Abstract
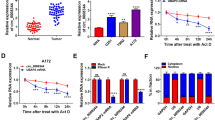
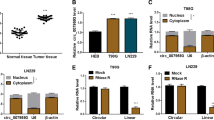
This study was aimed at probing into the regulatory effects of circular RNA (circRNA)_0001982 on glioma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle, and its underlying mechanism. CircRNA expression profile of glioma tissues/normal brain tissues was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and analyzed. Circ_0001982, microRNA (miRNA, miR)-1205, and E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) expressions in glioma tissues and cell lines were quantified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and/or Western blot. Glioma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle were detected employing cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU), scratch-healing, Transwell, and flow cytometry assays, respectively. The targeting relationships between miR-1205 and circ_0001982, and miR-1205 and E2F1 3′UTR were verified using bioinformatics, dual-luciferase reporter experiments, and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. Pearson’s correlation analysis was applied to detect the correlations among circ_0001982, miR-1205, and E2F1 expression levels. Circ_0001982 expression level was increased in glioma tissues and correlated with larger tumor size. Circ_0001982 overexpression enhanced glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and accelerated cell cycle progression while knocking down circ_0001982 exerted opposite effects. Circ_0001982 directly targeted miR-1205, and miR-1205 directly targeted E2F1. Besides, circ_0001982 could up-regulate E2F1 expression via repressing miR-1205 expression. Circ_0001982 accelerates glioma progression by modulating the miR-1205/E2F1 axis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Ohgaki, H., Burger, P., & Kleihues, P. (2014). Definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma–response. Clinical Cancer Research, 20(7), 2013. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-14-0238
Banan, R., & Hartmann, C. (2017). The new WHO 2016 classification of brain tumors-what neurosurgeons need to know. Acta Neurochirurgica. Supplementum, 159(3), 403–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-3062-3
Iwamoto, F. M., Kreisl, T. N., Kim, L., Duic, J. P., Butman, J. A., Albert, P. S., et al. (2010). Phase 2 trial of talampanel, a glutamate receptor inhibitor, for adults with recurrent malignant gliomas. Cancer, 116(7), 1776–1782. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24957
Mrugala, M. M. (2013). Advances and challenges in the treatment of glioblastoma: A clinician’s perspective. Discovery Medicine, 15(83), 221–230.
Chen, L. L., & Yang, L. (2015). Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biology, 12(4), 381–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271
Li, Z., Huang, C., Bao, C., Chen, L., Lin, M., Wang, X., et al. (2015). Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 22(3), 256–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2959
Chen, D., Ma, W., Ke, Z., & Xie, F. (2018). CircRNA hsa_circ_100395 regulates miR-1228/TCF21 pathway to inhibit lung cancer progression. Cell Cycle, 17(16), 2080–2090. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1515553
Li, J., Li, Z., Jiang, P., Peng, M., Zhang, X., Chen, K., et al. (2018). Circular RNA IARS (circ-IARS) secreted by pancreatic cancer cells and located within exosomes regulates endothelial monolayer permeability to promote tumor metastasis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 37(1), 177. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0822-3
Shi, F., Shi, Z., Zhao, Y., & Tian, J. (2019). CircRNA hsa-circ-0014359 promotes glioma progression by regulating miR-153/PI3K signaling. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 510(4), 614–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.019
Deng, Q., Wang, C. J., Hao, R., & Yang, Q. Y. (2020). Circ_0001982 accelerates the progression of colorectal cancer via sponging microRNA-144. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 24(4), 1755–1762. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202002_20352
Tang, Y. Y., Zhao, P., Zou, T. N., Duan, J. J., Zhi, R., Yang, S. Y., et al. (2017). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001982 promotes breast cancer cell carcinogenesis through decreasing miR-143. DNA and Cell Biology, 36(11), 901–908. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2017.3862
Xiong, J., Wang, T., Tang, H., Lv, Z., & Liang, P. (2019). Circular RNA circMAN2B2 facilitates glioma progression by regulating the miR-1205/S100A8 axis. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(12), 22996–23004. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28860
Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, B., Ding, L., Mu, Z., & Li, Y. (2019). Elevation of circular RNA circ-POSTN facilitates cell growth and invasion by sponging miR-1205 in glioma. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120(10), 16567–16574. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28916
He, J., Zhao, Y., Zhao, E., Wang, X., Dong, Z., Chen, Y., et al. (2018). Cancer-testis specific gene OIP5: A downstream gene of E2F1 that promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in glioblastoma by stabilizing E2F1 signaling. Neuro-Oncology, 20(9), 1173–1184. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy037
Blum, R., Nakdimon, I., Goldberg, L., Elkon, R., Shamir, R., Rechavi, G., et al. (2006). E2F1 identified by promoter and biochemical analysis as a central target of glioblastoma cell-cycle arrest in response to Ras inhibition. International Journal of Cancer, 119(3), 527–538. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21735
Patop, I. L., Wüst, S., & Kadener, S. (2019). Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO Journal, 38(16), e100836. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100836
Wang, Y., Liu, J., Ma, J., Sun, T., Zhou, Q., Wang, W., et al. (2019). Exosomal circRNAs: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1041-z
Pamudurti, N. R., Bartok, O., Jens, M., Ashwal-Fluss, R., Stottmeister, C., Ruhe, L., et al. (2017). Translation of CircRNAs. Molecular Cell, 66(1), 9-21.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.021
Zhu, Y. J., Zheng, B., Luo, G. J., Ma, X. K., Lu, X. Y., Lin, X. M., et al. (2019). Circular RNAs negatively regulate cancer stem cells by physically binding FMRP against CCAR1 complex in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics., 9(12), 3526–3540. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.32796
Li, H., Yang, F., Hu, A., Wang, X., Fang, E., Chen, Y., et al. (2019). Therapeutic targeting of circ-CUX1/EWSR1/MAZ axis inhibits glycolysis and neuroblastoma progression. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 11(12), e10835. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201910835
Lu, T. X., & Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 141(4), 1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Shukuya, T., Ghai, V., Amann, J. M., Okimoto, T., Shilo, K., Kim, T. K., et al. (2020). Circulating MicroRNAs and extracellular vesicle-containing microRNAs as response biomarkers of anti-programmed cell death protein 1 or programmed death-ligand 1 therapy in NSCLC. Journal of Thoracic Oncology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2020.05.022
Luo, J. W., Wang, X., Yang, Y., & Mao, Q. (2015). Role of micro-RNA (miRNA) in pathogenesis of glioblastoma. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 19(9), 1630–1639.
Wu, W., Yu, T., Wu, Y., Tian, W., Zhang, J., & Wang, Y. (2019). The miR155HG/miR-185/ANXA2 loop contributes to glioblastoma growth and progression. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 38(1), 133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1132-0
Xu, T. J., Qiu, P., Zhang, Y. B., Yu, S. Y., Xu, G. M., & Yang, W. (2019). MiR-148a inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioblastoma by targeting ITGA9. Human Cell, 32(4), 548–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00279-9
Kent, L. N., & Leone, G. (2019). The broken cycle: E2F dysfunction in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 19(6), 326–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0143-7
Denechaud, P. D., Fajas, L., & Giralt, A. (2017). E2F1, a novel regulator of metabolism. Frontiers in endocrinology., 8, 311. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00311
Ertosun, M. G., Hapil, F. Z., & Osman, N. O. (2016). E2F1 transcription factor and its impact on growth factor and cytokine signaling. Cytokine & growth factor reviews., 31, 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.02.001
Tsantoulis, P. K., & Gorgoulis, V. G. (2005). Involvement of E2F transcription factor family in cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 41(16), 2403–2414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2005.08.005
Alonso, M. M., Alemany, R., Fueyo, J., & Gomez-Manzano, C. (2008). E2F1 in gliomas: A paradigm of oncogene addiction. Cancer Letters, 263(2), 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.001
Meng, X., Zhao, Y., Han, B., Zha, C., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., et al. (2020). Dual functionalized brain-targeting nanoinhibitors restrain temozolomide-resistant glioma via attenuating EGFR and MET signaling pathways. Nature Communications, 11(1), 594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14036-x
Dos Reis, V. L., Pujiz, R. S., Strauss, B. E., & Krieger, J. E. (2010). Knockdown of E2f1 by RNA interference impairs the proliferation of rat cells in vitro. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 33(1), 17–22. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1415-47572009005000104
Yan, H., Chen, X., Li, Y., Fan, L., Tai, Y., Zhou, Y., et al. (2019). MiR-1205 functions as a tumor suppressor by disconnecting the synergy between KRAS and MDM4/E2F1 in non-small cell lung cancer. American Journal of Cancer Research, 9(2), 312–329.
Lin, J., Liao, S., Li, E., Liu, Z., Zheng, R., Wu, X., et al. (2020). circCYFIP2 acts as a sponge of miR-1205 and affects the expression of its target gene E2F1 to regulate gastric cancer metastasis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids., 21, 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.05.007
Acknowledgements
We thank Hubei Yican Health Industry Co., Ltd for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Our study was approved by the Ethics Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Ma, J., Lang, B. et al. Circ_0001982 Up-regulates the Expression of E2F1 by Adsorbing miR-1205 to Facilitate the Progression of Glioma. Mol Biotechnol 65, 466–476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00540-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00540-x