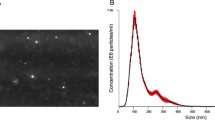
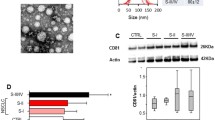
Abstract
Prognosis of lung cancer still remains grim largely due to recurrence and aggressive metastasis of the disease. In this study, we examined the potential of exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers of recurrent lung cancer. Initially, in vitro miRNA profiles of normal lung (Beas-2b) and lung cancer (H1299) cells and of exosomes isolated from conditioned media were determined. In vivo study involved establishing subcutaneous primary and recurrent lung cancer xenografts in nude mouse model and examining tumor and serum exosomal miRNA alteration in secondary/recurrent lung tumors. A total of 77 miRNAs were observed to be significantly modulated in the H1299 cells (47 miRNA upregulated and 30 downregulated) compared to the Beas-2b cells. The exosomes isolated from conditioned media indicated several miRNAs which were in agreement with cells of origin. A similarity was also observed between miRNAs from serum exosomes and tumors, indicating their origin from the lung tumors. Two miRNAs, miR-21 and miR-155, were found to be significantly upregulated in recurrent tumors compared to primary tumors. These miRNAs were also upregulated in serum exosomes of recurrent tumor-bearing animals versus non-tumor- or primary tumor-bearing animals. Increased expression of the recurrent disease markers were also observed in recurrent tumors compared with primary tumors. Serum exosomes from recurrent tumor mice mirrored its tumor profile in expressing higher levels of these proteins compared with exosomes from primary tumor mice. Our data suggest that exosomal miRNA signatures may be a true representation of a pathological profile of lung cancer; thus, miRNAs could serve as promising biomarkers for non-invasive diagnosis of the disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2012.
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2012. National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2012/. based on November 2014 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2015.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654–U72. doi:10.1038/ncb1596.
Urbanelli L, Magini A, Buratta S, Brozzi A, Sagini K, Polchi A, et al. Signaling pathways in exosomes biogenesis, secretion and fate. Genes. 2013;4(2):152–70. doi:10.3390/genes4020152.
Roma-Rodrigues C, Fernandes AR, Baptista PV. Exosome in Tumour Microenvironment: Overview of the Crosstalk between Normal and Cancer Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2014. doi:Artn 179486 10.1155/2014/179486.
Peinado H, Aleckovic M, Lavotshkin S, Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med. 2012;18(6):883−+. doi:10.1038/nm.2753.
Rana S, Malinowska K, Zoller M. Exosomal tumor microRNA modulates premetastatic organ cells. Neoplasia. 2013;15(3):281–95.
Chen LT, Xu SD, Xu H, Zhang JF, Ning JF, Wang SF. MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion and tumor angiogenesis. Med Oncol. 2012;29(3):1673–80. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-0083-x.
Lin PY, Yu SL, Yang PC. MicroRNA in lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010;103(8):1144–8. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605901.
Wang X, Ling C, Bai Y, Zhao J. MicroRNA-206 is associated with invasion and metastasis of lung cancer. Anat Rec. 2011;294(1):88–92. doi:10.1002/ar.21287.
Hennessey PT, Sanford T, Choudhary A, Mydlarz WW, Brown D, Adai AT, et al. Serum microRNA biomarkers for detection of non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(2), e32307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032307.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):189–98. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.025.
Gao W, Xu J, Shu YQ. miRNA expression and its clinical implications for the prevention and diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2011;5(5):699–709. doi:10.1586/ers.11.55.
Markou A, Liang Y, Lianidou E. Prognostic, therapeutic and diagnostic potential of microRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49(10):1591–603. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2011.661.
Feng B, Zhang K, Wang R, Chen L. Non-small-cell lung cancer and miRNAs: novel biomarkers and promising tools for treatment. Clin Sci. 2015;128(10):619–34. doi:10.1042/CS20140530.
Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM, Shamburek RD, Remaley AT. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(4):423–33. doi:10.1038/ncb2210.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033.
Rabinowits G, Gercel-Taylor C, Day JM, Taylor DD, Kloecker GH. Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10(1):42–6. doi:10.3816/CLC.2009.n.006.
Hornick NI, Huan J, Doron B, Goloviznina NA, Lapidus J, Chang BH et al. Serum Exosome MicroRNA as a Minimally-Invasive Early Biomarker of AML. Sci Rep-Uk. 2015;5. doi:Artn 11295 10.1038/Srep11295.
Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D, Honma Y, Yamada Y, Furuta K et al. Circulating Exosomal microRNAs as Biomarkers of Colon Cancer. PloS one. 2014;9(4). doi:ARTN e92921 10.1371/journal.pone.0092921.
Tokuhisa M, Ichikawa Y, Kosaka N, Ochiya T, Yashiro M, Hirakawa K et al. Exosomal miRNAs from Peritoneum Lavage Fluid as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers of Peritoneal Metastasis in Gastric Cancer. PloS one. 2015;10(7). doi:ARTN e0130472 10.1371/journal.pone.0130472.
Zhu CQ, Shih W, Ling CH, Tsao MS. Immunohistochemical markers of prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer: a review and proposal for a multiphase approach to marker evaluation. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59(8):790–800. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.031351.
Zhang LQ, Jiang F, Xu L, Wang J, Bai JL, Yin R, et al. The role of cyclin D1 expression and patient's survival in non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Clin Lung Cancer. 2012;13(3):188–95. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2011.10.003.
Singhal S, Vachani A, Antin-Ozerkis D, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM. Prognostic implications of cell cycle, apoptosis, and angiogenesis biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer: a review. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(11):3974–86. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2661.
Lasser C. Identification and analysis of circulating exosomal microRNA in human body fluids. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1024:109–28. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-453-1_9.
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Di Nicola M, Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN, et al. microRNAs derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening and diagnosing lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(9):1156–62. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318299ac32.
Lin J, Li J, Huang B, Liu J, Chen X, Chen XM, et al. Exosomes: novel biomarkers for clinical diagnosis. Sci World J. 2015;2015:657086. doi:10.1155/2015/657086.
Lussier YA, Khodarev NN, Regan K, Corbin K, Li H, Ganai S, et al. Oligo- and polymetastatic progression in lung metastasis(es) patients is associated with specific microRNAs. PLoS One. 2012;7(12), e50141. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050141.
Wang R, Chen XF, Shu YQ. Prediction of non-small cell lung cancer metastasis-associated microRNAs using bioinformatics. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(1):32–51.
Saito M, Schetter AJ, Mollerup S, Kohno T, Skaug V, Bowman ED, et al. The association of microRNA expression with prognosis and progression in early-stage, non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of three cohorts. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(7):1875–82. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2961.
Matsumura T, Sugimachi K, Iinuma H, Takahashi Y, Kurashige J, Sawada G, et al. Exosomal microRNA in serum is a novel biomarker of recurrence in human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;113(2):275–81. doi:10.1038/bjc.2015.201.
Hessvik NP, Sandvig K, Llorente A. Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers for prostate cancer. Front Genet. 2013;4:36. doi:10.3389/fgene.2013.00036.
Huang LL, Wang XY, Wen CY, Yang XL, Song MM, Chen JX et al. Hsa-miR-19a is associated with lymph metastasis and mediates the TNF-alpha induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep-Uk. 2015;5. doi:Artn 13350 10.1038/Srep13350.
Rong BX, Zhao CC, Liu H, Ming ZJ, Cai XG, Gao WL, et al. Identification and verification of Hsp90-beta as a potential serum biomarker for lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2014;4(6):874–85.
Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Han N, Chu Q, Yu S, et al. Meta-analysis reveals the correlation of Notch signaling with non-small cell lung cancer progression and prognosis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10338. doi:10.1038/srep10338.
D'Amico TA, Massey M, Herndon JE, Moore MB, Harpole DH. A biologic risk model for stage I lung cancer: Immunohistochemical analysis of 408 patients with the use of ten molecular markers. J Thorac Cardiov Sur. 1999;117(4):736–42. doi:Doi 10.1016/S0022-5223(99)70294-1.
Sterlacci W, Fiegl M, Hilbe W, Jamnig H, Oberaigner W, Schmid T, et al. Deregulation of p27 and Cyclin D1/D3 control over mitosis is associated with unfavorable prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, as determined in 405 operated patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(9):1325–36.
Zhu J, Yu L, Zhan P, Song Y, Wang Q. The relationships between cyclin D1 expression and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo fei ai za zhi =Chinese J Lung Cancer. 2010;13(8):803–8. doi:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.08.10.
Li R, An SJ, Chen ZH, Zhang GC, Zhu JQ, Nie Q, et al. Expression of cyclin D1 splice variants is differentially associated with outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Hum Pathol. 2008;39(12):1792–801. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2008.05.008.
Burke L, Flieder DB, Guinee DG, Brambilla E, Freedman AN, Bennett WP, et al. Prognostic implications of molecular and immunohistochemical profiles of the Rb and p53 cell cycle regulatory pathways in primary non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(1):232–41.
Khoury T, Alrawi S, Ramnath N, Li Q, Grimm M, Black J, et al. Eukaryotic initiation factor-4E and cyclin D1 expression associated with patient survival in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10(1):58–66. doi:10.3816/CLC.2009.n.009.
Dworakowska D, Jassem E, Jassem J, Boltze C, Wiedorn KH, Dworakowski R, et al. Prognostic value of cyclin D1 overexpression in correlation with pRb and p53 status in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005;131(7):479–85. doi:10.1007/s00432-004-0661-9.
Dworakowska D, Jassem E, Jassem J, Karmolinski A, Lapinski M, Tomaszewski D, et al. Prognostic value of the apoptotic index analysed jointly with selected cell cycle regulators and proliferation markers in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2009;66(1):127–33. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.01.008.
Wu Y, Huang B, Liu Q, Liu Y. Heat shock protein 90-beta over-expression is associated with poor survival in stage I lung adenocarcinoma patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(7):8252–9.
Zheng CL, Qiu C, Shen MX, Qu X, Zhang TH, Zhang JH, et al. Prognostic impact of elevation of vascular endothelial growth factor family expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: an updated meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(5):1881–95.
Passlick B, Sienel W, Seen-Hibler R, Wockel W, Thetter O, Mutschler W, et al. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 predicts unfavorable outcome in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6(10):3944–8.
Qian Q, Wang Q, Zhan P, Peng L, Wei SZ, Shi Y, et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinase 2 on the survival of patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cancer Invest. 2010;28(6):661–9. doi:10.3109/07357901003735634.
Liang Y, Guo S, Zhou Q. Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(4):3717–24. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1491-7.
Dragovic RA, Gardiner C, Brooks AS, Tannetta DS, Ferguson DJP, Hole P, et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomed-Nanotechnol. 2011;7(6):780–8. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2011.04.003.
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Current protocols in cell biology / editorial board, Juan S Bonifacino [et al.]. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3 22. doi:10.1002/0471143030.cb0322s30.
Munagala R, Aqil F, Vadhanam MV, Gupta RC. MicroRNA 'signature' during estrogen-mediated mammary carcinogenesis and its reversal by ellagic acid intervention. Cancer Lett. 2013;339(2):175–84. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.012.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported from the Agnes Brown Duggan Endowment and Helmsley Trust Funds. Ramesh C. Gupta holds the Agnes Brown Duggan Chair in Oncological Research. The Microarray core is gratefully acknowledged for assisting with sample analysis and Xiaohong Li, Biostatistician, University of Louisville Bioinformatics Core, for her assistance in analysis of the data. We thank Manicka V. Vadhanam for useful discussions during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Table S1: Significantly modulated miRNAs in cancer (H1299) vs normal (Beas-2b) cell line. Table S2: Significantly modulated miRNAs in serum exosomes from tumor bearing vs normal (non-tumor) mice. Table S3: Significantly modulated miRNAs in recurrent vs primary tumors. (DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munagala, R., Aqil, F. & Gupta, R.C. Exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers of recurrent lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 10703–10714 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4939-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4939-8