Abstract
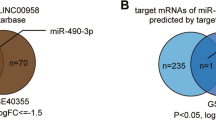
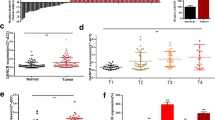
This study is to clarify the effect of the long non-coding RNA ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 1-antisense RNA 1 (ARAP1-AS1)/microRNA (miR)-3918/kinesin family member 20A (KIF20A) on bladder cancer cell function. ARAP1-AS1, miR-3918, and KIF20A expression levels in bladder cancer cells were determined using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The effects of ARAP1-AS1, miR-3918, and KIF20A on bladder cell activity, proliferation, apoptosis, and in vivo growth were examined using the cell counting kit-8, colony formation, caspase-3 activity, and xenograft tumor growth assays, respectively, in nude mice. The binding relationships among ARAP1-AS1, miR-3918, and KIF20A were analyzed using luciferase and RNA immunoprecipitation assays. ARAP1-AS1 and KIF20A were overexpressed in bladder cancer, while miR-3918 was underexpressed. The downregulation of ARAP1-AS1 or KIF20A expression significantly inhibited the viability and proliferation of cancer cells and promoted apoptosis, whereas low expression of miR-3918 or high expression of ARAP1-AS1/KIF20A showed the opposite effect. miR-3918 was sponged by ARAP1-AS1, and targeted KIF20A. In addition, miR-3918 expression was inversely correlated with ARAP1-AS1 and KIF20a expression levels in bladder cancer tissues. In addition, the rescue experiment showed that interference with miR-3918 could reverse the effect of low ARAP1-AS1 or KIF20A expression on bladder cancer cell malignancy. ARAP1-AS1 facilitates the malignant behavior of bladder cancer cells via the regulation of KIF20A expression by sponging miR-3918.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hase, K., Kanda, A., Hirose, I., Noda, K., & Ishida, S. (2017). Systemic factors related to soluble (pro)renin receptor in plasma of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE, 12, e0189696.
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 68, 394–424.
Espinoza, F., Cecchini, L., Morote, J., Marcos, R., & Pastor, S. (2019). Micronuclei frequency in urothelial cells of bladder cancer patients, as a biomarker of prognosis. Environmental and molecular mutagenesis, 60, 168–173.
Saginala, K., Barsouk, A., Aluru, J. S., Rawla, P., Padala, S. A., & Barsouk, A. (2020). Epidemiology of bladder cancer. Medical Sciences, 8, 15.
Xu, J., Bai, J., Zhang, X., Lv, Y., Gong, Y., Liu, L., Zhao, H., Yu, F., Ping, Y., Zhang, G., Lan, Y., Xiao, Y., & Li, X. (2017). A comprehensive overview of lncRNA annotation resources. Briefings in bioinformatics, 18, 236–249.
Jathar, S., Kumar, V., Srivastava, J., & Tripathi, V. (2017). Technological developments in lncRNA biology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1008, 283–323.
Charles Richard, J. L., & Eichhorn, P. J. A. (2018). Platforms for investigating LncRNA functions. SLAS Technology, 23, 493–506.
Peng, W. X., Koirala, P., & Mo, Y. Y. (2017). LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene, 36, 5661–5667.
Tang, Q., & Hann, S. S. (2018). HOTAIR: An oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancer. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 47, 893–913.
Liu, S., Li, J., Kang, L., Tian, Y., & Xue, Y. (2019). Retracted article: Degradation of long non-coding RNA-CIR decelerates proliferation, invasion and migration, but promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. Cancer cell international, 19, 349.
Hu, X., Feng, H., Huang, H., Gu, W., Fang, Q., Xie, Y., Qin, C., & Hu, X. (2019). Downregulated long noncoding RNA PART1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in bladder cancer. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 18, 1533033819846638.
Ye, T., Ding, W., Wang, N., Huang, H., Pan, Y., & Wei, A. (2017). Long noncoding RNA linc00346 promotes the malignant phenotypes of bladder cancer. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 491, 79–84.
Ye, Y., Gu, B., Wang, Y., Shen, S., & Huang, W. (2019). YY1-induced upregulation of long noncoding RNA ARAP1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in colorectal cancer through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biotherapy & Radiopharmaceuticals, 34, 519–528.
Zhang, Y., Wu, D., & Wang, D. (2020). Long non‐coding RNA ARAP1‐AS1 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis through facilitating proto‐oncogene c‐Myc translation via dissociating PSF/PTB dimer in cervical cancer. Cancer medicine, 9, 1855–1866.
Jiang, Y. H., Zhu, X. Y., Guo, Z. Y., & Yang, Z. H. (2020). Increased long non-coding RNA ARAP1-AS1 expression and its prognostic significance in human gastric cancer: a preliminary study. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 24, 1815–1820.
Teng, J., Ai, X., Jia, Z., Wang, K., Guan, Y., & Guo, Y. (2019). Long non-coding RNA ARAP1-AS1 promotes the progression of bladder cancer by regulating miR-4735-3p/NOTCH2 axis. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 20, 552–561.
Lau, E. (2014). Nature reviews. Genetics, 15, 574–575.
Yang, G., Wang, X., Liu, B., Lu, Z., Xu, Z., Xiu, P., Liu, Z., & Li, J. (2019). circ-BIRC6, a circular RNA, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting the miR-3918/Bcl2 axis. Cell Cycle, 18, 976–989.
Fu, T., Ji, K., Jin, L., Zhang, J., Wu, X., Ji, X., Fan, B., Jia, Z., Wang, A., Liu, J., Bu, Z., & Ji, J. (2021). ASB16-AS1 up-regulated and phosphorylated TRIM37 to activate NF-κB pathway and promote proliferation, stemness, and cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer, 24, 45–59.
Shen, T., Yang, L., Zhang, Z., Yu, J., Dai, L., Gao, M., Shang, Z., & Niu, Y. (2019). KIF20A affects the prognosis of bladder cancer by promoting the proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer cells. Disease Markers, 2019, 4863182.
Tian, Y., Guan, Y., Su, Y., Luo, W., Yang, G., & Zhang, Y. (2020). MiR-582-5p inhibits bladder cancer-genesis by suppressing TTK expression. Cancer Management and Research, 12, 11933–11944.
Chen, F., Wu, P., Hu, H., Tian, D., Jiang, N., & Wu, C. (2018). Protein kinase TTK promotes proliferation and migration and mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bladder cancer cells. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 11, 4854–4861.
Lu, C., Wang, X., Zhao, X., Xin, Y. & Liu, C. (2020) Bioscience Reports. (Vol.40). Portland Press on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Ren, X., Chen, X., Ji, Y., Li, L., Li, Y., Qin, C., & Fang, K. (2020). Upregulation of KIF20A promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in renal clear cell carcinoma and is associated with adverse clinical outcome. Aging, 12, 25878–25894.
Sheng, Y., Wang, W., Hong, B., Jiang, X., Sun, R., Yan, Q., Zhang, S., Lu, M., Wang, S., Zhang, Z., Lin, W., & Li, Y. (2018). Upregulation of KIF20A correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Management and Research, 10, 6205–6216.
Zhang, Z., Chai, C., Shen, T., Li, X., Ji, J., Li, C., Shang, Z., & Niu, Y. (2019). Aberrant KIF20A expression is associated with adverse clinical outcome and promotes tumor progression in prostate cancer. Disease Markers, 2019, 4782730.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This work was supported by Wuhan Key Project: Research on Molecular Phenotyping Spectrum Identification and Clinical Application Evaluation of Circulating Prostate Cancer Cells [grant number WX18A05].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ and JYZ conducted the experiments and analyzed data. ZH and WS offered the experimental consideration. LX and HC analyzed and interpreted data. XW did the analysis and interpretation of data. QF collected materials and resources. The manuscript was read and approved through all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No potential competing interest was reported by the author.
Ethical Approval
Ethics Committee of Wuhan Third Hospital (Wuhan, China) approved the present study. Clinical analysis complied with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent acquired from all patients.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, J., Hu, Z. et al. LncRNA ARAP1-AS1 Promotes Bladder Cancer Development by Regulating the miR-3918/KIF20A Axis. Mol Biotechnol 64, 1259–1269 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00489-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00489-x