Abstract
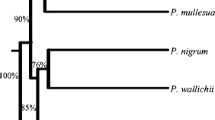
The genetic diversity of eight species of Piper (Piperaceae) viz., P. nigrum, P. longum, P. betle, P. chaba, P. argyrophyllum, P. trichostachyon, P. galeatum, and P. hymenophyllum from Kerala state, India were analyzed by Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Out of 22 10-mer RAPD primers screened, 11 were selected for comparative analysis of different species of Piper. High genetic variations were found among different Piper species studied. Among the total of 149 RAPD fragments amplified, 12 bands (8.05%) were found monomorphic in eight species. The remaining 137 fragments were found polymorphic (91.95%). Species-specific bands were found in all eight species studied. The average gene diversity or heterozygosity (H) was 0.33 across all the species, genetic distances ranged from 0.21 to 0.69. The results of this study will facilitate germplasm identification, management, and conservation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubitzki, K., Rohwer, J. G., & Brittrich, V. (1993). Flowering plants. Dycotyledons, Magnoliid, Hamamelid and Caryophyliid families. Berlin: Springer.
Frodin, D. G. (2004). History and concepts of big plant genera. Taxon, 53, 753–776.
Barret, B. (1994). Medicinal plants of Nicaragua’s Atlantic Coast. Economic Botany, 48, 8–20.
Colvard, M. D., Cordell, G. A., Villalobos, R., Sancho, G., Soejarto, D. D., Pestle, W., et al. (2006). Survey of medical ethnobotanicals for dental and oral medicine conditions and pathologies. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 107, 134–142.
Raj, H. G., Gupta, K., Rohil, V., Bose, M., Biswas, G., Singh, S. K., et al. (1998). Aflatoxin B1-induced micronuclei and cell cycle alterations in lung and bone marrow cells and their modulation by Piper argyrophyllum extract. Teratogenesis, Carcinogenesis, and Mutagenesis, 18, 249–261.
Prasad, A. K., Kumar, V., Arya, P., Kumar, S., Rajesh Dabur, R., Naresh Singh, N., et al. (2005). Investigations toward new lead compounds from medicinally important plants. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 77(1), 25–40.
Aggarwal, A. K., Tripathi, D. M., Sahai, R., Gupta, N., Saxena, R. P., Singh, M., et al. (1997). Management of giardiasis by a herbal drug ‘Pippali Rasayana’: A clinical study. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 56, 233–236.
Parthasarathy, U., Saji, K. V., Jayarajan, K., & Parthasarathy, V. A. (2006). Biodiversity of Piper in South India—application of GIS and cluster analysis. Current Science, 91(5), 652–658.
Dyer, L. A., & Palmer, A. N. (2004). Piper: A model genus for studies of evolution, chemical ecology and trophic interactions. Boston: Kluwer.
Jaramillo, M. A., Callejas, R., Davidson, C., Smith, J. F., Stevens, A. C., & Tepe, E. J. (2008). A phylogeny of the tropical genus Piper using ITS and the chloroplast intron psbJ–petA. Systematic Botany, 33(4), 647–660.
Wadt, L. H. O., Ehringhaus, C., Yoshio, P., & Kageyama, P. Y. (2004). Genetic diversity of “Pimenta longa” genotypes (Piper spp., Piperaceae) of the Embrapa Acre germplasm collection. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 27, 74–82.
Pradeepkumar, T., Karihaloo, J. L., & Archak, S. (2001). Molecular characterization of Piper nigrum L. cultivars using RAPD markers. Current Science, 81, 3.
Nazeem, P. A., Keshavachandran, R., Babu, T. D., Achuthan, C. R., Girija, D., & Peter, K. V. (2007). Assessment of genetic variability in Black Pepper (Piper nigrum L.) varieties through RAPD and AFLP analyses. In R. Keshavachandran, P. A. Nazeem, D. Girija, P. S. John, & K. V. Peter (Eds.), Recent trends in horticultural biotechnology (pp. 485–490). New Delhi, India: New India Publishing Agency.
Ravindran, P. N., Balakrishnan, R., & Nirmalbabu, K. (1992). Numerical taxonomy of South Indian Piper L. (Piperaceae) cluster analysis. Rheedea, 2, 55–61.
Sharma, A. K., & Bhattacharya, N. K. (1959). Chromosome studies on two genera of family Piperaceae. Genetica, 29, 256–289.
Sebastian, A., & Sujatha, V. S. (1996). Isoenzyme variation and species relationship in the genus Piper. Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 34, 136–137.
Morell, M. K., Peakall, R., Appels, R., Preston, L. R., & Lloyd, H. L. (1995). DNA profiling technique for plant variety identification. Australian Journal of the Experimental Agriculture, 35, 807–819.
Rodriguez, J. M., Berke, T., Engle, L., & Nienhuis, J. (1999). Variation among and within Capsicum species revealed by RAPD markers. Theoretical Applied Genetics, 99, 147–156.
Welsh, J., & McClelland, M. (1990). Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Research, 18, 7213–7218.
Williams, J. G. K., Kubelik, A. R., Livak, K. J., Reafalski, J. A., & Tingey, S. V. (1990). DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Research, 18, 6531–6535.
Clark, A. G., & Lanigan, C. M. S. (1993). Prospects for estimating nucleotide divergence with RAPDs. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 10, 1096–1111.
Chalmers, K. Y., Newton, A. C., Waugh, R., & Powell, W. (1994). Evaluation of the extent of genetic variation in mahoganies (Meliaceae) using RAPD markers. Theoretical Applied Genetics, 89, 504–508.
Plomion, C., Bahrman, N., Durel, C. E., & Malley, D. M. O. (1995). Genome mapping in Pinus pinaster (Maritime pine) using RAPD and protein marker. Heredity, 74, 661–668.
Chaveerach, R., Kunitakeb, H., Nuchadomrongc, S., Sattayasaic, N., & Komatsud, H. (2002). RAPD patterns as a useful tool to differentiate Thai Piper from morphologically alike Japanese Piper. Science Asia, 28, 221–225.
Chikkaswamy, B. K., Pramanik, C. R., Varadara, J. N., Pramanik, A., Ramesh, L. H., Shivasankar, M., et al. (2007). Determination of genetic variation in Piper using 4C nuclear DNA and RAPD markers. Cytologia, 72, 243–249.
Ranade, S. A., Verma, A., Gupta, M., & Kumar, N. (2002). RAPD profile analysis of Betle Vine Cultivars. Biologia Plantarum, 45, 523–527.
Ravindran, P. N. (2000). Black Pepper, Piper nigrum (553 pp). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Harwood Academic.
Nayar, T. S., Beegam, A. R., Mohanan, N., & Rajkumar, G. (2006). Flowering plants of Kerala, A hand book.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd ed., Vol. 1–3). Cold Spring Habor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory press.
Lynch, M., & Milligan, B. G. (1994). Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Molecular Ecology, 3, 91–99.
Yeh, F. C., Yang, R. C., & Boyle, T. (1999). POPGENE 32—version 1.31. Population genetics software. http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/fyeh/.
Nei, M. (1987). Molecular evolutionary genetics. New York: Columbia University Press.
Sneath, P. H. A., & Sokal, R. R. (1973). Numerical taxonomy (573 pp). San Francisco, CA: W.H. Freeman and Co.
Felsenstein, J. (1993). PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package), version 3.5, Distributed by the author. University of Washington, Seattle.
Nei, M. (1978). Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics, 89, 583–590.
Choudhury, P. R., Tanveer, H., & Dixit, G. P. (2006). Identification and detection of genetic relatedness among important varieties of pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown in India. Genetica, 130(2), 183–191.
Wright, S. (1951). The genetical structure of populations. Annals of Eugenics, 15, 324–354.
Wu, Y. J., Chen, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, C. X., & Xu, B. L. (2006). RAPD analysis of Jasmine rice specific genomic structure. Genome, 49, 716–719.
Muneer, P. M. A., Gopalakrishnan, A., Musammilu, K. K., Lal, K. K., Mohindra, V., Basheer, V. S., et al. (2008). Genetic variation and population structure of endemic yellow catfish, Horabagrus brachysoma (Bagridae) among three populations of Western Ghat region using RAPD and microsatellite markers. Molecular Biology Reports, 36, 1779–1791.
Archak, S., Karihaloo, J. L., & Jain, A. (2002). RAPD markers reveal narrowing genetic base of Indian tomato cultivars. Current Science, 82, 1139–1143.
Pradeepkumar, T., Karihaloo, J. L., Archak, S., & Baldev, A. (2003). Analysis of genetic diversity in Piper nigrum L. using RAPD markers. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 50, 469–475.
Caetano-Anollés, G. (1993). Amplifying DNA with arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. Genome Research, 3, 85–94.
Adams, R. P., & Rieseberg, L. H. (1998). The effects of non-homology in RAPD bands on similarity and multivariate statistical ordination in Brassica and Helianthus. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 97(1–2), 323–326.
Penner, G. A., Bush, A., Wise, R., Kim, W., Domier, L., Kasha, K., et al. (1993). Reproducibility of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis among laboratories. Genome Research, 12, 341–345.
Rajput, S. G., Wable, K. J., Sharma, K. M., Kubde, P. D., & Mulay, S. A. (2006). Reproducibility testing of RAPD and SSR markers in tomato. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5(2), 108–112.
Bhuyan, N., Borah, B. K., & Sarma, R. N. (2007). Genetic diversity analysis in traditional lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) of Assam using RAPD and ISSR markers. Current Science, 93, 967–972.
Caetno-Anolles, G., Bassam, B. J., & Gresshoff, P. M. (1991). DNA amplification fingerprinting: A strategy for genome analysis. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 9, 294–307.
Ko, H. L., Cowan, D. C., Henry, R. J., Graham, G. C., Blakeney, A. B., & Lewin, L. G. (1994). Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of Australian rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Euphytica, 80, 179–189.
Callejas, C., & Ochando, M. D. (2002). Phylogenetic relationships among Spanish Barbus species (Pisces, Cyprinidae) shown by RAPD. Heredity, 89, 36–43.
Grandclement, C., & Thomas, G. (1996). Detection and analysis of QTLs based on RAPD markers for polygenic resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae Woron in Brassica oleracea L. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 93(1–2), 86–90.
Chagué, V., Mercier, J. C., Guénard, M., de Courcel, A., & Vedel, F. (1997). Identification of RAPD markers linked to a locus involved in quantitative resistance to TYLCV in tomato by bulked segregant analysis. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 95(4), 671–677.
Sharma, R., Aggarwal, R. A., Kumar, R., Mohapatra, T., & Sharma, R. P. (2002). Construction of an RAPD linkage map and localization of QTLs for oleic acid level using recombinant inbreds in mustard (Brassica juncea). Genome, 45(3), 467–472.
Khan, M. A., Durel, C., Duffy, B., Drouet, D., Kellerhals, M., Gessler, C., et al. (2007). Development of molecular markers linked to the ‘Fiesta’ linkage group 7 major QTL for fire blight resistance and their application for marker-assisted selection. Genome, 50(6), 568–577.
Paran, I., & Michelmore, R. W. (1993). Development of reliable PCR based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 85, 985–993.
Parka, S. O., Coynea, D. P., Steadmanb, J. R., Crosbyc, K. M., & Brickd, M. A. (2004). RAPD and SCAR markers linked to the Ur-6 Andean gene controlling specific rust resistance in common bean. Crop Science, 44, 1799–1807.
Janila, P., & Sharma, B. (2008). RAPD and SCAR markers for powdery mildew resistance gene er in pea. Plant Breeding, 123(3), 271–274.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Rev. Dr. Abraham Mulamoottil, Principal; Dr. C. Balagopalan, Dean, School of Biosciences; and Dr. P. K. Shaji, Prof. Phytomedical Science and Technology, MACFAST for encouragement, support, and guidance. The authors are also gratefully acknowledged to Dr. A. Gopalakrishnan, Principal Scientist, NBFGR Cochin Unit, CMFRI for providing the excellent facilities for gel documentation. We also thank to Dr. Anathbandhu Chaudhuri, Dr. Adam Szlachetka, University of Nebraksa Medical Center, Omaha, USA and Dr. G. Ravikanth, Conservation Genetics Lab, ATREE, Bangalore for critical reading and comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, S., Skaria, R. & Muneer, P.M.A. Genetic Diversity Analysis in Piper Species (Piperaceae) Using RAPD Markers. Mol Biotechnol 46, 72–79 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9281-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9281-6