Abstract
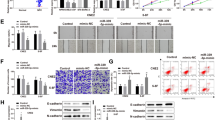
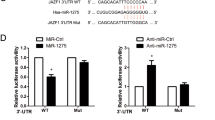
NPC is a type of cancer with a poor prognosis. We aim to excavate the regulatory roles of miR-135b-5p in NPC and uncover the underlying mechanism. The levels of miR-135b-5p and Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) in NPC and normal tissues and cells were tested via quantitative real-time PCR, western blotting, and immunohistochemistry, respectively. The binding relationship between them was predicted with ENCORI databases and validated with dual-luciferase reporter assay. The impact of miR-135b-5p and SIRT1 on the expressions of matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7) and epithelial–mesenchymal transformation (EMT) proteins in NPC cells was evaluated by western blotting. Metastasis of NPC cells was evaluated by Transwell assay. The binding of c-JUN at the MMP7 promoter and deacetylation of c-JUN were examined using chromatin-immunoprecipitation and co-immunoprecipitation, respectively. The level of miR-135b-5p was increased and SIRT1 was decreased in NPC tissues and cells. miR-135b-5p was validated to target SIRT1. Silencing of miR-135b-5p accelerated EMT and metastasis of NPC cells, whereas knockdown of SIRT1 showed opposite results. Notably, knockdown of SIRT1 partially reversed the miR-135b-5p-induced change of EMT markers and metastasis of NPC cells. Mechanistically, miR-135b-5p disrupted SIRT1-induced deacetylation of c-JUN to promote the activation of MMP7 in NPC cells. miR-135b-5p targeted SIRT1 to inhibit deacetylation of c-JUN and increase MMP7 expression to promote malignancy of NPC cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- miRs/miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- DLR:
-
Dual-luciferase reporter
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- EBV:
-
Epstein-Barr virus
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transformation
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin 1
- Sir2:
-
Silent information regulator 2
- MMP7:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 7
- RFS:
-
Relapse-free survival
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin-immunoprecipitation
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
References
Mahdavifar, N., Ghoncheh, M., Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A., Khosravi, B., & Salehiniya, H. (2016). Epidemiology and inequality in the incidence and mortality of nasopharynx cancer in Asia. Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives, 7, 360–372.
Jia, W. H., Collins, A., Zeng, Y. X., Feng, B. J., Yu, X. J., Huang, L. X., Feng, Q. S., Huang, P., Yao, M. H., & Shugart, Y. Y. (2005). Complex segregation analysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Guangdong, China: Evidence for a multifactorial mode of inheritance (complex segregation analysis of NPC in China). European Journal of Human Genetics, 13, 248–252.
Xu, F. H., Xiong, D., Xu, Y. F., Cao, S. M., Xue, W. Q., Qin, H. D., Liu, W. S., Cao, J. Y., Zhang, Y., Feng, Q. S., Chen, L. Z., Li, M. Z., Liu, Z. W., Liu, Q., Hong, M. H., Shugart, Y. Y., Zeng, Y. X., Zeng, M. S., & Jia, W. H. (2012). An epidemiological and molecular study of the relationship between smoking, risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and Epstein-Barr virus activation. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 104, 1396–1410.
Ma, J., Mai, H. Q., Hong, M. H., Cui, N. J., Lu, T. X., Lu, L. X., Mo, H. Y., & Min, H. Q. (2001). Is the 1997 AJCC staging system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma prognostically useful for Chinese patient populations? International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 50, 1181–1189.
Lai, S. Z., Li, W. F., Chen, L., Luo, W., Chen, Y. Y., Liu, L. Z., Sun, Y., Lin, A. H., Liu, M. Z., & Ma, J. (2011). How does intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy influence the treatment results in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients? International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 80, 661–668.
Ha, M., & Kim, V. N. (2014). Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 15, 509–524.
Didiano, D., & Hobert, O. (2008). Molecular architecture of a miRNA-regulated 3′ UTR. RNA (New York, NY), 14, 1297–1317.
Rupaimoole, R., Calin, G. A., Lopez-Berestein, G., & Sood, A. K. (2016). miRNA deregulation in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discovery, 6, 235–246.
Han, X., Saiyin, H., Zhao, J., Fang, Y., Rong, Y., Shi, C., Lou, W., & Kuang, T. (2017). Overexpression of miR-135b-5p promotes unfavorable clinical characteristics and poor prognosis via the repression of SFRP4 in pancreatic cancer. OncoTarget, 8, 62195–62207.
Xu, Z., Han, Y., Liu, J., Jiang, F., Hu, H., Wang, Y., Liu, Q., Gong, Y., & Li, X. (2015). miR-135b-5p and miR-499a-3p promote cell proliferation and migration in atherosclerosis by directly targeting MEF2C. Scientific Reports, 5, 12276.
Chen, Z., Gao, Y., Gao, S., Song, D., & Feng, Y. (2020). miR-135b-5p promotes viability, proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4). Archives of Medical Science, 16, 167–176.
Zhang, Z., Che, X., Yang, N., Bai, Z., Wu, Y., Zhao, L., & Pei, H. (2017). miR-135b-5p promotes migration, invasion and EMT of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting NR3C2. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 96, 1341–1348.
Sreedharan, L., Mayne, G. C., Watson, D. I., Bright, T., Lord, R. V., Ansar, A., Wang, T., Kist, J., Astill, D. S., & Hussey, D. J. (2017). MicroRNA profile in neosquamous esophageal mucosa following ablation of Barrett’s esophagus. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 23, 5508–5518.
Tang, J. F., Yu, Z. H., Liu, T., Lin, Z. Y., Wang, Y. H., Yang, L. W., He, H. J., Cao, J., Huang, H. L., & Liu, G. (2014). Five miRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarker candidates for primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 15, 7575–7581.
Haigis, M. C., & Sinclair, D. A. (2010). Mammalian sirtuins: Biological insights and disease relevance. Annual Review of Pathology, 5, 253–295.
Dai, Y., & Faller, D. V. (2008). Transcription regulation by Class III histone deacetylases (HDACs)-sirtuins. Translational Oncogenomics, 3, 53–65.
Wang, R. H., Sengupta, K., Li, C., Kim, H. S., Cao, L., Xiao, C., Kim, S., Xu, X., Zheng, Y., Chilton, B., Jia, R., Zheng, Z. M., Appella, E., Wang, X. W., Ried, T., & Deng, C. X. (2008). Impaired DNA damage response, genome instability, and tumorigenesis in SIRT1 mutant mice. Cancer Cell, 14, 312–323.
Buhrmann, C., Shayan, P., Popper, B., Goel, A., & Shakibaei, M. (2016). Sirt1 is required for resveratrol-mediated chemopreventive effects in colorectal cancer cells. Nutrients, 8, 145.
Sun, L., Li, H., Chen, J., Iwasaki, Y., Kubota, T., Matsuoka, M., Shen, A., Chen, Q., & Xu, Y. (2013). PIASy mediates hypoxia-induced SIRT1 transcriptional repression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells. Journal of Cell Science, 126, 3939–3947.
Dong, G., Wang, B., An, Y., Li, J., Wang, X., Jia, J., & Yang, Q. (2018). SIRT1 suppresses the migration and invasion of gastric cancer by regulating ARHGAP5 expression. Cell Death and Disease, 9, 977.
Schütte, J., Minna, J. D., & Birrer, M. J. (1989). Deregulated expression of human c-jun transforms primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with an activated c-Ha-ras gene and transforms rat-1a cells as a single gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 86, 2257–2261.
Eferl, R., Ricci, R., Kenner, L., Zenz, R., David, J. P., Rath, M., & Wagner, E. F. (2003). Liver tumor development. c-Jun antagonizes the proapoptotic activity of p53. Cell, 112, 181–192.
Banday, M. Z., Sameer, A. S., Mir, A. H., Mokhdomi, T. A., Chowdri, N. A., & Haq, E. (2016). Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, -7 and -9 promoter polymorphisms in colorectal cancer in ethnic Kashmiri population—A case–control study and a mini review. Gene, 589, 81–89.
Zhang, Q., Liu, S., Parajuli, K. R., Zhang, W., Zhang, K., Mo, Z., Liu, J., Chen, Z., Yang, S., Wang, A. R., Myers, L., & You, Z. (2017). Interleukin-17 promotes prostate cancer via MMP7-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene, 36, 687–699.
Chen, J., Kwong, D. L., Zhu, C. L., Chen, L. L., Dong, S. S., Zhang, L. Y., Tian, J., Qi, C. B., Cao, T. T., Wong, A. M., Kong, K. L., Li, Y., Liu, M., Fu, L., & Guan, X. Y. (2012). RBMS3 at 3p24 inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma development via inhibiting cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and inducing apoptosis. PLoS ONE, 7, e44636.
Wong, A. M., Kong, K. L., Chen, L., Liu, M., Wong, A. M., Zhu, C., Tsang, J. W., & Guan, X. Y. (2013). Characterization of CACNA2D3 as a putative tumor suppressor gene in the development and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer, 133, 2284–2295.
Chen, I. C., Chiang, W. F., Huang, H. H., Chen, P. F., Shen, Y. Y., & Chiang, H. C. (2014). Role of SIRT1 in regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Molecular Cancer, 13, 254.
Liu, D., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., & Gu, X. (2020). LncRNA SNHG5 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by regulating miR-1179/HMGB3 axis. BMC Cancer, 20, 178.
Vaziri, H., Dessain, S. K., Ng Eaton, E., Imai, S. I., Frye, R. A., Pandita, T. K., Guarente, L., & Weinberg, R. A. (2001). hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell, 107, 149–159.
Zhang, J., Lee, S. M., Shannon, S., Gao, B., Chen, W., Chen, A., Divekar, R., McBurney, M. W., Braley-Mullen, H., Zaghouani, H., & Fang, D. (2009). The type III histone deacetylase Sirt1 is essential for maintenance of T cell tolerance in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 119, 3048–3058.
Stoker, S. D., van Diessen, J. N., de Boer, J. P., Karakullukcu, B., Leemans, C. R., & Tan, I. B. (2013). Current treatment options for local residual nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Current Treatment Options in Oncology, 14, 475–491.
Wei, P., Niu, M., Pan, S., Zhou, Y., Shuai, C., Wang, J., Peng, S., & Li, G. (2014). Cancer stem-like cell: A novel target for nasopharyngeal carcinoma therapy. Stem Cell Research and Therapy, 5, 44.
Liu, N., Tang, L. L., Sun, Y., Cui, R. X., Wang, H. Y., Huang, B. J., He, Q. M., Jiang, W., & Ma, J. (2013). miR-29c suppresses invasion and metastasis by targeting TIAM1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Letters, 329, 181–188.
Liu, N., Jiang, N., Guo, R., Jiang, W., He, Q. M., Xu, Y. F., Li, Y. Q., Tang, L. L., Mao, Y. P., Sun, Y., & Ma, J. (2013). miR-451 inhibits cell growth and invasion by targeting MIF and is associated with survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Molecular Cancer, 12, 123.
Wang, X., Chen, L., Jin, H., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Tang, X., & Tang, G. (2016). Screening miRNAs for early diagnosis of colorectal cancer by small RNA deep sequencing and evaluation in a Chinese patient population. OncoTargets and Therapy, 9, 1159–1166.
Lauvrak, S. U., Munthe, E., Kresse, S. H., Stratford, E. W., Namløs, H. M., Meza-Zepeda, L. A., & Myklebost, O. (2013). Functional characterisation of osteosarcoma cell lines and identification of mRNAs and miRNAs associated with aggressive cancer phenotypes. British Journal of Cancer, 109, 2228–2236.
Pu, T., Shen, M., Li, S., Yang, L., Gao, H., Xiao, L., Zhong, X., Zheng, H., Liu, Y., Ye, F., & Bu, H. (2019). Repression of miR-135b-5p promotes metastasis of early-stage breast cancer by regulating downstream target SDCBP. Laboratory Investigation: A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology, 99, 1296–1308.
Eades, G., Yao, Y., Yang, M., Zhang, Y., Chumsri, S., & Zhou, Q. (2011). miR-200a regulates SIRT1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like transformation in mammary epithelial cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 25992–26002.
Yang, N., Cheng, H., Mo, Q., Zhou, X., & Xie, M. (2020). miR-155-5p downregulation inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting SIRT1 in human nasal epithelial cells. Molecular Medicine Reports, 22, 3695–3704.
Lu, M., Huang, Y., Sun, W., Li, P., Li, L., & Li, L. (2018). miR-135b-5p promotes gastric cancer progression by targeting CMTM3. International Journal of Oncology, 52, 589–598.
Li, Z., Qin, Y., Chen, P., Luo, Q., Shi, H., & Jiang, X. (2020). miR-135b-5p enhances the sensitivity of HER-2 positive breast cancer to trastuzumab via binding to cyclin D2. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 46, 1514–1524.
Simic, P., Williams, E. O., Bell, E. L., Gong, J. J., Bonkowski, M., & Guarente, L. (2013). SIRT1 suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis and organ fibrosis. Cell Reports, 3, 1175–1186.
Li, L., Zhang, H. N., Chen, H. Z., Gao, P., Zhu, L. H., Li, H. L., Lv, X., Zhang, Q. J., Zhang, R., Wang, Z., She, Z. G., Zhang, R., Wei, Y. S., Du, G. H., Liu, D. P., & Liang, C. C. (2011). SIRT1 acts as a modulator of neointima formation following vascular injury in mice. Circulation Research, 108, 1180–1189.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC performed all of the work of this research and gave final approval of the version to be published; have agreed on the journal to which the article has been submitted; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The methodologies of this research were approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University and obeyed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y. miR-135b-5p Targets SIRT1 to Inhibit Deacetylation of c-JUN and Increase MMP7 Expression to Promote Migration and Invasion of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells. Mol Biotechnol 64, 693–701 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00457-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00457-5