Abstract
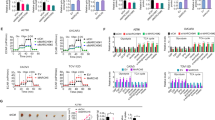
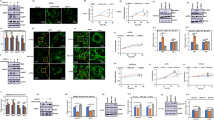
Gastric cancer represents a significant global health concern, necessitating the exploration of novel therapeutic options. Diosmetin, a natural flavonoid derived from citrus and vegetables, has demonstrated promising anti-tumor activity against various tumor cells. However, the potential anticancer effect of diosmetin in gastric cancer and its underlying mechanism have yet to be elucidated. In this study, we aimed to investigate the impact of diosmetin on cell proliferation, migration, cell cycle progression and apoptosis in human gastric cancer HGC-27 cells. Our findings revealed that diosmetin effectively suppressed cell proliferation, induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest, and triggered cell apoptosis. Mechanistically, diosmetin downregulated the expression of antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, while upregulated the level of proapoptotic proteins such as Bax, cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3. Additionally, diosmetin inhibited Akt and FoxO1 phosphorylation, while activated the MAPK signaling pathway. Notably, pretreatment of IGF-1, an Akt activator, attenuated the diosmetin-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, pretreatment with SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, significantly reduced the protein level of LC3B, while promoted the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP. Collectively, our results suggest that diosmetin holds promise as an effective therapeutic agent against gastric cancer by inducing apoptosis through inhibition of the Akt/FoxO1 pathway and promoting protective autophagy via the MAPK/JNK signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HGC-27:
-
Human gastric cancer cell line
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- Bcl-xL:
-
B-cell lymphoma-extra large
- Bax:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- FoxO1:
-
Forkhead box protein O1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- JNK:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- LC3B:
-
Microtubule Associated Protein 1 Light Chain 3 Beta
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- MTS:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2 H-tetrazolium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- JC-1:
-
5,5′,6,6′-Tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine, iodide
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick-End Labeling
References
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer: Lancet. 2020;396(10251):635–48.
Thrift AP, Wenker TN, El-Serag HB. Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20(5):338–49.
de Jongh C, van der Veen A, Brosens LAA, Nieuwenhuijzen GAP, Stoot J, Ruurda JP, van Hillegersberg R, Group LS. Distal Versus Total D2-Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: a Secondary Analysis of Surgical and Oncological Outcomes Including Quality of Life in the Multicenter Randomized LOGICA-Trial: J Gastrointest Surg. 2023.
Xu Q, Pan G, Wang Z, Wang L, Tang Y, Dong J, Qin JJ. Platycodin-D exerts its anti-cancer effect by promoting c-Myc protein ubiquitination and degradation in gastric cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1138658.
Lossi L. The concept of intrinsic versus extrinsic apoptosis. Biochem J. 2022;479(3):357–84.
Lin NY, Beyer C, Giessl A, Kireva T, Scholtysek C, Uderhardt S, Munoz LE, Dees C, Distler A, Wirtz S, et al. Autophagy regulates TNFalpha-mediated joint destruction in experimental arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(5):761–8.
Lim SM, Mohamad Hanif EA, Chin SF. Is targeting autophagy mechanism in cancer a good approach? The possible double-edge sword effect. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):56.
Dai QS, Liu W, Wang XB, Lu N, Gong DD, Kong LY, Guo QL. NCPMF-60 induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22(1):46–57.
Hu B, Shen KP, An HM, Wu Y, Du Q. Aqueous extract of Curcuma aromatica induces apoptosis and G2/M arrest in human colon carcinoma LS-174-T cells independent of p53. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2011;26(1):97–104.
Liu B, Zhang M, Liu S, Ying J, Zhang J, Kurihara H, Zheng W, He RR, Zhu R. Diosmetin, a potential p53 activator, performs Anticancer Effect by regulating Cell Cycling and Cell Proliferation in HepG2 cells. Protein Pept Lett. 2017;24(5):413–8.
Ning R, Chen G, Fang R, Zhang Y, Zhao W, Qian F. Diosmetin inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis through STAT3/c-Myc signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):40.
Kale J, Osterlund EJ, Andrews DW. BCL-2 family proteins: changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(1):65–80.
Zhang N, Qiu J, Zheng T, Zhang X, Hua K, Zhang Y. Goserelin promotes the apoptosis of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by upregulating forkhead box O1 through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(3):1034–42.
Cui H, Zhang Q. Dexmedetomidine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway. J Anesth. 2021;35(3):394–404.
Li W, Cheng M, Zhang W, He R, Yang H. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Polyphenol from Plum Fruit Inducing apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer A549 cells Via PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2021;76(1):125–32.
Shen F, Ge C, Yuan P. Aloe-emodin induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells via Akt/mTOR and MAPK signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;886:173550.
Neagu M, Constantin C, Popescu ID, Zipeto D, Tzanakakis G, Nikitovic D, Fenga C, Stratakis CA, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis AM. Inflammation and metabolism in Cancer Cell-Mitochondria Key Player. Front Oncol. 2019;9:348.
Kroemer G, Pouyssegur J. Tumor cell metabolism: cancer’s Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell. 2008;13(6):472–82.
Korgaonkar N, Yadav KS. Understanding the biology and advent of physics of cancer with perspicacity in current treatment therapy. Life Sci. 2019;239:117060.
Adamante G, de Almeida AS, Rigo FK, da Silva Silveira E, Coelho YO, De Pra SD, Milioli AM, Camponogara C, Casoti R, Bellinaso F, et al. Diosmetin as a novel transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 antagonist with antinociceptive activity in mice. Life Sci. 2019;216:215–26.
Ma A, Zhang R. Diosmetin inhibits cell proliferation, induces cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in Liver Cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:3537–46.
Oak C, Khalifa AO, Isali I, Bhaskaran N, Walker E, Shukla S. Diosmetin suppresses human prostate cancer cell proliferation through the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Int J Oncol. 2018;53(2):835–43.
Wang C, Li S, Ren H, Sheng Y, Wang T, Li M, Zhou Q, He H, Liu C. Anti-Proliferation and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of Diosmetin via modulating cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:4639–47.
Liu J, Peng Y, Wei W. Cell cycle on the crossroad of tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2022;32(1):30–44.
Koosha S, Mohamed Z, Sinniah A, Alshawsh MA. Investigation into the Molecular Mechanisms underlying the anti-proliferative and anti-tumorigenesis activities of diosmetin against HCT-116 human colorectal Cancer. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):5148.
Sarkar A, Paul A, Banerjee T, Maji A, Saha S, Bishayee A, Maity TK. Therapeutic advancements in targeting BCL-2 family proteins by epigenetic regulators, natural, and synthetic agents in cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;944:175588.
Li F, Chen L, Zheng J, Yang J, Song X, Wang Y, Zhou X. Mechanism of Gegen Qinlian Decoction regulating ABTB1 expression in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis based on PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8131531.
Altan B, Yokobori T, Ide M, Mochiki E, Toyomasu Y, Kogure N, Kimura A, Hara K, Bai T, Bao P, et al. Nuclear PRMT1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and chemosensitivity in gastric cancer patients. Gastric Cancer. 2016;19(3):789–97.
Wu Z, Sun H, Zeng W, He J, Mao X. Upregulation of MircoRNA-370 induces proliferation in human prostate cancer cells by downregulating the transcription factor FOXO1. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e45825.
Almasi S, Kennedy BE, El-Aghil M, Sterea AM, Gujar S, Partida-Sanchez S, El Hiani Y. TRPM2 channel-mediated regulation of autophagy maintains mitochondrial function and promotes gastric cancer cell survival via the JNK-signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(10):3637–50.
Tripathi D, Cheekatla SS, Paidipally P, Radhakrishnan RK, Welch E, Thandi RS, Tvinnereim AR, Vankayalapati R. c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 defective CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ cells prolong islet allograft survival in diabetic mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3310.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Competitive Allocation Project of Zhanjiang Municipal Science and Technology Development Special Fund (2021A05124 and 2022A01165).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of this.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Z., Tan, Z., Li, H. et al. Diosmetin induces apoptosis and protective autophagy in human gastric cancer HGC-27 cells via the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 and MAPK/JNK pathways. Med Oncol 40, 319 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02180-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02180-w