Abstract
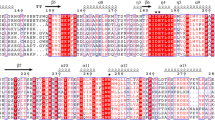
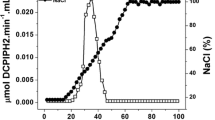
A novel pyrroloquinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase like enzyme (PQQ GDH) was isolated from Sorangium cellulosum So ce56. The putative coding region was cloned, over expressed in E. coli and the resulting enzyme was characterized. The recombinant protein has a relative molecular mass of 63 kDa and shows 43% homology to PQQ GDH-B from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. In the presence of PQQ and CaCl2 the enzyme has dehydrogenase activity with the substrate glucose as well as with other mono- and disaccharides. The thermal stability and its pH activity profile mark the enzyme as a potential glucose biosensor enzyme. In order to decrease the activity on maltose, which is unwanted for a potential application in biosensors, the protein was rationally modified at three specified positions. The best variant showed a 59% reduction in activity on maltose compared to the wild type enzyme. The catalytic efficiency (k cat/K M) was reduced fivefold but the specific activity still amounted to 63% of the wild type activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Costa, E. J., Higgins, I. J., & Turner, A. P. (1986). Quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase and its application in an amperometric glucose sensor. Biosensors, 2, 71–87.
Ling, Y., Haemmerle, M., Olsthoorn, A. J. J., Schuhmann, W., Schmidt, H.-L., Duine, J. A., et al. (1993). High current density “wired” quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase electrode. Analytical Chemistry, 65, 238–241.
Laurinavicius, V., Razumiene, J., Ramanavicius, A., & Ryabov, A. D. (2004). Wiring of PQQ-dehydrogenases. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 20, 1217–1222.
Tsujimura, S., Kojima, S., Kano, K., Ikeda, T., Sato, M., Sanada, H., et al. (2006). Novel FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase for a dioxygen-insensitive glucose biosensor. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 70, 654–659.
Turner, A. P. F., & Wilson, R. (1992). Glucose oxidase: An ideal enzyme. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 7, 165–185.
Bankar, S. B., Bule, M. V., Singhal, R. S., & Ananthanarayan, L. (2009). Glucose oxidase—an overview. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 489–501.
Dokter, P., Frank, J., & Duine, J. A. (1986). Purification and characterization of quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus L.M.D. 79.41. Biochemical Journal, 239, 163–167.
Igarashi, S., Ohtera, T., Yoshida, H., Witarto, A. B., & Sode, K. (1999). Construction and characterization of mutant water-soluble PQQ glucose dehydrogenases with altered K(m) values—site-directed mutagenesis studies on the putative active site. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 264, 820–824.
Igarashi, S., Hirokawa, T., & Sode, K. (2004). Engineering PQQ glucose dehydrogenase with improved substrate specificity. Site-directed mutagenesis studies on the active center of PQQ glucose dehydrogenase. Biomolecular Engineering, 21, 81–89.
Hamamatsu, N., Suzumura, A., Nomiya, Y., Sato, M., Aita, T., Nakajima, M., et al. (2006). Modified substrate specificity of pyrroloquinoline quinone glucose dehydrogenase by biased mutation assembling with optimized amino acid substitution. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 73, 607–617.
Sode, K., Ootera, T., Shirahane, M., Witarto, A. B., Igarashi, S., & Yoshida, H. (2000). Increasing the thermal stability of the water-soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone glucose dehydrogenase by single amino acid replacement. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 26, 491–496.
Tanaka, S., Igarashi, S., Ferri, S., & Sode, K. (2005). Increasing stability of water-soluble PQQ glucose dehydrogenase by increasing hydrophobic interaction at dimeric interface. BMC Biochemistry, 6, 1.
Schneiker, S., Perlova, O., Kaiser, O., Gerth, K., Alici, A., Altmeyer, M. O., et al. (2007). Complete genome sequence of the myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum. Nature Biotechnology, 25, 1281–1289.
Cleton-Jansen, A. M., Goosen, N., Vink, K., & van de Putte, P. (1989). Cloning, characterization and DNA sequencing of the gene encoding the Mr 50, 000 quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Molecular and General Genetics, 217, 430–436.
Datsenko, K. A., & Wanner, B. L. (2000). One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 97, 6640–6645.
Cozier, G. E., Salleh, R. A., & Anthony, C. (1999). Characterization of the membrane quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli and characterization of a site-directed mutant in which histidine-262 has been changed to tyrosine. Biochemical Journal, 340, 639–647.
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schaffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Larkin, M. A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., et al. (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23, 2947–2948.
Oubrie, A., Rozeboom, H. J., Kalk, K. H., Olsthoorn, A. J., Duine, J. A., & Dijkstra, B. W. (1999). Structure and mechanism of soluble quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase. EMBO Journal, 18, 5187–5194.
Bendtsen, J. D., Nielsen, H., von Heijne, G., & Brunak, S. (2004). Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. Journal of Molecular Biology, 340, 783–795.
Juncker, A. S., Willenbrock, H., von Heijne, G., Brunak, S., Nielsen, H., & Krogh, A. (2003). Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative bacteria. Protein Science, 12, 1652–1662.
Hommes, R. W. J., Postma, P. W., Neijssel, O. M., Tempest, D. W., Dokter, P., & Duine, J. A. (1984). Evidence of a quinoprotein glucose-dehydrogenase apoenzyme in several strains of Escherichia-Coli. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 24, 329–333.
Olsthoorn, A. J., & Duine, J. A. (1996). Production, characterization, and reconstitution of recombinant quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase (soluble type; EC 1.1.99.17) apoenzyme of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 336, 42–48.
Cleton-Jansen, A. M., Goosen, N., Vink, K., & van de Putte, P. (1989). Cloning of the genes encoding the two different glucose dehydrogenases from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 56, 73–79.
James, P. L., & Anthony, C. (2003). The metal ion in the active site of the membrane glucose dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1647, 200–205.
Wang, J. (2008). Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chemical Reviews, 108, 814–825.
Davies, D. S. (1994). Kinetics of icodextrin. Peritoneal Dialysis International, 14, 45–50.
Sode, K., Igarashi, S., Morimoto, A., & Yoshida, H. (2002). Construction of engineered water-soluble PQQ glucose dehydrogenase with improved substrate specificity. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 20, 405–412.
Patrick, W. M., Firth, A. E., & Blackburn, J. M. (2003). User-friendly algorithms for estimating completeness and diversity in randomized protein-encoding libraries. Protein Engineering Design & Selection, 16, 451–457.
Igarashi, S., Okuda, J., Ikebukuro, K., & Sode, K. (2004). Molecular engineering of PQQGDH and its applications. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 428, 52–63.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the BMBF Innovationsinitiative Neue Länder (Unternehmen Region, InnoProfile). We would like to thank Bernd Gründig of Senslab GmbH for the helpful discussions, Christian Seidl for his help with the computer model, and Rolf Müller for his kind gift of S.cellulosum So ce56 genomic DNA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofer, M., Bönsch, K., Greiner-Stöffele, T. et al. Characterization and Engineering of a Novel Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase from Sorangium cellulosum So ce56. Mol Biotechnol 47, 253–261 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9339-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9339-5