Abstract
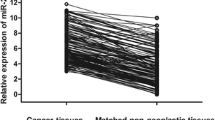
Since the discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) as a class of important regulatory molecules, miRNAs are involved in the occurrence and development of tumors. In this paper, we aimed to identify the role of miR-1274a in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The miR-1274a expression levels in four NSCLC cells and tissues from 125 patients were determined by qRT-PCR assays. Kaplan–Meier survival curves and Cox regression analysis were used to examine the prognostic significance of miR-1274a in NSCLC patients. The CCK-8 and Transwell assays were performed to evaluate the cell proliferation, invasion, and migration ability of NSCLC cells. The miR-1274a expression levels were significantly higher in NSCLC tissues than in adjacent normal tissues, and overexpression of miR-1274a had a poor prognosis in NSCLC patients. Functional studies in two NSCLC cell lines have shown that overexpression of miR-1274a could promote cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. miR-1274a expression levels are upregulated in NSCLC tissues, and a high expression is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC. Moreover, miR-1274a promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Based on our findings, miR-1274a may act as a tumor miRNA in the occurrence and development of NSCLC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Herbst, R. S., Morgensztern, D., & Boshoff, C. (2018). The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature, 553(7689), 446–454.
Ruan, L., Chen, J., Ruan, L., Yang, T., & Wang, P. (2018). MicroRNA-186 suppresses lung cancer progression by targeting SIRT6. Cancer Biomarkers: Section A of Disease Markers, 21(2), 415–423.
Sun, Y., Li, L., Xing, S., Pan, Y., Shi, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2017). miR-503-3p induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells by regulating p21 and CDK4 expression. Cancer Biomarkers: Section A of Disease Markers, 20(4), 597–608.
Falzone, L., Salomone, S., & Libra, M. (2018). Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the third millennium. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 1300.
Yuan, M., Huang, L. L., Chen, J. H., Wu, J., & Xu, Q. (2019). The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 4, 61.
Christofi, T., Baritaki, S., Falzone, L., Libra, M., & Zaravinos, A. (2019). Current perspectives in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers, 11(10), 1472.
Yang, Z. Q., Wu, C. A., & Cheng, Y. X. (2018). Prognostic value of microRNA-133a expression and its clinicopathologic significance in non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive study based on meta-analysis and the TCGA database. Oncology Research and Treatment, 41(12), 762–768.
Bulgakova, O., Zhabayeva, D., Kussainova, A., Pulliero, A., Izzotti, A., & Bersimbaev, R. (2018). miR-19 in blood plasma reflects lung cancer occurrence but is not specifically associated with radon exposure. Oncology Letters, 15(6), 8816–8824.
Li, H., Feng, C., & Shi, S. (2018). miR-196b promotes lung cancer cell migration and invasion through the targeting of GATA6. Oncology Letters, 16(1), 247–252.
Chu, G. C. W., Lazare, K., & Sullivan, F. (2018). Serum and blood based biomarkers for lung cancer screening: A systematic review. BMC Cancer, 18(1), 181.
Shao, C., Yang, F., Qin, Z., Jing, X., Shu, Y., & Shen, H. (2019). The value of miR-155 as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Cancer, 19(1), 1103.
Shen, Y. Y., Cui, J. Y., Yuan, J., & Wang, X. (2018). MiR-451a suppressed cell migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer through targeting ATF2. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 22(17), 5554–5561.
Xiao, H. (2019). MiR-7-5p suppresses tumor metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting NOVA2. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 24, 60.
Zhang, L., & Yu, S. (2018). Role of miR-520b in non-small cell lung cancer. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 16(5), 3987–3995.
Wang, Q., & Zhang, L. (2019). Possible molecular mechanisms for the roles of MicroRNA-21 played in lung cancer. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 18, 1533033819875130.
Lu, C., Shan, Z., Hong, J., & Yang, L. (2017). MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer metastasis. International Journal of Oncology, 51(1), 235–244.
Munagala, R., Aqil, F., & Gupta, R. C. (2016). Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers of recurrent lung cancer. Tumour Biology: The Journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine., 37(8), 10703–10714.
Hashemi, Z. S., Khalili, S., Forouzandeh Moghadam, M., & Sadroddiny, E. (2017). Lung cancer and miRNAs: A possible remedy for anti-metastatic, therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine, 11(2), 147–157.
Mao, Y., Yang, D., He, J., & Krasna, M. J. (2016). Epidemiology of lung cancer. Surgical Oncology Clinics of North America, 25(3), 439–445.
Rodriguez-Canales, J., Parra-Cuentas, E., & Wistuba, I. I. (2016). Diagnosis and molecular classification of lung cancer. Cancer Treatment and Research, 170, 25–46.
Sheervalilou, R., Lotfi, H., Shirvaliloo, M., Sharifi, A., Nazemiyeh, M., & Zarghami, N. (2019). Circulating MiR-10b, MiR-1 and MiR-30a expression profiles in lung cancer: possible correlation with clinico-pathologic characteristics and lung cancer detection. International Journal of Molecular and Cellular Medicine, 8(2), 118–129.
Zhang, H., Wang, R., & Wang, M. (2019). miR-331-3p suppresses cell invasion and migration in colorectal carcinoma by directly targeting NRP2. Oncology Letters, 18(6), 6501–6508.
Alizadeh, M., Safarzadeh, A., Beyranvand, F., Ahmadpour, F., Hajiasgharzadeh, K., Baghbanzadeh, A., et al. (2019). The potential role of miR-29 in health and cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(11), 19280–19297.
Zhu, L., Deng, H., Hu, J., Huang, S., Xiong, J., & Deng, J. (2018). The promising role of miR-296 in human cancer. Pathology, Research and Practice, 214(12), 1915–1922.
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Qi, P., & Ma, Z. (2018). Biology of MiR-17-92 cluster and its progress in lung cancer. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 15(13), 1443–1448.
Zhou, Y., & Shen, S. (2019). MiR-520f acts as a biomarker for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Medicine, 98(30), e16546.
Said, R., Garcia-Mayea, Y., Trabelsi, N., Setti Boubaker, N., Mir, C., Blel, A., et al. (2018). Expression patterns and bioinformatic analysis of miR-1260a and miR-1274a in Prostate Cancer Tunisian patients. Molecular Biology Reports, 45(6), 2345–2358.
Yoshino, H., Yonezawa, T., Yonemori, M., Miyamoto, K., Sakaguchi, T., Sugita, S., et al. (2018). Downregulation of microRNA-1274a induces cell apoptosis through regulation of BMPR1B in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncology Reports, 39(1), 173–181.
Ren, B., Yang, B., Li, P., & Ge, L. (2020). Upregulation of MiR-1274a is correlated with survival outcomes and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer. OncoTargets and Therapy, 13, 6957–6966.
Wang, G. J., Liu, G. H., Ye, Y. W., Fu, Y., & Zhang, X. F. (2015). The role of microRNA-1274a in the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer: Accelerating cancer cell proliferation and migration via directly targeting FOXO4. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 459(4), 629–635.
Feng, X. T., Wang, C., Zhang, F. J., Wu, X. Q., & Zhang, Z. (2021). MicroRNA-1274a serves as a prognostic biomarker in patients with osteosarcoma and is involved in tumor progression via targeting ADAM9. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents, 35(1), 151–160.
Zhou, C., Liu, J., Li, Y., Liu, L., Zhang, X., Ma, C. Y., et al. (2011). microRNA-1274a, a modulator of sorafenib induced a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 9 (ADAM9) down-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Letters, 585(12), 1828–1834.
Farhan, M., Wang, H., Gaur, U., Little, P. J., Xu, J., & Zheng, W. (2017). FOXO signaling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 13(7), 815–827.
Coomans de Brachène, A., & Demoulin, J. B. (2016). FOXO transcription factors in cancer development and therapy. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (CMLS), 73(6), 1159–1172.
Li, H., Ouyang, R., Wang, Z., Zhou, W., Chen, H., Jiang, Y., et al. (2016). MiR-150 promotes cellular metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting FOXO4. Scientific Reports, 6, 39001.
Tuaeva, N. O., Falzone, L., Porozov, Y. B., Nosyrev, A. E., Trukhan, V. M., Kovatsi, L., et al. (2019). Translational application of circulating DNA in oncology: Review of the last decades achievements. Cells, 8(10), 1251.
Funding
This work was supported by scientific research fund of Petrel (Grant No. JJQN2016-11]; the financial assistance of Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Fund (Grant No. LBH-Z16227).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the hospital ethics committee of the affiliated Tumor Hospital of Harbin Medical University.
Consent to Participate
All patients signed a written informed consent form.
Consent to Publish
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Sj., Wang, X., Hu, Sl. et al. Clinical Significance and Biological Function of miR-1274a in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol Biotechnol 64, 9–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00385-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00385-w