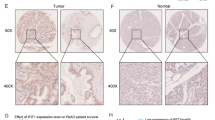
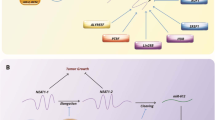
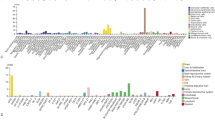
Abstract
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the common malignant tumors in China, which occurs on the top and sidewalls of the nasopharyngeal cavity. The incidence of malignant tumors of the ear, nose and throat is the highest. However, little is known about the growth of the cells. Therefore, this study constructed a multi-regulator-driven NPC cell growth-related module, aiming to explore the mechanism of functional pathways regulating the proliferation of NPC cells in an all-round way. Firstly, differential expression analysis, co-expression analysis, enrichment analysis and connectivity analysis were synthesized to identify the intrinsic genes of expression disorder module. Subsequently, we analyzed the module by crosstalk, and observed the interaction between modules intuitively. Finally, based on hypergeometric test, the significance of multi-regulators on the regulation of potential modules is calculated. We obtained 17 cell growth-related expression disorder modules by 2148 gene modules focusing. These modules are mainly involved in the growth cycle of NPC cells, including cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis. At the same time, they mainly affect the proliferation and apoptosis of NPC cells through PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, NF-kappa B signaling pathway and Wnt signaling pathway. Based on the growth-related modules of NPC cells, we have obtained a series of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) including microRNA-92a-3p, microRNA-19a-3p and microRNA-130a-3p, play an important role in regulating the growth of NPC cells. Similarly, we also predicted transcription factors (involving E2F1, NFKB1, SP1, etc.) that may play a key role in cell growth-related modules. This study is based on cell growth-related expression disorder module to explore the regulatory role of its functional pathway on cell proliferation mechanism, which will help researchers to have a deeper understanding of the potential pathogenesis of NPC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Wang, G., Zhuang, J., Ni, J., Ye, Y., He, S., & Xia, W. (2018). Combined effects of lenvatinib and iodine-131 on cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 16(4), 3325–3332.
Shuai, M., Hong, J., Huang, D., Zhang, X., & Tian, Y. (2018). Upregulation of circRNA_0000285 serves as a prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is involved in radiosensitivity. Oncology letters, 16(5), 6495–6501.
Tang, J., Zhong, G., Wu, J., Chen, H., & Jia, Y. (2018). SOX2 recruits KLF4 to regulate nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncogenesis, 7(8), 61.
Hu, Q., Lin, X., Ding, L., Zeng, Y., Pang, D., & Ouyang, N. (2018). ARHGAP42 promotes cell migration and invasion involving PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Medicine, 7(8), 3862–3874.
Lu, J., Liu, Q. H., Wang, F., Tan, J. J., Deng, Y. Q., & Peng, X. H. (2018). Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 37(1), 147.
Zhu, Z., Ni, H., You, B., Shi, S., Shan, Y., & Bao, L. (2018). Elevated EGFL6 modulates cell metastasis and growth via AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Medicine, 7(12), 6281–6289.
Cui, M., Chang, Y., Fang, Q. G., Du, W., Wu, J. F., & Wang, J. H. (2018). Non-coding RNA Pvt1 promotes cancer stem cell-like traits in nasopharyngeal cancer via inhibiting miR-1207. Pathology and Oncology Research, 24(4), 1411–1422.
Chen, J., Li, H. L., Li, B. B., Li, W., Ma, D., & Li, Y. H. (2018). Serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 3 is a potential oncogene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 85(6), 705–715.
Lo, A. K., Lung, R. W., Dawson, C. W., Young, L. S., Ko, C. W., & Yeung, W. W. (2018). Activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1)-mediated lipogenesis by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) promotes cell proliferation and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The Journal of Pathology, 246(2), 180–190.
Huang, G., Du, M. Y., Zhu, H., Zhang, N., Lu, Z. W., & Qian, L. X. (2018). MiRNA-34a reversed TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppression of SMAD4 in NPC cells. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 106, 217–224.
Pan, Y., Zhang, Y., Gong, L., Zou, J., Hu, B., & Zhang, S. (2018). IMB-6G induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 16(5), 4187–4192.
Gallardo, F., Mariame, B., Gence, R., & Tilkin-Mariame, A. F. (2018). Macrocyclic lactones inhibit nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells proliferation through PAK1 inhibition and reduce in vivo tumor growth. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 12, 2805–2814.
Liu, Z. B., Tang, C., Jin, X., Liu, S. H., & Pi, W. (2018). Increased expression of lncRNA SNHG12 predicts a poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and regulates cell proliferation and metastasis by modulating notch signal pathway. Cancer Biomarkers, 23(4), 603–613.
Lin, Y. T., Wang, H. C., Chuang, H. C., Hsu, Y. C., Yang, M. Y., & Chien, C. Y. (2018). Pre-treatment with angiotensin-(1–7) inhibits tumor growth via autophagy by downregulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 96(12), 1407–1418.
Shi, L., Xiao, R., Wang, M., Zhang, M., Weng, N., & Zhao, X. (2018). MicroRNA3423p suppresses proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by directly targeting Cdc42. Oncology Reports, 40(5), 2750–2757.
Li, B. S., Huang, J. Y., Guan, J., & Chen, L. H. (2018). Camptothecin inhibits the progression of NPC by regulating TGF-beta-induced activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncology Letters, 16(1), 552–558.
Peng, L., Chen, Y. P., Xu, C., Tang, L. L., Chen, L., & Lin, A. H. (2018). A novel scoring model to predict benefit of additional induction chemotherapy to concurrent chemoradiotherapy in stage II-IVa nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncology, 86, 258–265.
He, H., Lin, K., Su, Y., Lin, S., Zou, C., & Pan, J. (2018). Overexpression of beta-catenin decreases the radiosensitivity of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2 Cells. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 50(5), 1929–1944.
Zhang, Z., Huo, H., Liao, K., Wang, Z., Gong, Z., & Li, Y. (2018). RPA1 downregulation enhances nasopharyngeal cancer radiosensitivity via blocking RAD51 to the DNA damage site. Experimental Cell Research, 371(2), 330–341.
Liang, Z. G., Lin, G. X., Yu, B. B., Su, F., Li, L., & Qu, S. (2018). The role of autophagy in the radiosensitivity of the radioresistant human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2R. Cancer Management and Research, 10, 4125–4134.
Barrett, T., Wilhite, S. E., Ledoux, P., Evangelista, C., Kim, I. F., & Tomashevsky, M. (2013). NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1), D991–D995.
Brown, G. R., Hem, V., Katz, K. S., Ovetsky, M., Wallin, C., & Ermolaeva, O. (2015). Gene: A gene-centered information resource at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(D1), D36–D42.
Amberger, J. S., & Hamosh, A. (2017). Searching online mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM): A knowledge base of human genes and genetic phenotypes. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.27
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C. W., & Shi, W. (2015). Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(7), e47.
Langfelder, P., & Horvath, S. (2008). WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 559.
Zou, Z., Liu, S., Ha, Y., & Huang, B. (2020). Construction and analysis of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network in nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on weighted correlation network analysis. BioMed Research International, 2020, 1468980.
Zhang, S., Yue, W., Xie, Y., Liu, L., Li, S., Dang, W., Xin, S., Yang, L., Zhai, X., Cao, P., & Lu, J. (2019). The four-microRNA signature identified by bioinformatics analysis predicts the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Oncology Reports, 42(5), 1767–1780.
Yu, G., Wang, L. G., Han, Y., & He, Q. Y. (2012). Cluster profiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 16(5), 284–287.
Carlin, D. E., Demchak, B., Pratt, D., Sage, E., & Ideker, T. (2017). Network propagation in the cytoscape cyberinfrastructure. PLoS Computational Biology, 13(10), e1005598.
Hopf, T. A., Green, A. G., Schubert, B., Mersmann, S., Scharfe, C. P. I., & Ingraham, J. B. (2018). The EVcouplings python framework for coevolutionary sequence analysis. Bioinformatics, 13(6), e1005575.
Ma, J. J., Liu, H. M., Xu, X. H., Guo, L. X., & Lin, Q. (2019). Study on gene expression patterns and functional pathways of peripheral blood monocytes reveals potential molecular mechanism of surgical treatment for periodontitis. World Journal of Clinical Cases., 7(12), 1383–1392. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1383
Song, J., & Song, M. (2020). Identification of hydatidosis-related modules and key regulatory genes. PeerJ, 8, e9280.
Han, H., Cho, J. W., Lee, S., Yun, A., Kim, H., & Bae, D. (2018). TRRUST v2: An expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(D1), D380–D386.
Yi, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, C., Zhang, L., Huang, H., & Li, Y. (2017). RAID v2.0: An updated resource of RNA-associated interactions across organisms. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(D1), D115–D118.
Yi, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, C., Zhang, L., Huang, H., Li, Y., Liu, L., Hou, P., Cui, T., Tan, P., Hu, Y., Zhang, T., Huang, Y., Li, X., Yu, J., & Wang, D. (2017). RAID v2.0: An updated resource of RNA-associated interactions across organisms. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, D115–D118.
Chen, F., Shen, C., Wang, X., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Yu, C., Lv, J., He, J., & Wen, Z. (2017). Identification of genes and pathways in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis. Oncotarget, 8(38), 63738–63749.
Wu, J., Du, M., Zhang, Q., Zhang, W., Fan, Y., & Yin, L. (2018). Long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes the proliferation, invasion, and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via modulation of miR-145. OncoTargets and Therapy, 11, 7483–7492.
Li, M. Y., Liu, J. Q., Chen, D. P., Li, Z. Y., Qi, B., & He, L. (2017). Radiotherapy induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the ATM and smad pathways. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 18(9), 681–693.
Bradbury, P. A., Zhai, R., Hopkins, J., Kulke, M. H., Heist, R. S., & Singh, S. (2009). Matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 12 polymorphisms and esophageal adenocarcinoma risk and prognosis. Carcinogenesis, 30(5), 793–798.
Hu, X., Tang, J., Pan, J., & Wu, G. (2010). Study of the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B, matrix metalloproteinase-3, -9 on nasopharyngeal carcinoma and their clinical significance. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery, 24(15), 678–682.
Lee, D. C., Chua, D. T., Wei, W. I., Sham, J. S., & Lau, A. S. (2007). Induction of matrix metalloproteinases by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 isolated from nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 61(9), 520–526.
Gong, Y., Luo, X., Yang, J., Jiang, Q., & Liu, Z. (2018). RIPK4 promoted the tumorigenicity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 108, 1–6.
Zhu, J. F., Huang, W., Yi, H. M., Xiao, T., Li, J. Y., & Feng, J. (2018). Annexin A1-suppressed autophagy promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by PI3K/AKT signaling activation. Cell Death & Disease, 9(12), 1154.
Cheng, C., Xiaohua, W., Ning, J., Dan, Z., Chengyun, Y., & Lijun, Z. (2018). MiR-122 exerts anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cellular and Molecular Biology, 64(13), 21–25.
Cao, W., & Sun, J. (2019). MicroRNA-200c promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting dachshund family transcription factor 1 by the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 30(3), 218–224.
Tan, G. X., Wang, X. N., Tang, Y. Y., Cen, W. J., Li, Z. H., & Wang, G. C. (2019). PP-22 promotes autophagy and apoptosis in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2 by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress, downregulating STAT3 signaling, and modulating the MAPK pathway. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(3), 2618–2630.
Zhang, S., Li, P., Zhao, L., & Xu, L. (2018). LINC00210 as a miR-328–5p sponge promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis by activating NOTCH3 pathway. Bioscience Reports. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20181168
Wang, C., Pan, Z., Hou, H., Li, D., Mo, Y., & Mo, C. (2016). The enhancement of radiation sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via activation of the Rac1/NADPH signaling pathway. Radiation Research, 185(6), 638–646.
Qi, Y., Huang, B., Yu, L., Wang, Q., Lan, G., & Zhang, Q. (2009). Prognostic value of Tiam1 and Rac1 overexpression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. ORL, 71(3), 163–171.
Wang, J., Chang, L., Lai, X., Li, X., Wang, Z., & Huang, Z. (2018). Tetrandrine enhances radiosensitivity through the CDC25C/CDK1/cyclin B1 pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle, 17(6), 671–680.
Chen, X., Yue, B., Zhang, C., Qi, M., Qiu, J., & Wang, Y. (2017). MiR-130a-3p inhibits the viability, proliferation, invasion, and cell cycle, and promotes apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing BACH2 expression. Bioscience Reports. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20160576
Qu, R., Sun, Y., Li, Y., Hu, C., Shi, G., & Tang, Y. (2017). MicroRNA-130a-3p suppresses cell viability, proliferation and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibiting CXCL12. American Journal of Translational Research, 9(8), 3586–3598.
Xuefang, Z., Ruinian, Z., Liji, J., Chun, Z., Qiaolan, Z., Jun, J., Yuming, C., & Junrong, H. (2020). miR-331-3p inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by targeting elf4B-PI3K-AKT pathway. Technology in Cancer Research and Treatment, 19, 1533033819892251.
Yang, Y., Li, Q., & Guo, L. (2018). MicroRNA-122 acts as tumor suppressor by targeting TRIM29 and blocking the activity of PI3K/AKT signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro. Molecular Medicine Reports, 17(6), 8244–8252.
Dai, W., Dong, P., Liu, J., Gao, Y., Hu, Y., Lin, H., Song, Y., & Mei, Q. (2019). Euscaphic acid inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by silencing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. American Journal of Translational Research, 11(4), 2090–2098.
Zheng, D., Zhu, G., Liao, S., Yi, W., Luo, G., He, J., Pei, Z., Li, G., & Zhou, Y. (2015). Dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway affects cell cycle and apoptosis of side population cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncology Letters, 10(1), 182–188.
Jiang, H., Gao, M., Shen, Z., Luo, B., Li, R., Jiang, X., Ding, R., Ha, Y., Wang, Z., & Jie, W. (2014). Blocking PI3K/Akt signaling attenuates metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through induction of mesenchymal-epithelial reverting transition. Oncology Reports, 32(2), 559–566.
Huang, Q., Hou, S., Zhu, X., & Liu, S. (2020). MicroRNA-192 promotes the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through targeting RB1 and activating PI3K/AKT pathway. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 18(1), 29.
Zhang, L. Y., Ho-Fun Lee, V., Wong, A. M., Kwong, D. L., Zhu, Y. H., Dong, S. S., Kong, K. L., Chen, J., Tsao, S. W., Guan, X. Y., & Fu, L. (2013). MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN. Carcinogenesis, 34, 454–463.
Yu, G., Wang, L. G., Han, Y., & He, Q. Y. (2012). clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 16(5), 284–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL, HM, and ML conceived the designed that study, wrote the manuscript and approved the manuscript, and offered the funding support and project supervision during the revision stage. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital, Jining, 272000, Shandong, P.R. China.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Ma, H. & Liu, M. Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis-Related Genes Affect the Development of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Through PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Mol Biotechnol 63, 1081–1091 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00357-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00357-0