Abstract
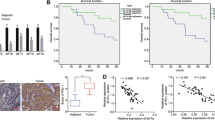
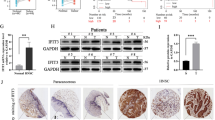
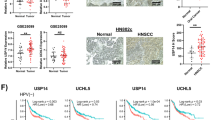
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a lethal malignancy. Given the essential roles of E3 ligases in cancer immunotherapies, this paper explored the effect of E3 ubiquitin ligase ring finger protein 125 (RNF125) on immune escape in HNSCC. After delivering overexpressed (oe)-RNF125, interferon-gamma, or oe-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) into HNSCC cells and cell culture with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-labeled CD8+ T cells, RNF125 and PD-L1 levels were determined via RT-qPCR and Western blot, with HNSCC cell behaviors assessed via colony formation assay, Transwell assays and flow cytometry, and inflammatory factors measured via ELISA. PD-L1 ubiquitination level and PD-L1’s interaction with RNF125 were analyzed via co-immunoprecipitation. The in vivo action of RNF125 on HNSCC was validated via nude mouse tumorigenicity assay. Briefly, RNF125 was weakly expressed in HNSCC cells. RNF125 overexpression inhibited immune escape of HNSCC cells, evidenced by decreased TSCCA cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, increased CD8+ T cell proliferation, and elevated IL-2 and TNF-α levels. RNF125 downregulated PD-L1 in TSCCA cells and facilitated PD-L1 ubiquitinational degradation. PD-L1 overexpression partially abated RNF125-mediated suppression on TSCCA cell immune escape. Moreover, RNF125 suppressed tumorigenesis and tumor growth in vivo. Overall, RNF125 promoted PD-L1 ubiquitinational degradation, hence inhibiting immune escape in HNSCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Johnson, D. E., Burtness, B., Leemans, C. R., Lui, V. W. Y., Bauman, J. E., & Grandis, J. R. (2020). Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nature Reviews, Disease Primers, 6, 92.
Economopoulou, P., de Bree, R., Kotsantis, I., & Psyrri, A. (2019). Diagnostic tumor markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) in the clinical setting. Frontiers in Oncology, 9, 827.
Vucicevic Boras, V., Fucic, A., Baranovic, S., Blivajs, I., Milenovic, M., Bisof, V., Rakusic, Z., Ceppi, M., & Bruzzone, M. (2019). Environmental and behavioural head and neck cancer risk factors. Central European Journal of Public Health, 27, 106–109.
Cohen, N., Fedewa, S., & Chen, A. Y. (2018). Epidemiology and demographics of the head and neck cancer population. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America, 30, 381–395.
Li, H., Liu, Y. T., Chen, L., Zhou, J. J., Chen, D. R., Li, S. J., & Sun, Z. J. (2021). CMTM4 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition and PD‐L1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 60, 556–566.
Wei, G. G., Gao, L., Tang, Z. Y., Lin, P., Liang, L. B., Zeng, J. J., Chen, G., & Zhang, L. C. (2019). Drug repositioning in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An integrated pathway analysis based on connectivity map and differential gene expression. Pathology, Research and Practice, 215, 152378.
Tang, S., Ning, Q., Yang, L., Mo, Z., & Tang, S. (2020). Mechanisms of immune escape in the cancer immune cycle. International Immunopharmacology, 86, 106700.
Angell, T. E., Lechner, M. G., Jang, J. K., Correa, A. J., LoPresti, J. S., & Epstein, A. L. (2014). BRAFV600E in papillary thyroid carcinoma is associated with increased programmed death ligand 1 expression and suppressive immune cell infiltration. Thyroid, 24, 1385–1393.
Zhi, J., Zhang, P., Zhang, W., Ruan, X., Tian, M., Guo, S., Zhang, W., Zheng, X., Zhao, L., & Gao, M. (2021). Inhibition of BRAF sensitizes thyroid carcinoma to immunotherapy by enhancing tsMHCII-mediated immune recognition. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 106, 91–107.
Kythreotou, A., Siddique, A., Mauri, F. A., Bower, M., & Pinato, D. J. (2018). PD-L1. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 71, 189–194.
Svajger, U., Tesic, N., & Rozman, P. (2021). Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays a vital part in DC tolerogenicity induced by IFN-γ. International Immunopharmacology, 99, 107978.
Hsieh, C. Y., Lien, M. Y., Lin, C. Y., Lo, W. J., Hua, C. H., Chang, W. C., Chiu, C. F., & Lin, C. C. (2022). Rituximab in combination with gemcitabine plus cisplatin in patients with recurrent and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a phase I trial. BMC Cancer, 22, 169.
Zhou, A. L., Wang, X., Yu, W., Yang, L., Wei, F., Sun, Q., Wang, Y., Kou, F., Dong, R., Ren, X., & Zhang, X. (2020). Expression level of PD-L1 is involved in ALDH1A1-mediated poor prognosis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Pathology, Research and Practice, 216, 153093.
Yu, D., Liu, X., Han, G., Liu, Y., Zhao, X., Wang, D., Bian, X., Gu, T., & Wen, L. (2019). The let-7 family of microRNAs suppresses immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by promoting PD-L1 degradation. Cell Communication and Signaling: CCS, 17, 173.
Yin, G., Guo, W., Duan, H., & Huang, Z. (2021). Role of PD‐1/PD‐L1 inhibitors in the treatment of recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clinical Otolaryngology, 46, 1013–1020.
Shen, B., Huang, D., Ramsey, A. J., Ig-Izevbekhai, K., Zhang, K., Lajud, S. A., O’Malley, B. W., & Li, D. (2020). PD-L1 and MRN synergy in platinum-based chemoresistance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. British Journal of Cancer, 122, 640–647.
Li, J., Yu, T., Yan, M., Zhang, X., Liao, L., Zhu, M., Lin, H., Pan, H., & Yao, M. (2019). DCUN1D1 facilitates tumor metastasis by activating FAK signaling and up-regulates PD-L1 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Experimental Cell Research, 374, 304–314.
De, S., Holvey-Bates, E. G., Mahen, K., Willard, B., & Stark, G. R. (2021). The ubiquitin E3 ligase FBXO22 degrades PD-L1 and sensitizes cancer cells to DNA damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(47), e2112674118.
Ho, S. R., Lee, Y. C., Ittmann, M. M., Lin, F. T., Chan, K. S., & Lin, W. C. (2021). RNF144A deficiency promotes PD-L1 protein stabilization and carcinogen-induced bladder tumorigenesis. Cancer Letters, 520, 344–360.
Giannini, A. L., Gao, Y., & Bijlmakers, M. J. (2008). T-cell regulator RNF125/TRAC-1 belongs to a novel family of ubiquitin ligases with zinc fingers and a ubiquitin-binding domain. The Biochemical Journal, 410, 101–111.
Zhao, H., Li, C. C., Pardo, J., Chu, P. C., Liao, C. X., Huang, J., Dong, J. G., Zhou, X., Huang, Q., Huang, B., Bennett, M. K., Molineaux, S. M., Lu, H., Daniel-Issakani, S., Payan, D. G., & Masuda, E. S. (2005). A novel E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAC-1 positively regulates T cell activation. The Journal of Immunology, 174, 5288–5297.
Tang, J., Tu, S., Lin, G., Guo, H., Yan, C., Liu, Q., Huang, L., Tang, N., Xiao, Y., Pope, R. M., Rajaram, M. V. S., Amer, A. O., Ahmer, B. M., Gunn, J. S., Wozniak, D. J., Tao, L., Coppola, V., Zhang, L., Langdon, W. Y., et al. (2020). Sequential ubiquitination of NLRP3 by RNF125 and Cbl-b limits inflammasome activation and endotoxemia. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 217(4).
Kim, H., Frederick, D. T., Levesque, M. P., Cooper, Z. A., Feng, Y., Krepler, C., Brill, L., Samuels, Y., Hayward, N. K., Perlina, A., Piris, A., Zhang, T., Halaban, R., Herlyn, M. M., Brown, K. M., Wargo, J. A., Dummer, R., Flaherty, K. T., & Ronai, Z. A. (2015). Downregulation of the ubiquitin ligase RNF125 underlies resistance of melanoma cells to BRAF inhibitors via JAK1 deregulation. Cell Reports, 11, 1458–1473.
Li, T., Qin, Y., Zhen, Z., Shen, H., Cong, T., Schiferle, E., & Xiao, S. (2019). Long non‐coding RNA HOTAIR/microRNA‐206 sponge regulates STC2 and further influences cell biological functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Proliferation, 52, e12651.
Kang, S. H., Keam, B., Ahn, Y. O., Park, H. R., Kim, M., Kim, T. M., Kim, D. W., & Heo, D. S. (2019). Inhibition of MEK with trametinib enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 inhibitor by regulating anti-tumor immunity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology, 8, e1515057.
Luo, Y., Hao, T., Zhang, J., Zhang, M., Sun, P., & Wu, L. (2019). MicroRNA-592 suppresses the malignant phenotypes of thyroid cancer by regulating lncRNA NEAT1 and downregulating NOVA1. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 44, 1172–1182.
Li, P., Luo, X., Xie, Y., Li, P., Hu, F., Chu, J., Chen, X., Song, W., Wang, A., Tian, G., & Gu, X. (2020). GC-derived EVs enriched with microRNA-675-3p contribute to the MAPK/PD-L1-mediated tumor immune escape by targeting CXXC4. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids, 22, 615–626.
Tian, P., Wei, J. X., Li, J., Ren, J. K., & Yang, J. J. (2021). LncRNA SNHG1 regulates immune escape of renal cell carcinoma by targeting miR‐129‐3p to activate STAT3 and PD‐L1. Cell Biology International, 45, 1546–1560.
Qian, M., Ling, W., & Ruan, Z. (2020). Long non-coding RNA SNHG12 promotes immune escape of ovarian cancer cells through their crosstalk with M2 macrophages. Aging, 12, 17122–17136.
Yuan, L., Ye, J., & Fan, D. (2020). The B7-H4 gene induces immune escape partly via upregulating the PD-1/Stat3 pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Human Immunology, 81, 254–261.
Zhu, Y., Zhang, C., Huang, M., Lin, J., Fan, X., & Ni, T. (2021). TRIM26 induces ferroptosis to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation and mitigate liver fibrosis through mediating SLC7A11 ubiquitination. Front Cell Dev Biol, 9, 644901.
Liu, S., Yang, N., Wang, L., Wei, B., Chen, J., & Gao, Y. (2020). lncRNA SNHG11 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and migration via activation of Wnt/β‐catenin signaling pathway. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 235, 7541–7553.
Sharp, M. F., Bythell-Douglas, R., Deans, A. J., & Crismani, W. (2021). The Fanconi anemia ubiquitin E3 ligase complex as an anti-cancer target. Molecular Cell, 81, 2278–2289.
Jiang, X., Wang, J., Deng, X., Xiong, F., Ge, J., Xiang, B., Wu, X., Ma, J., Zhou, M., Li, X., Li, Y., Li, G., Xiong, W., Guo, C., & Zeng, Z. (2019). Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Molecular Cancer, 18, 10.
Qian, J., Wang, C., Wang, B., Yang, J., Wang, Y., Luo, F., Xu, J., Zhao, C., Liu, R., & Chu, Y. (2018). The IFN-γ/PD-L1 axis between T cells and tumor microenvironment: hints for glioma anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 15, 290.
Cousin, N., Cap, S., Dihr, M., Tacconi, C., Detmar, M., & Dieterich, L. C. (2021). Lymphatic PD-L1 expression restricts tumor-specific CD8+ T-cell responses. Cancer Research, 81, 4133–4144.
Clin, B., Gramond, C., Thaon, I., Brochard, P., Delva, F., Chammings, S., Gislard, A., Laurent, F., Paris, C., Lacourt, A., & Pairon, J. C. (2022). Head and neck cancer and asbestos exposure. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 79, 690–696.
Wang, G., Zhang, M., Cheng, M., Wang, X., Li, K., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Chen, S., Chen, J., Xiong, G., Xu, X., Wang, C., & Chen, D. (2021). Tumor microenvironment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Functions and regulatory mechanisms. Cancer Letters, 507, 55–69.
Li, H., Yang, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, F., Wang, J., Wu, Z., Wanyan, C., Meng, Q., Gao, W., Yang, X., & Wei, J. (2022). LINC01123 promotes immune escape by sponging miR-214-3p to regulate B7–H3 in head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma. Cell Death & Disease, 13, 109.
Seliger, B., Massa, C., Yang, B., Bethmann, D., Kappler, M., Eckert, A. W., & Wickenhauser, C. (2020). Immune escape mechanisms and their clinical relevance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7032.
Fujita, Y., Tinoco, R., Li, Y., Senft, D., & Ronai, Z. A. (2019). Ubiquitin ligases in cancer immunotherapy–balancing antitumor and autoimmunity. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 25, 428–443.
Yang, L., Zhou, B., Li, X., Lu, Z., Li, W., Huo, X., & Miao, Z. (2015). RNF125 is a ubiquitin-protein ligase that promotes p53 degradation. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 35, 237–245.
Veigas, F., Mahmoud, Y. D., Merlo, J., Rinflerch, A., Rabinovich, G. A., & Girotti, M. R. (2021). Immune checkpoints pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers, 13(5), 1018.
Gajewski, T. F., Schreiber, H., & Fu, Y. X. (2013). Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nature Immunology, 14, 1014–1022.
Fu, C., & Jiang, A. (2018). Dendritic cells and CD8 T cell immunity in tumor microenvironment. Frontiers in Immunology, 9, 3059.
Yao, L., Xu, L., Zhou, L., Wu, S., Zou, W., Chen, M., Chen, J., & Peng, H. (2021). Toxoplasma gondii Type-I ROP18 targeting human E3 ligase TRIM21 for immune escape. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 9, 685913.
Li, K., Zheng, X., Tang, H., Zang, Y. S., Zeng, C., Liu, X., Shen, Y., Pang, Y., Wang, S., Xie, F., Lu, X., Luo, Y., Li, Z., Bi, W., Jia, X., Huang, T., Wei, R., Huang, K., Chen, Z., et al. (2021). E3 ligase MKRN3 is a tumor suppressor regulating PABPC1 ubiquitination in non–small cell lung cancer. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 218(8), e20210151.
Chen, D., Wang, Y., Lu, R., Jiang, X., Chen, X., Meng, N., & Yan, G. R. (2020). E3 ligase ZFP91 inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism Reprogramming by regulating PKM splicing. Theranostics, 10(19), 8558.
Peng, R., Cao, J., Su, B. B., Bai, X. S., Jin, X., Wang, A. Q., Wang, Q., Liu, R. J., Jiang, G. Q., Jin, S. J., Zhang, C., & Bai, D. S. (2022). Down-regulation of circPTTG1IP induces hepatocellular carcinoma development via miR-16-5p/RNF125/JAK1 axis. Cancer Letters, 543, 215778.
Wang, Q., Cao, T., Zhang, X., Hui, J., Wang, C., Zhang, W., Wang, P., Zhou, Y., & Han, S. (2022). ATXN2-mediated PI3K/AKT activation confers gastric cancer chemoresistance and attenuates CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. Journal of Immunology Research, 2022, 6863240.
Cheng, T., Xu, M., Zhang, H., Lu, B., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., & Huang, J. (2022). KLHDC8A expression in association with macrophage infiltration and oxidative stress predicts unfavorable prognosis for glioma. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 2694377.
Wu, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, X., He, Z., Shan, B., Zeng, Q., Zhao, Q., Zhu, H., Liao, H., Cen, X., Xu, X., Zhang, M., Hou, T., Wang, Z., Yan, H., Yang, S., Sun, Y., Chen, Y., Wu, R., et al. (2021). ARIH1 signaling promotes anti-tumor immunity by targeting PD-L1 for proteasomal degradation. Nature Communications, 12, 2346.
Gao, Y., Yang, J., Cai, Y., Fu, S., Zhang, N., Fu, X., & Li, L. (2018). IFN‐γ‐mediated inhibition of lung cancer correlates with PD‐L1 expression and is regulated by PI3K‐AKT signaling. International Journal of Cancer, 143, 931–943.
Liu, W., Liu, R., Yuan, R., & Wang, X. (2021). Regulates PD-L1 expression to enhance anti-tumor immunity in NSCLC via targeting STAT3. Molecular Biotechnology, 63, 1268–1279.
Gou, Q., Dong, C., Xu, H., Khan, B., Jin, J., Liu, Q., Shi, J., & Hou, Y. (2020). PD-L1 degradation pathway and immunotherapy for cancer. Cell Death & Disease, 11, 955.
Kim, D. H., Kim, H., Choi, Y. J., Kim, S. Y., Lee, J. E., Sung, K. J., Sung, Y. H., Pack, C. G., Jung, M. K., Han, B., Kim, K., Kim, W. S., Nam, S. J., Choi, C. M., Yun, M., Lee, J. C., & Rho, J. K. (2019). Exosomal PD-L1 promotes tumor growth through immune escape in non-small cell lung cancer. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 51, 1–13.
Eichberger, J., Schulz, D., Pscheidl, K., Fiedler, M., Reichert, T. E., Bauer, R. J., & Ettl, T. (2020). PD-L1 influences cell spreading, migration and invasion in head and neck cancer cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8089.
Zhou, B., Yan, J., Guo, L., Zhang, B., Liu, S., Yu, M., Chen, Z., Zhang, K., Zhang, W., Li, X., Xu, Y., Xiao, Y., Zhou, J., Fan, J., Hung, M. C., Li, H., & Ye, Q. (2020). Hepatoma cell-intrinsic TLR9 activation induces immune escape through PD-L1 upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics, 10, 6530–6543.
Wang, S., Yao, F., Lu, X., Li, Q., Su, Z., Lee, J. H., Wang, C., & Du, L. (2019). Temozolomide promotes immune escape of GBM cells via upregulating PD-L1. American Journal of Cancer Research, 9, 1161–1171.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The funding body did not participate in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CHJ is guarantor of integrity of the entire study and responsible for study concepts, manuscript review; LLH is responsible for study design, definition of intellectual content, data analysis, manuscript preparation; SX is responsible for literature research, experimental studies; WQW is responsible for clinical studies, manuscript editing; QZ is responsible for data acquisition; FL is responsible for statistical analysis; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interests in this study.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
The animal-associated experimental procedures were ratified by the ethics committee for animal welfare at Hunan Cancer Hospital (Approval number: 2022-085). Significant efforts were contributed to the reduction of animal number and suffering. The animal experiments have been carried out in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., He, L., Xiao, S. et al. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase RNF125 Suppresses Immune Escape in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating PD-L1 Expression. Mol Biotechnol 65, 891–903 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00587-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00587-w