Abstract
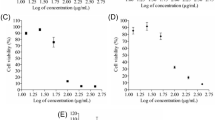
Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule (EpCAM) is overexpressed in a variety of cancers such as colon, stomach, pancreas, and prostate adenocarcinomas. Inhibition of EpCAM is considered as a potential target for cancer therapy. In current study, anti-EpCAM immunotoxin (α-EpCAM IT) was developed using genetic fusion of α-EpCAM single domain antibody (nanobody) (α-EpCAM Nb) to truncated form of diphtheria toxin. The expression of recombinant α-EpCAM IT was induced by Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and confirmed by SDS-PAGE and western blot. Recombinant α-EpCAM IT was purified from the inclusion bodies and refolded using urea gradient procedure. The cytotoxicity and apoptosis activity of α-EpCAM IT on EpCAM over-expressing (MCF7), low-expressing (HEK293), and no-expressing (HUVEC) cells were evaluated by 3–4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl (MTT) assay and annexin V-FITC-PI assay as well. In addition, anti-tumor activity of α-EpCAM IT was evaluated on nude mice bearing MCF7 tumor cells. Results showed success expression and purification of α-EpCAM IT. The α-EpCAM IT showed time and dose-dependent anti-proliferative activity on MCF-7 cells. However, α-EpCAM IT did not show any anti-proliferative activity on HEK293 and HUVEC cells as well. In addition, the annexin V-FITC-PI assay results showed that α-EpCAM IT significantly increased apoptotic rate in MCF-7 cells with no effect on HEK293 and HUVEC as well. Moreover, α-EpCAM IT significantly reduced tumor size in vivo study. The achieved results indicate the potential of designing α-EpCAM IT as a novel therapeutic for cancer therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao, M.-Y., Lai, J.-K., Kuo, M.Y.-P., Lu, R.-M., Lin, C.-W., Cheng, P.-C., et al. (2015). An anti-EpCAM antibody EpAb2–6 for the treatment of colon cancer. Oncotarget, 6(28), 24947.
Spizzo, G., Fong, D., Wurm, M., Ensinger, C., Obrist, P., Hofer, C., et al. (2011). EpCAM expression in primary tumour tissues and metastases: An immunohistochemical analysis. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 64(5), 415–420.
Yamashita, T., Budhu, A., Forgues, M., & Wang, X. W. (2007). Activation of hepatic stem cell marker EpCAM by Wnt–β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Research, 67(22), 10831–10839.
Riesenberg, R., Buchner, A., Pohla, H., & Lindhofer, H. (2001). Lysis of prostate carcinoma cells by trifunctional bispecific antibodies (αEpCAM× αCD3). Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry, 49(7), 911–917.
Fischer, R., Köhler, K., Fotin-Mleczek, M., & Brock, R. (2004). A stepwise dissection of the intracellular fate of cationic cell-penetrating peptides. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(13), 12625–12635.
Khalil, I. A., Kogure, K., Futaki, S., & Harashima, H. (2006). High density of octaarginine stimulates macropinocytosis leading to efficient intracellular trafficking for gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(6), 3544–3551.
Kawamura, K. S., Sung, M., Bolewska-Pedyczak, E., & Gariépy, J. (2006). Probing the impact of valency on the routing of arginine-rich peptides into eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry, 45(4), 1116–1127.
Richard, J. P., Melikov, K., Brooks, H., Prevot, P., Lebleu, B., & Chernomordik, L. V. (2005). Cellular uptake of unconjugated TAT peptide involves clathrin-dependent endocytosis and heparan sulfate receptors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(15), 15300–15306.
Wadia, J. S., Stan, R. V., & Dowdy, S. F. (2004). Transducible TAT-HA fusogenic peptide enhances escape of TAT-fusion proteins after lipid raft macropinocytosis. Nature Medicine, 10(3), 310–315.
Beilhartz, G. L., Sugiman-Marangos, S. N., & Melnyk, R. A. (2017). Repurposing bacterial toxins for intracellular delivery of therapeutic proteins. Biochemical Pharmacology, 142, 13–20.
Holmes, R. K. (2000). Biology and molecular epidemiology of diphtheria toxin and the tox gene. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 181, S156–S167.
Bennett, M., & Eisenberg, D. (1994). Refined structure of monomelic diphtheria toxin at 2.3 Å resolution. Protein Science, 3(9), 1464–1475.
Collier, R. (2001). Understanding the mode of action of diphtheria toxin: A perspective on progress during the 20th century. Toxicon, 39(11), 1793–1803.
Shapira, A., & Benhar, I. (2010). Toxin-based therapeutic approaches. Toxins, 2(11), 2519–2583.
Steeland, S., Vandenbroucke, R. E., & Libert, C. (2016). Nanobodies as therapeutics: Big opportunities for small antibodies. Drug Discovery Today, 21(7), 1076–1113.
Dumoulin, M., Conrath, K., Van Meirhaeghe, A., Meersman, F., Heremans, K., Frenken, L. G., et al. (2002). Single-domain antibody fragments with high conformational stability. Protein Science, 11(3), 500–515.
Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Behdani, M., Rahimpour, A., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., Poshang-Bagheri, K., & Shahbazzadeh, D. (2015). Selection and characterization of specific nanobody against human immunoglobulin G. Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy, 34(3), 201–205.
Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Behdani, M., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., & Shahbazzadeh, D. (2016). Production and characterization of novel camel single domain antibody targeting mouse vascular endothelial growth factor. Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy, 35(3), 167–171.
Farnoodian, M., Wang, S., Dietz, J., Nickells, R. W., Sorenson, C. M., & Sheibani, N. (2017). Negative regulators of angiogenesis: Important targets for treatment of exudative AMD. Clinical Science, 131(15), 1763–1780.
Alirahimi, E., Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Shahbazzadeh, D., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., Chafi, M. H., Sotoudeh, N., et al. (2018). Nanobodies as novel therapeutic agents in envenomation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 1862(12), 2955–2965.
Crawford, T. N., Alfaro, D. V., III., Kerrison, J. B., & Jablon, E. P. (2009). Diabetic retinopathy and angiogenesis. Current Diabetes Reviews, 5(1), 8–13.
Alirahimi, E., Ashkiyan, A., Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Azadmanesh, K., Hosseininejad-Chafi, M., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., et al. (2017). Intrabody targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 mediates downregulation of surface localization. Cancer Gene Therapy, 24(1), 33–37.
Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Muyldermans, S., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., & Behdani, M. (2018). Design of a humanized anti vascular endothelial growth factor nanobody and evaluation of its in vitro function. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 21(3), 260.
Bagheri, M., Babaei, E., Shahbazzadeh, D., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., Alirahimi, E., Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., et al. (2017). Development of a recombinant camelid specific diabody against the heminecrolysin fraction of Hemiscorpius lepturus scorpion. Toxin Reviews, 36(1), 7–11.
Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Behdani, M., Bagheri, K. P., Anbouhi, M. H., Abolhassani, M., Khanahmad, H., et al. (2014). Expression and purification of functional human vascular endothelial growth factor-a121; the most important angiogenesis factor. Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 4(4), 323.
Sadeghi, A., Behdani, M., Muyldermans, S., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., & Kazemi-Lomedasht, F. (2020). Development of a mono-specific anti-VEGF bivalent nanobody with extended plasma half-life for treatment of pathologic neovascularization. Drug Testing and Analysis, 12(1), 92–100.
Karami, E., Sabatier, J.-M., Behdani, M., Irani, S., & Kazemi-Lomedasht, F. (2020). A nanobody-derived mimotope against VEGF inhibits cancer angiogenesis. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 35(1), 1233–1239.
Beatty, J. D., Beatty, B. G., & Vlahos, W. G. (1987). Measurement of monoclonal-antibody affinity by noncompetitive enzyme-immunoassay. Journal of Immunological Methods, 100(1–2), 173–179.
Cohen, M. H., Shen, Y. L., Keegan, P., & Pazdur, R. (2009). FDA drug approval summary: Bevacizumab (Avastin®) as treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. The Oncologist, 14(11), 1131–1138.
Ahadi, M., Ghasemian, H., Behdani, M., & Kazemi-Lomedasht, F. (2019). Oligoclonal selection of nanobodies targeting vascular endothelial growth factor. Journal of Immunotoxicology, 16(1), 34–42.
Naderi, S., Roshan, R., Ghaderi, H., Behdani, M., Mahmoudi, S., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., et al. (2020). Selection and characterization of specific nanobody against neuropilin-1 for inhibition of angiogenesis. Molecular Immunology, 128, 56–63.
Roshan, R., Naderi, S., Behdani, M., Cohan, R. A., Ghaderi, H., Shokrgozar, M. A., et al. (2021). Isolation and characterization of nanobodies against epithelial cell adhesion molecule as novel theranostic agents for cancer therapy. Molecular Immunology, 129, 70–77.
Kazemi-Lomedasht, F., Pooshang-Bagheri, K., Habibi-Anbouhi, M., Hajizadeh-Safar, E., Shahbazzadeh, D., Mirzahosseini, H., et al. (2017). In vivo immunotherapy of lung cancer using cross-species reactive vascular endothelial growth factor nanobodies. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 20(5), 489.
Jamnani, F. R., Rahbarizadeh, F., Shokrgozar, M. A., Ahmadvand, D., Mahboudi, F., & Sharifzadeh, Z. (2012). Targeting high affinity and epitope-distinct oligoclonal nanobodies to HER2 over-expressing tumor cells. Experimental Cell Research, 318(10), 1112–1124.
Van Der Gun, B., Huisman, C., Stolzenburg, S., Kazemier, H., Ruiters, M., Blancafort, P., et al. (2013). Bidirectional modulation of endogenous EpCAM expression to unravel its function in ovarian cancer. British Journal of Cancer, 108(4), 881–886.
Homayouni, V., Ganjalikhani-Hakemi, M., Rezaei, A., Khanahmad, H., Behdani, M., & Lomedasht, F. K. (2016). Preparation and characterization of a novel nanobody against T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-3 (TIM-3). Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 19(11), 1201.
Shafiee, F., Aucoin, M. G., & Jahanian, N. A. (2019). Targeted diphtheria toxin based therapy: A review article. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 2340.
Simon, N., & FitzGerald, D. (2016). Immunotoxin therapies for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent cancers. Toxins, 8(5), 137.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Pasteur Institute of Iran
Funding
This study was funded by Pasteur Institute of Iran (Grant Number BD-9470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roshan, R., Naderi, S., Behdani, M. et al. A Novel Immunotoxin Targeting Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Using Single Domain Antibody Fused to Diphtheria Toxin. Mol Biotechnol 65, 637–644 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00565-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00565-2