Abstract
Objective
To explore the effect and mechanism of the miR-339-3p/KAT6A/TRIM24 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cell growth and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression.
Methods
CNE2 and 5-8F NPC cell lines were transfected with miR-339-3p-mimic or sh-KAT6A alone or co-transfected with miR-339-3p-mimic and oe-KAT6A. The expression levels of miR-339-3p, KAT6A, TRIM24, and EMT-related proteins were assessed, in addition to cell biological behaviors. Then, the relationship between miR-339-3p and KAT6A was predicted and validated. The correlations between miR-339-3p and KAT6A or between KAT6A and TRIM24 were analyzed by Pearson coefficient and the enrichment of H3K23ac in TRIM24 promoter region was measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation.
Results
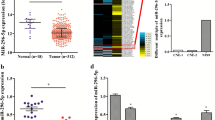
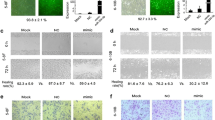
miR-339-3p was downregulated, but KAT6A and TRIM24 were highly expressed in NPC cells and tissues. Upregulated miR-339-3p or downregulated KAT6A could inhibit the growth and EMT of NPC cells. Further experiments showed that miR-339-3p regulated NPC cell growth and EMT by mediating KAT6A in a targeted fashion. KAT6A was positively correlated with TRIM24, and the enrichment of H3K23ac was much higher in NPC tissues. miR-339-3p suppressed the growth and EMT of NPC cells by the KAT6A/TRIM24 axis. In a xenograft study, miR-339-3p overexpression inhibited NPC tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion
Conclusively, miR-339-3p inhibited the growth and EMT of NPC cells via the KAT6A/TRIM24 axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lung RW, Hau PM, Yu KH et al (2018) EBV-encoded miRNAs target ATM-mediated response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pathol 244(4):394–407
Tian Y, Tang L, Yi P et al (2020) MiRNAs in radiotherapy resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer 11(13):3976–3985
Lan X, Liu X (2019) LncRNA SNHG1 functions as a ceRNA to antagonize the effect of miR-145a-5p on the down-regulation of NUAK1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell. J Cell Mol Med 23(4):2351–2361
Jiang N, Jiang X, Chen Z et al (2017) MiR-203a-3p suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting LASP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):138
Nowicka Z, Stawiski K, Tomasik B et al (2019) Extracellular miRNAs as biomarkers of head and neck cancer progression and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 20(19):1
Mohr AM, Mott JL (2015) Overview of microRNA biology. Semin Liver Dis 35(1):3–11
Trakunram K, Chaniad P, Geater SL et al (2020) Serum miR-339-3p as a potential diagnostic marker for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Med 17(3):652–663
Liang R, Tang Y (2020) LINC00467 knockdown repressed cell proliferation but stimulated cell apoptosis in glioblastoma via miR-339-3p/IP6K2 axis. Cancer Biomark 28(2):169–180
Luo A, Zhou X, Shi X et al (2019) Exosome-derived miR-339-5p mediates radiosensitivity by targeting Cdc25A in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 38(25):4990–5006
Kennedy J, Goudie D, Blair E et al (2019) KAT6A Syndrome: genotype-phenotype correlation in 76 patients with pathogenic KAT6A variants. Genet Med 21(4):850–860
Yu L, Liang Y, Cao X et al (2017) Identification of MYST3 as a novel epigenetic activator of ERalpha frequently amplified in breast cancer. Oncogene 36(20):2910–2918
Pei J, Cooper H, Flieder DB et al (2019) NEAT1-TFE3 and KAT6A-TFE3 renal cell carcinomas, new members of MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol 32(5):710–716
Yu B, Luo F, Sun B et al (2021) KAT6A acetylation of SMAD3 regulates myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment, metastasis, and immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh) 8(20):e2100014
Gechijian LN, Buckley DL, Lawlor MA et al (2018) Functional TRIM24 degrader via conjugation of ineffectual bromodomain and VHL ligands. Nat Chem Biol 14(4):405–412
Fang Z, Deng J, Zhang L et al (2017) TRIM24 promotes the aggression of gastric cancer via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 13(3):1797–1806
Wang P, Shen N, Liu D et al (2018) TRIM24 siRNA induced cell apoptosis and reduced cell viability in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 18(1):369–376
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT et al (2019) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 394(10192):64–80
Zhang SQ, Pan SM, Liang SX et al (2021) Research status and prospects of biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the era of highthroughput omics (Review). Int J Oncol 58(4):1
Tang J, Zhong G, Wu J et al (2018) SOX2 recruits KLF4 to regulate nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncogenesis 7(8):61
Benson EA, Skaar TC, Liu Y et al (2015) Carboplatin with decitabine therapy, in recurrent platinum resistant ovarian cancer, alters circulating miRNAs concentrations: a pilot study. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0141279
Weber CE, Luo C, Hotz-Wagenblatt A et al (2016) miR-339-3p is a tumor suppressor in melanoma. Cancer Res 76(12):3562–3571
Li S, Liu F, Zheng K et al (2021) CircDOCK1 promotes the tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance of osteogenic sarcoma via the miR-339-3p/IGF1R axis. Mol Cancer 20(1):161
Zhou C, Lu Y, Li X (2015) miR-339-3p inhibits proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett 10(5):2842–2848
Zhang J, Jia L, Liu T et al (2019) mTORC2-mediated PDHE1alpha nuclear translocation links EBV-LMP1 reprogrammed glucose metabolism to cancer metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene 38(24):4669–4684
Xiang T, Lin YX, Ma W et al (2018) Vasculogenic mimicry formation in EBV-associated epithelial malignancies. Nat Commun 9(1):5009
Wu LZ, Huang ML, Qi CL et al (2021) Overexpression of Notch2 enhances radiosensitivity via inhibition of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Bioengineered 12(1):3398–3409
Wu XM, Ji KQ, Wang HY et al (2018) MicroRNA-339-3p alleviates inflammation and edema and suppresses pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in mice with severe acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury by regulating Anxa3 via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 119(8):6704–6714
Saglam O, Tang Z, Tang G et al (2020) KAT6A amplifications are associated with shorter progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with endometrial serous carcinoma. PLoS ONE 15(9):e0238477
Liu W, Zhan Z, Zhang M et al (2021) KAT6A, a novel regulator of beta-catenin, promotes tumorigenicity and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer by acetylating COP1. Theranostics 11(13):6278–6292
Xu D, Jiang J, He G et al (2022) miR-143-3p represses leukemia cell proliferation by inhibiting KAT6A expression. Anticancer Drugs 33(1):e662–e669
Heair HM, Kemper AG, Roy B et al (2015) MicroRNA 665 regulates dentinogenesis through MicroRNA-mediated silencing and epigenetic mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 35(18):3116–3130
Tsai WW, Wang Z, Yiu TT et al (2010) TRIM24 links a non-canonical histone signature to breast cancer. Nature 468(7326):927–932
Zhao W, Mo H, Liu R et al (2022) Matrix stiffness-induced upregulation of histone acetyltransferase KAT6A promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating SOX2 expression. Br J Cancer 127:202
Cui Z, Cao W, Li J et al (2013) TRIM24 overexpression is common in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and correlates with aggressive malignant phenotypes. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63887
Lv D, Jia F, Hou Y et al (2017) Histone Acetyltransferase KAT6A Upregulates PI3K/AKT Signaling through TRIM24 Binding. Cancer Res 77(22):6190–6201
Xie W, Zhang Y, Wang B et al (2020) Tripartite motif containing 24 regulates cell proliferation in colorectal cancer through YAP signaling. Cancer Med 9(17):6367–6376
Shamloo B, Usluer S (2019) p21 in cancer research. Cancers (Basel) 11(8):1
Liu X, Huang Y, Yang D et al (2014) Overexpression of TRIM24 is associated with the onset and progress of human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85462
Pathiraja TN, Thakkar KN, Jiang S et al (2015) TRIM24 links glucose metabolism with transformation of human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 34(22):2836–2845
Wang H, Xue W, Jiang X (2018) Overexpression of TRIM24 stimulates proliferation and glucose metabolism of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Res Int
Zhang LH, Yin AA, Cheng JX et al (2015) TRIM24 promotes glioma progression and enhances chemoresistance through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncogene 34(5):600–610
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG is the guarantor of integrity of the entire study and contributed to the experimental studies and manuscript preparation. KZ contributed to the experimental studies. Wuhao Lu contributed to the manuscript preparation and statistical analysis. LW contributed to the experimental studies. PZ contributed to the experimental studies and manuscript preparation. KZ contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data. Wu contributed to the literature research. Liang Wang contributed to the data acquisition and literature research. PZ contributed to the statistical analysis. PG drafted the article and revised it critically. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, P., Zhao, K., Lu, W. et al. miR-339-3p inhibits cell growth and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by modulating the KAT6A/TRIM24 axis. Int J Clin Oncol 27, 1684–1697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-022-02231-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-022-02231-8