Abstract
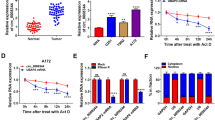
Glioma is a common brain tumor with high mortality. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play crucial roles in tumor occurrence and development. However, the function and molecular basis of circ_0079593 in glioma remain unknown. Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and Western blot were used for expression determination of circ_0079593, microRNA-324-5p (miR-324-5p) and X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), colony formation, flow cytometry, transwell assays, and tube formation assay were employed to evaluate cell functions. Glycolysis was determined via detecting glucose consumption, lactate production and ATP level. The binding relationship between miR-324-5p and circ_0079593 or XBP1 was validated by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. Besides, xenograft assay was applied to test tumor growth in vivo. Circ_0079593 and XBP1 levels were elevated, while miR-324-5p level was declined in glioma. Silencing of circ_0079593 restrained proliferation, mobility, angiogenesis and glycolysis and induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Circ_0079593 accelerated glioma progression via sequestering miR-324-5p, one of the targets of circ_0079593. XBP1 was a target gene of miR-324-5p, and miR-324-5p alleviated the malignant growth of glioma by repressing XBP1. Furthermore, silence of circ_0079593 hindered tumor growth in vivo. Circ_0079593 contributed to the malignant evolution of glioma via modulating miR-324-5p and downstream XBP1 gene, suggesting that circ_0079593 might be a promising therapeutic target for glioma. Circ_0079593 was boosted in glioma. Circ_0079593 depletion restrained glioma progression. Circ_0079593 triggered glioma development via miR-324-5p/XBP1 axis. Circ_0079593 silence suppressed glioma tumorigenesis in vivo.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chen J, Liu T, Wang H, Wang Z, Lv Y, Zhao Y, Yang N, Yuan X (2020a) Elevation in the expression of circ_0079586 predicts poor prognosis and accelerates progression in glioma via interactions with the miR-183-5p/MDM4 signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther 13(5135–5143). https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S234758
Chen S, Chen J, Hua X, Sun Y, Cui R, Sha J, Zhu X (2020b) The emerging role of XBP1 in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 127(110069). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110069
Chen W, Hong L, Hou C, Wang Y, Wang F, Zhang J (2020c) MicroRNA-585 inhibits human glioma cell proliferation by directly targeting MDM2. Cancer Cell Int 20(469). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01528-w
Cheng S, Cheng J (2021) Sevoflurane suppresses glioma tumorigenesis via regulating circ_0079593/miR-633/ROCK1 axis. Brain Res 1767(147543). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147543
Cui X, Wang J, Guo Z, Li M, Li M, Liu S, Liu H, Li W, Yin X, Tao J et al (2018) Emerging function and potential diagnostic value of circular RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer 17(1):123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0877-y
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W (2010) Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 79(351–379). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103
Hao Z, Hu S, Liu Z, Song W, Zhao Y, Li M (2019) Circular RNAs: functions and prospects in glioma. J Mol Neurosci 67(1):72–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1211-2
Janjua TI, Rewatkar P, Ahmed-Cox A, Saeed I, Mansfeld FM, Kulshreshtha R, Kumeria T, Ziegler DS, Kavallaris M, Mazzieri R et al (2021) Frontiers in the treatment of glioblastoma: past, present and emerging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 171(108–138). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.01.012
Li J, Sun D, Pu W, Wang J, Peng Y (2020) Circular RNAs in Cancer: biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Trends Cancer 6(4):319–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.012
Li P, Wang Z, Li S, Wang L (2021) Circ_0006404 accelerates prostate Cancer progression through regulating miR-1299/CFL2 signaling. Onco Targets Ther 14(83–95). https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s277831
Liu Y, Zhang X, Liang Y, Yu H, Chen X, Zheng T, Zheng B, Wang L, Zhao L, Shi C et al (2011) Targeting X box-binding protein-1 (XBP1) enhances sensitivity of glioma cells to oxidative stress. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37(4):395–405. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01155.x
Liu Y, Hou X, Liu M, Yang Z, Bi Y, Zou H, Wu J, Che H, Li C, Wang X et al (2016) XBP1 silencing decreases glioma cell viability and glycolysis possibly by inhibiting HK2 expression. J Neuro-Oncol 126(3):455–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2003-y
Liu J, Hou K, Ji H, Mi S, Yu G, Hu S, Wang J (2020) Overexpression of circular RNA circ-CDC45 facilitates glioma cell progression by sponging miR-516b and miR-527 and predicts an adverse prognosis. J Cell Biochem 121(1):690–697. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29315
Lu J, Li Y (2020) Circ_0079593 facilitates proliferation, metastasis, glucose metabolism and inhibits apoptosis in melanoma by regulating the miR-516b/GRM3 axis. Mol Cell Biochem 475(1–2):227–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03875-8
Ma Y, Liu Y, Jiang Z (2020a) CircRNAs: a new perspective of biomarkers in the nervous system. Biomed Pharmacother 128(110251). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110251
Ma Z, Shuai Y, Gao X, Wen X, Ji J (2020b) Circular RNAs in the tumour microenvironment. Mol Cancer 19(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1113-0
Mehta SL, Chokkalla AK, Vemuganti R (2021) Noncoding RNA crosstalk in brain health and diseases. Neurochem Int 149(105139). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105139
Nisar S, Bhat AA, Singh M, Karedath T, Rizwan A, Hashem S, Bagga P, Reddy R, Jamal F, Uddin S et al (2021) Insights into the role of CircRNAs: biogenesis, characterization, functional, and clinical impact in human malignancies. Front cell. Dev Biol 9(617281). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.617281
Qu Y, Zhu J, Liu J, Qi L (2019) Circular RNA circ_0079593 indicates a poor prognosis and facilitates cell growth and invasion by sponging miR-182 and miR-433 in glioma. J Cell Biochem 120(10):18005–18013. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29103
Rajesh Y, Pal I, Banik P, Chakraborty S, Borkar SA, Dey G, Mukherjee A, Mandal M (2017) Insights into molecular therapy of glioma: current challenges and next generation blueprint. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38(5):591–613. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.167
Shen H, Xu L, You C, Tang H, Wu H, Zhang Y, Xie M (2021) miR-665 is downregulated in glioma and inhibits tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting high mobility group box 1. Oncol Lett 21(2):156. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.12417
Solé C, Mentxaka G, Lawrie CH (2021) The use of circRNAs as biomarkers of Cancer. Methods Mol Biol 2348(307–341). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1581-2_21
Song D, Ye L, Xu Z, Jin Y, Zhang L (2021) CircRNA hsa_circ_0030018 regulates the development of glioma via regulating the miR-1297/RAB21 axis. Neoplasma 68(2):391–403. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_200702N682
Sun J, Li B, Shu C, Ma Q, Wang J (2020) Functions and clinical significance of circular RNAs in glioma. Mol Cancer 19(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1121-0
Tateishi K (2021) Glioma Cell Biology. No Shinkei Geka 49(3):476–484. https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.1436204419
Tavernier Q, Legras A, Didelot A, Normand C, Gibault L, Badoual C, Le Pimpec-Barthes F, Puig PL, Blons H, Pallet N (2020) High expression of spliced X-box binding protein 1 in lung tumors is associated with cancer aggressiveness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Sci Rep 10(1):10188. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67243-8
Thomas AA, Brennan CW, DeAngelis LM, Omuro AM (2014) Emerging therapies for glioblastoma. JAMA Neurol 71(11):1437–1444. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1701
Wan Y, Luo H, Yang M, Tian X, Peng B, Zhan T, Chen X, Ding Y, He J, Cheng X et al (2020) miR-324-5p contributes to cell proliferation and apoptosis in pancreatic Cancer by targeting KLF3. Mol Ther Oncolytics 18(432–442). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2020.07.011
Wang S, Yin Y, Liu S (2019) Roles of microRNAs during glioma tumorigenesis and progression. Histol Histopathol 34(3):213–222. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-18-040
Wang B, Li B, Si T (2020) Knockdown of circ0082374 inhibits cell viability, migration, invasion and glycolysis in glioma cells by miR-326/SIRT1. Brain Res 1748(147108). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147108
Wei G, Zhu J, Hu HB, Liu JQ (2021) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Gene 771(145365). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145365
Weller M, Wick W, Aldape K, Brada M, Berger M, Pfister SM, Nishikawa R, Rosenthal M, Wen PY, Stupp R et al (2015) Glioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1(15017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.17
Xiao B, Lv SG, Wu MJ, Shen XL, Tu W, Ye MH, Zhu XG (2021) Circ_CLIP2 promotes glioma progression through targeting the miR-195-5p/HMGB3 axis. J Neuro-Oncol 154(2):131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03814-7
Xie P, Han Q, Liu D, Yao D, Lu X, Wang Z, Zuo X (2020) miR-525-5p modulates proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma by targeting Stat-1. Onco Targets Ther 13(9957–9966). https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S257951
Xu HS, Zong HL, Shang M, Ming X, Zhao JP, Ma C, Cao L (2014) MiR-324-5p inhibits proliferation of glioma by target regulation of GLI1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18(6):828–832
Xu TJ, Qiu P, Zhang YB, Yu SY, Xu GM, Yang W (2019) MiR-148a inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioblastoma by targeting ITGA9. Hum Cell 32(4):548–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00279-9
Xu S, Tang L, Li X, Fan F, Liu Z (2020a) Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application. Cancer Lett 476(1–12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.002
Xu W, Wang C, Hua J (2020b) X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) function in diseases. Cell Biol Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11533
Yang Z, Li C, Fan XY, Liu LJ (2020) Circular RNA circ_0079593 promotes glioma development through regulating KPNA2 expression by sponging miR-499a-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(3):1288–1301. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202001_20186
You A, Rao G, Wang J, Li J, Zhang Y, Gu J, Ge X, Zhang K, Gao X, Wu X et al (2021) MiR-433-3p restrains the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells via targeting SMC4. Brain Res 1767(147563). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147563
Zhang GH, Kai JY, Chen MM, Ma Q, Zhong AL, Xie SH, Zheng H, Wang YC, Tong Y, Tian Y et al (2019) Downregulation of XBP1 decreases serous ovarian cancer cell viability and enhances sensitivity to oxidative stress by increasing intracellular ROS levels. Oncol Lett 18(4):4194–4202. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10772
Zhao WJ, Yi SJ, Ou GY, Qiao XY (2021) Neuregulin 2 (NRG2) is expressed in gliomas and promotes migration of human glioma cells. Folia Neuropathol 59(2):189–197. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2021.106460
Zheng Z, Li J, An J, Feng Y, Wang L (2021) High miR-324-5p expression predicts unfavorable prognosis of gastric cancer and facilitates tumor progression in tumor cells. Diagn Pathol 16(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-020-01063-2
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, Ren D, Ye X, Li C, Wang Y et al (2018) Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer 17(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0827-8
Zong Z, Song Y, Xue Y, Ruan X, Liu X, Yang C, Zheng J, Cao S, Li Z, Liu Y (2019) Knockdown of LncRNA SCAMP1 suppressed malignant biological behaviours of glioma cells via modulating miR-499a-5p/LMX1A/NLRC5 pathway. J Cell Mol Med 23(8):5048–5062. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14362
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: Jie Bai and Wenzheng Luo; Formal analysis and Data curation: Wenzheng Luo and Jingliang Cheng; Validation and Investigation: Shanshan Zhao and Jie Bai; Writing - original draft preparation and Writing - review and editing: Shanshan Zhao, Jie Bai and Wenzheng Luo; Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of Weifang People’s Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Patient consent for publication
The results presented in this paper have not been published preciously in whole or in part
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information

Supplementary Fig. 1
The binding sites between circ_0079593 and miR-516b, miR-324-5p, miR-433, miR-633, and miR-665 were obtained from circinteractome. (PNG 423 kb)

Supplementary Fig. 2
The possible miRNA targets of circ_0079593 and the candidate mRNA targets of miR-324-5p. (A and B) We screened out five possible miRNA targets of circ_0079593, including miR-516b, miR-324-5p, miR-433, miR-633, and miR-665. RT-qPCR was conducted to detect the expression of five miRNAs in glioma cells transfected with si-con or si-circ_0079593. (C and D) Four possible mRNA targets of miR-324-5p were screened out, including LMX1A, XBP1, ITGA9, and NRG2. The mRNA expression of LMX1A, XBP1, ITGA9, and NRG2 was measured by RT-qPCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (PNG 172 kb)

Supplementary Fig. 3
The representative images of Fig. 4. (A) The representative images of colony formation assay in Fig. 4C. (B) The representative images of flow cytometry in Fig. 4F. (C) The representative images of transwell migration assay in Fig. 4I. (D) The representative images of transwell invasion assay in Fig. 4J. (E) The representative images of tube formation assay in Fig. 4K. (PNG 2975 kb)

Supplementary Fig. 4
The representative images of Fig. 6. (A) The representative images of colony formation assay in Fig. 6C. (B) The representative images of flow cytometry in Fig. 6F. (C) The representative images of transwell migration assay in Fig. 6I. (D) The representative images of transwell invasion assay in Fig. 6J. (E) The representative images of tube formation assay in Fig. 6K. (PNG 2345 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Wang, T., Dong, L. et al. Circular RNA circ_0079593 facilitates glioma development via modulating miR-324-5p/XBP1 axis. Metab Brain Dis 37, 2389–2403 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01040-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01040-2