Abstract
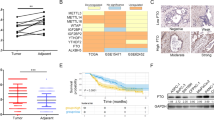
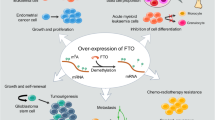
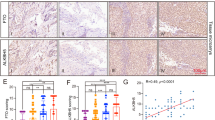
Enhanced expression of fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) has been reported in gastric cancer (GC). Bioinformatical studies indicate that FTO expression is correlated with the patients’ overall survival (OS). How FTO exerts its promotion effects on GC development and affects OS remains largely unknown. In this study, the prognostic relevance of FTO expression in human GC tissues and the molecular mechanisms underlying FTO’s promotion roles were investigated. Kaplan–Meier survival curve analysis revealed that the patients with high FTO levels had shorter OS compared to those with low FTO expression (p < 0.0001). Univariate and multivariate COX regression analyses showed that the patients’ OS was affected by FTO status (p < 0.0001, p = 0.001, respectively). FTO knockdown in HGC27 cells by shRNAs reduced cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion, while FTO overexpression in AGS cells had reverse effects. FTO knockdown in HGC27 cells also suppressed the tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model. High-throughput transcriptome sequencing indicated that FTO enhanced the PI3K/Akt signaling, which was confirmed in vitro. In summary, our research revealed that FTO is a potent prognostic biomarker of GC. FTO enhances the PI3K/Akt signaling and thus, promotes GC development.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- m6A:
-
N6-methyladenosine
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- TNM:
-
Tumor node metastasis
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–32.
Liu D, Lu M, Li J, Yang Z, Feng Q, Zhou M, Zhang Z, Shen L. The patterns and timing of recurrence after curative resection for gastric cancer in China. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14(1):305.
Liu X, Zhang D, Lin E, Chen Y, Li W, Chen Y, Sun X, Zhou Z. Preoperative controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score as a predictor of long-term outcome after curative resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II–III gastric Cancer. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):699.
Yoon KJ, Ringeling FR, Vissers C, Jacob F, Pokrass M, Jimenez-Cyrus D, Su Y, Kim NS, Zhu Y, Zheng L, Kim S, Wang X, Doré LC, Jin P, Regot S, Zhuang X, Canzar S, He C, Ming GL, Song H. Temporal control of mammalian cortical neurogenesis by m(6)A methylation. Cell. 2017;171(4):877-889.e17.
Geula S, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D, Mansour AA, Kol N, Salmon-Divon M, Hershkovitz V, Peer E, Mor N, Manor YS, Ben-Haim MS, Eyal E, Yunger S, Pinto Y, Jaitin DA, Viukov S, Rais Y, Krupalnik V, Chomsky E, Zerbib M, Maza I, Rechavi Y, Massarwa R, Hanna S, Amit I, Levanon EY, Amariglio N, Stern-Ginossar N, Novershtern N, Rechavi G, Hanna JH. Stem cells. m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naïve pluripotency toward differentiation. Science. 2015; 347(6225):1002–1006.
Shi H, Zhang X, Weng YL, Lu Z, Liu Y, Lu Z, Li J, Hao P, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wu Y, Delgado JY, Su Y, Patel MJ, Cao X, Shen B, Huang X, Ming GL, Zhuang X, Song H, He C, Zhou T. m(6)A facilitates hippocampus-dependent learning and memory through YTHDF1. Nature. 2018;563(7730):249–53.
Weng H, Huang H, Wu H, Qin X, Zhao BS, Dong L, Shi H, Skibbe J, Shen C, Hu C, Sheng Y, Wang Y, Wunderlich M, Zhang B, Dore LC, Su R, Deng X, Ferchen K, Li C, Sun M, Lu Z, Jiang X, Marcucci G, Mulloy JC, Yang J, Qian Z, Wei M, He C, Chen J. METTL14 inhibits hematopoietic stem/progenitor differentiation and promotes leukemogenesis via mRNA m(6)A modification. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(2):191-205.e9.
Du Y, Hou G, Zhang H, Dou J, He J, Guo Y, Li L, Chen R, Wang Y, Deng R, Huang J, Jiang B, Xu M, Cheng J, Chen GQ, Zhao X, Yu J. SUMOylation of the m6A-RNA methyltransferase METTL3 modulates its function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(10):5195–208.
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J, Cheng CL, Tsang LH, Ho DW, Chiu DK, Lee JM, Wong CC, Ng IO, Wong CM. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67(6):2254–70.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, Majumder S, He C, Huang S. m(6)A Demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 Expression and Cell Proliferation Program. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):591-606.e6.
Liu J, Eckert MA, Harada BT, Liu SM, Lu Z, Yu K, Tienda SM, Chryplewicz A, Zhu AC, Yang Y, Huang JT, Chen SM, Xu ZG, Leng XH, Yu XC, Cao J, Zhang Z, Liu J, Lengyel E, He C. m(6)A mRNA methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(9):1074–83.
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, Riggs AD, He C, Shi Y. m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Rep. 2017;18(11):2622–34.
Zhao X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Shi Y, Yang X, Xiao W, Hao YJ, Ping XL, Chen YS, Wang WJ, Jin KX, Wang X, Huang CM, Fu Y, Ge XM, Song SH, Jeong HS, Yanagisawa H, Niu Y, Jia GF, Wu W, Tong WM, Okamoto A, He C, Rendtlew Danielsen JM, Wang XJ, Yang YG. FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res. 2014;24(12):1403–19.
Li Z, Weng H, Su R, Weng X, Zuo Z, Li C, Huang H, Nachtergaele S, Dong L, Hu C, Qin X, Tang L, Wang Y, Hong GM, Huang H, Wang X, Chen P, Gurbuxani S, Arnovitz S, Li Y, Li S, Strong J, Neilly MB, Larson RA, Jiang X, Zhang P, Jin J, He C, Chen J. FTO plays an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(1):127–41.
Zhou S, Bai ZL, Xia D, Zhao ZJ, Zhao R, Wang YY, Zhe H. FTO regulates the chemo-radiotherapy resistance of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) by targeting β-catenin through mRNA demethylation. Mol Carcinog. 2018;57(5):590–7.
Liu J, Ren D, Du Z, Wang H, Zhang H, Jin Y. m(6)A demethylase FTO facilitates tumor progression in lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating MZF1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502(4):456–64.
Xu D, Shao W, Jiang Y, Wang X, Liu Y, Liu X. FTO expression is associated with the occurrence of gastric cancer and prognosis. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(4):2285–92.
Xu Z, Chen Q, Shu L, Zhang C, Liu W, Wang P. Expression profiles of m6A RNA methylation regulators, PD-L1 and immune infiltrates in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12:970367.
Zhou Y, Wang Q, Deng H, Xu B, Zhou Y, Liu J, Liu Y, Shi Y, Zheng X, Jiang J. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via m(6)A modification of caveolin-1 and metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(1):72.
Wang D, Qu X, Lu W, Wang Y, Jin Y, Hou K, Yang B, Li C, Qi J, Xiao J, Che X, Liu Y. N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase FTO Promotes Gastric Cancer Metastasis by Down-Regulating the m6A Methylation of ITGB1. Front Oncol. 2021;11:681280.
Yue L, Zhang R, Chen S, Duan G. Risk score prediction model of prognosis in GC patients by age and gender combined with m6A modification genes FTO and RBM15. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:710708.
Zhao Y, Yan X, Wang Y, Zhou J, Yu Y. N6-methyladenosine regulators promote malignant progression of gastric adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2021;11:726018.
Xu X, Zhou E, Zheng J, Zhang C, Zou Y, Lin J, Yu J. Prognostic and predictive value of m6A “Eraser” related gene signature in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:631803.
Azzam SK, Alsafar H, Sajini AA. FTO m6A demethylase in obesity and cancer: implications and underlying molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073800
Chen XY, Zhang J, Zhu JS. The role of m(6)A RNA methylation in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):103.
Alzahrani AS. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: at the bench and bedside. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:125–32.
Wang C, Yang Z, Xu E, Shen X, Wang X, Li Z, Yu H, Chen K, Hu Q, Xia X, Liu S, Guan W. Apolipoprotein C-II induces EMT to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(8): e522.
Wu S, Chen M, Huang J, Zhang F, Lv Z, Jia Y, Cui YZ, Sun LZ, Wang Y, Tang Y, Verhoeft KR, Li Y, Qin Y, Lin X, Guan XY, Lam KO. ORAI2 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis through PI3K/Akt signaling and MAPK-dependent focal adhesion disassembly. Cancer Res. 2021;81(4):986–1000.
Wang L, Bo X, Yi X, Xiao X, Zheng Q, Ma L, Li B. Exosome-transferred LINC01559 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):723.
Huang Y, Zhang J, Hou L, Wang G, Liu H, Zhang R, Chen X, Zhu J. LncRNA AK023391 promotes tumorigenesis and invasion of gastric cancer through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):194.
Zhang F, Li K, Pan M, Li W, Wu J, Li M, Zhao L, Wang H. miR-589 promotes gastric cancer aggressiveness by a LIFR-PI3K/AKT-c-Jun regulatory feedback loop. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):152.
Acknowledgements
Gratitude should be expressed to the Comprehensive Experiment Center and the Department of Immunology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Anhui Medical University for giving precious help in this paper.
Funding
This study was supported by the grants from The National Natural Science Youth Foundation of China (No. 8190102788).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. ZF conceived and designed the study and experiments involved. YZ performed the experiments and analyzed the data. YL provided gastric cancer samples. JY made suggestions on bioinformatics analysis. YZ and JX wrote the manuscript. All authors read, commented and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (20190362). All animal experiments in this study were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (LLSC20190402).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Yang, J., Li, Y. et al. Demethylase FTO enhances the PI3K/Akt signaling to promote gastric cancer malignancy. Med Oncol 40, 130 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-01990-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-01990-2