Abstract
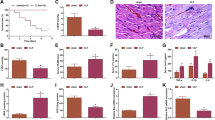
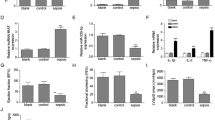
The heart is one of the most common organs involved in sepsis-induced organ dysfunction and about 50% septic patients complicated with myocardial injury. So far, the molecular mechanisms underlying sepsis-induced cardiac damage remain unclear. In this study we aimed to evaluate the effect of miR-642a on sepsis-induced cardiac injury in vitro and explore the possible lncRNA-microRNA mechanism. We first downloaded GSE101639 to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in sepsis. The expression of miR-642a in LPS-induced H9C2 cells was detected by qRT-PCR. MTT assay, cell migration, flow cytometry analysis, ELISA, qRT-PCR and Western blotting analysis were applied to evaluating the effect of miR-642a mimic on LPS-induced H9C2 cells. The bioinformatics analysis and the rescue experiment were devoted to the underlying mechanism. The results showed miR-642a expression was decreased in septic patients and LPS-induced H9C2 cells. Besides, MiR-642a mimic promoted cell viability and migration, inhibited cell apoptosis of LPS-induced H9C2 cells. Bioinformatics analysis showed miR-642a directly targets with 3’-UTR of ROCK1. Moreover, LUCAT1 regulated ROCK1 expression act as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-642a. Our data demonstrated that lncRNA LUCAT1 could function via sponging miR-642a to regulate ROCK1 expression in LPS-induced H9C2 cells. And knockdown of lncRNA LUCAT1 could suppress LPS-induced cardiac injury in vitro.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen T, Zhu C, Ye C (2020) LncRNA CYTOR attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating miR-24/XIAP. Cell Biochem Funct 38:976–985
Chousterman BG, Swirski FK, Weber GF (2017) Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin Immunopathol 39:517–528
Feng H, Chen J, Wang H, Cheng Y, Zou Z, Zhong Q, Xu J (2017) Roflumilast reverses polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver damage by inhibiting inflammation in mice. Lab Invest 97:1008–1019
Frencken JF, Donker DW, Spitoni C, Koster-Brouwer ME, Soliman IW, Ong DSY, Horn J, van der Poll T, van Klei WA, Bonten MJM, Cremer OL (2018) Myocardial injury in patients with sepsis and its association with long-term outcome. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 11:e004040
Gong J, Guan L, Tian P, Li C, Zhang Y (2018) Rho kinase type 1 (ROCK1) promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in corneal epithelial cells by activating toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated signaling. Med Sci Monit 24:3514–3523
Ishizaki T, Maekawa M, Fujisawa K, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Fujita A, Watanabe N, Saito Y, Kakizuka A, Morii N, Narumiya S (1996) The small GTP-binding protein Rho binds to and activates a 160 kDa Ser/Thr protein kinase homologous to myotonic dystrophy kinase. EMBO J 15:1885–1893
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K, Yasuda T (2016) Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care 4:22
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W (2010) The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet 11:597–610
Liu A, Wang W, Fang H, Yang Y, Jiang X, Liu S, Hu J, Hu Q, Dahmen U, Dirsch O (2015) Baicalein protects against polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury via inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 748:45–53
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Makic MBF, Bridges E (2018) CE: Managing sepsis and septic shock: current guidelines and definitions. Am J Nurs 118:34–39
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2009) Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10:155–159
Monterde-Cruz L, Ramirez-Salazar EG, Rico-Martinez G, Linares-Gonzalez LM, Guzman-Gonzalez R, Delgado-Cedillo E, Estrada-Villasenor E, Valdes-Flores M, Velazquez-Cruz R, Hidalgo-Bravo A (2018) Circulating miR-215-5p and miR-642a-5p as potential biomarker for diagnosis of osteosarcoma in Mexican population. Hum Cell 31:292–299
Ouyang H, Tan Y, Li Q, Xia F, Xiao X, Zheng S, Lu J, Zhong J, Hu Y (2020) MicroRNA-208-5p regulates myocardial injury of sepsis mice via targeting SOCS2-mediated NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 81:106204
Perner A, Cecconi M, Cronhjort M, Darmon M, Jakob SM, Pettila V, van der Horst ICC (2018) Expert statement for the management of hypovolemia in sepsis. Intensive Care Med 44:791–798
Rigoutsos I, Furnari F (2010) Gene-expression forum: decoy for microRNAs. Nature 465:1016–1017
Rudiger A, Singer M (2007) Mechanisms of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med 35:1599–1608
Sergi C, Shen F, Lim DW, Liu W, Zhang M, Chiu B, Anand V, Sun Z (2017) Cardiovascular dysfunction in sepsis at the dawn of emerging mediators. Biomed Pharmacother 95:153–160
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC (2016) The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA 315:801–810
Sun F, Yuan W, Wu H, Chen G, Sun Y, Yuan L, Zhang W, Lei M (2020) LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating miR-192-5p/XIAP axis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 245:620–630
Thai P, Statt S, Chen CH, Liang E, Campbell C, Wu R (2013) Characterization of a novel long noncoding RNA, SCAL1, induced by cigarette smoke and elevated in lung cancer cell lines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 49:204–211
Wang KC, Chang HY (2011) Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 43:904–914
Wang X, Yu Y (2018) MiR-146b protect against sepsis induced mice myocardial injury through inhibition of Notch1. J Mol Histol 49:411–417
Wang X, Song Z, Hu B, Chen Z, Chen F, Cao C (2021) MicroRNA642a5p inhibits colon cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting collagen type I alpha1. Oncol Rep 45:933–944
Yin Y, Yang ZF, Li XH, Zhou LQ, Zhang YJ, Yang B (2019) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 reverses high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte injury via targeting CYP11B2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:8560–8565
Yu Z, Du Y, Li H, Huang J, Jiang D, Fan J, Shen Y, Zhang L, Yu X, Xu N, Ke Q (2020) miR-642 serves as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SEMA4C and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 20:74
Zhai Y, Ding N (2018) MicroRNA-194 participates in endotoxemia induced myocardial injury via promoting apoptosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:2077–2083
Zhang J, Xiang J, Liu T, Wang X, Tang Y, Liang Y (2020) miR-495 targets ROCK1 to inhibit lipopolysaccharides-induced WI-38 cells apoptosis and inflammation. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36:607–614
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Tianjin Union Medical Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Xin, S., Yang, R. et al. Knockdown of lncRNA LUCAT1 attenuates sepsis‑induced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-642a. Mamm Genome 32, 457–465 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-021-09890-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-021-09890-4