair regulates autophagy via the Mir-20b-5p/Atg7 axis in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Gene. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.059
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Li, S., Jiang, W., Li, X., & Lv, J. (2019). Lncrna malat1 cessation antagonizes hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in hepatocytes by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation via the Hmgb1-Tlr4 axis. Molecular Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.04.015
Pei, L. J., Sun, P. J., Ma, K., Guo, Y. Y., Wang, L. Y., & Liu, F. D. (2021). Lncrna-Snhg7 interferes with Mir-34a to de-sensitize gastric cancer cells to cisplatin. Cancer Biomarkers, 30(1), 127–137. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-201621
Zeng, J., Ma, Y.-X., Liu, Z.-H., & Zeng, Y.-L. (2019). Lncrna Snhg7 contributes to cell proliferation, invasion and prognosis of cervical cancer. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences., 23(21), 9277–9285.
Cheng, D., Fan, J., Ma, Y., Zhou, Y., Qin, K., Shi, M., & Yang, J. (2019). Lncrna Snhg7 promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation through Id4 by sponging Mir-342-3p. Cell & Bioscience. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-019-0290-2
Yang, X., Sun, L., Wang, L., Yao, B., Mo, H., & Yang, W. (2019). Lncrna Snhg7 accelerates the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating Mir-122-5p and Rpl4. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109386
Yao, X., Liu, C., Liu, C., Xi, W., Sun, S., & Gao, Z. (2019). Lncrna Snhg7 sponges Mir-425 to promote proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatic carcinoma cells via Wnt/beta-catenin/Emt signalling pathway. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 37(7), 525–533. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3429
Sun, W., Sun, L., Sun, X., & Ma, S. (2021). Long non-coding Rna Snhg7 upregulates Fgf9 to alleviate oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced neuron cell injury in a Mir-134-5p-dependent manner. Metabolic Brain Disease, 36(8), 2483–2494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00852-y
Jonas, S., & Izaurralde, E. (2015). Towards a molecular understanding of microrna-mediated gene silencing. Nature Reviews Genetics, 16(7), 421–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3965
Friedman, R. C., Farh, K. K., Burge, C. B., & Bartel, D. P. (2009). Most mammalian Mrnas are conserved targets of micrornas. Genome Research, 19(1), 92–105. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.082701.108
Xiao, Y., Zhang, S., Li, Q., Liu, Z., Mai, W., Chen, W., Lei, J., & Hu, H. (2019). Mir-219a-5p ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via impairing Tp53bp2. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 64(8), 2177–2186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05535-4
Hao, W., Zhao, Z. H., Meng, Q. T., Tie, M. E., Lei, S. Q., & Xia, Z. Y. (2017). Propofol protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via Mir-133a-5p regulating the expression of Mapk6. Cell Biology International, 41(5), 495–504. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10745
Zhang, F.-M., Zheng, W.-H., & Wang, H.-J. (2020). Mir-34a-5p inhibition attenuates Lps-induced endothelial cell injury by targeting foxm1. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences., 24(20), 10829–10838.
Li, C., Wang, K., Guo, L., Sun, H., Huang, H., Lin, X., & Li, Q. (2018). Inhibition of Mir-34a-5p alleviates hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by enhancing autophagy in steatotic hepatocytes. Biology Open. https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.033290
Aghazadeh, Y., & Papadopoulos, V. (2016). The role of the 14–3-3 protein family in health, disease, and drug development. Drug Discovery Today, 21(2), 278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2015.09.012
Kawamoto, Y., Akiguchi, I., Tomimoto, H., Shirakashi, Y., Honjo, Y., & Budka, H. (2006). Upregulated expression of 14–3-3 proteins in astrocytes from human cerebrovascular ischemic lesions. Stroke, 37(3), 830–835. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000202587.63936.37
Zhou, X. Y., Hu, D. X., Chen, R. Q., Chen, X. Q., Dong, W. L., & Yi, C. L. (2017). 14–3-3 isoforms differentially regulate nfkappab signaling in the brain after ischemia-reperfusion. Neurochemical Research, 42(8), 2354–2362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2255-3
Pei, J., Sun, X., Yang, G., & Zhang, S. (2020). Lncrna Kcnq1ot1 ameliorates the liver injury induced by acetaminophen through the regulation of Mir-122-5p/Ces2 axis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 475(1–2), 107–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03863-y
Liu, J., Yao, L., Zhang, M., Jiang, J., Yang, M., & Wang, Y. (2019). Downregulation of Lncrna-Xist inhibited development of non-small cell lung cancer by activating Mir-335/Sod2/Ros signal pathway mediated pyroptotic cell death. Aging (Albany NY)., 11(18), 7830–7846. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102291
Bian, Z., Ji, W., Xu, B., Huang, W., Jiao, J., Shao, J., & Zhang, X. (2020). The role of long noncoding Rna Snhg7 in human cancers (review). Molecular and Clinical Oncology, 13(5), 45. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2020.2115
Xu, J., Pei, Y., Lu, J., Liang, X., Li, Y., Wang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Lncrna Snhg7 alleviates Il-1beta-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting Mir-214-5p-mediated Ppargc1b signaling pathways. International Immunopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107150
Xu, L., Yu, Y., Sang, R., Li, J., Ge, B., & Zhang, X. (2018). Protective effects of taraxasterol against ethanol-induced liver injury by regulating Cyp2e1/Nrf2/Ho-1 and Nf-Kappab signaling pathways in mice. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8284107
Tian, F., Wang, J., Zhang, Z., & Yang, J. (2020). Lncrna Snhg7/Mir-34a-5p/Syvn1 axis plays a vital role in proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy in osteoarthritis. Biological Research, 53(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-020-00275-6
Zhou, T., Wang, S., Lu, K., & Yin, C. (2020). Long non-coding Rna Snhg7 alleviates oxygen and glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury by modulating Mir-9/Sirt1 Axis in Pc12 cells: Potential role in ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S273421
Pei, Y. F., He, Y., Hu, L. Z., Zhou, B., Xu, H. Y., & Liu, X. Q. (2020). The Crosstalk between Lncrna-Snhg7/Mirna-181/Cbx7 modulates malignant character in lung adenocarcinoma. American Journal of Pathology, 190(6), 1343–1354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.02.011
Yue, X., Dong, C., Ye, Z., Zhu, L., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Mo, F., Li, Z., & Pan, B. (2021). Lncrna Snhg7 sponges Mir-449a to promote pituitary adenomas progression. Metabolic Brain Disease, 36(1), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00611-5
Zhou, X., Wang, Z., Xu, B., Ji, N., Meng, P., Gu, L., & Li, Y. (2021). Long non-coding Rna norad protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury induced brain damage, cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating Mir-30a-5p/Ywhag. Bioengineered, 12(2), 9174–9188. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1995115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, L., Tang, J., Zhu, S. et al. LncRNA SNHG7 Knockdown Aggravates Hepatic Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury and Promotes Apoptosis in Hemorrhagic Shock Pregnant Rats by Modulating miR-34a-5p/YWHAG Axis. Mol Biotechnol 65, 983–996 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00613-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00613-x