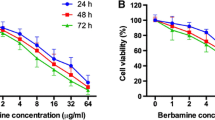
Abstract
Studies indicate that inhibiting a single signaling pathway or one single product of a gene is insufficient for the prevention and treatment of cancer. This is due to the fact that dysregulation must occur in more than 500 genes in order to produce a cancerous phenotype. Despite this evidence, available drugs used for cancer treatment focus on a single target. Meanwhile, berberine as a nutraceutical is capable of targeting various processes involved in tumor development including proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis. In comparison with synthetic agents, berberine is cheaper, safer, and more available. Berberine has shown anti-inflammatory properties which make it an ideal option in order to prevent inflammation-associated cancers. Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers all over the world and its incidence is increasing each day. Therefore, further investigations about berberine could be helpful in the discovery of novel agents for preventing and/or treating colorectal cancer. This review emphasizes the studies investigating the roles of berberine in colorectal cancer such as controlling cell signaling pathways, inducing apoptosis, regulating microRNAs, attenuating oxidative stress, and affecting inflammation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IMCE:
-
Immorto-min colonic epithelial
- AIF:
-
Apoptosis-inducing factor
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- CASC2:
-
Cancer susceptibility candidate 2
References
Marmol I, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ. Colorectal carcinoma: a general overview and future perspectives in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):E197.
Marley AR, Nan H. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2016;7:105–14.
Remo A, Fassan M, Vanoli A, Bonetti LR, Barresi V, Tatangelo F, et al. Morphology and molecular features of rare colorectal carcinoma histotypes. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(7):1036.
Delavari A, Mardan F, Salimzadeh H, Bishehsari F, Khosravi P, Khanehzad M, et al. Characteristics of colorectal polyps and cancer; a retrospective review of colonoscopy data in iran. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2014;6:144–50.
van Neerven SM, Vermeulen L. The interplay between intrinsic and extrinsic Wnt signaling in controlling intestinal transformation. Differentiation. 2019;108:17–23.
Aran V, Victorino AP, Thuler LC, Ferreira CG. Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, disease mechanisms and interventions to reduce onset and mortality. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2016;15:195–203.
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Sundaram C, Harikumar KB, Tharakan ST, Lai OS, et al. Cancer is a preventable disease that requires major lifestyle changes. Pharm Res. 2008;25:2097–116.
Lee J, Shin A, Oh JH, Kim J. Colors of vegetables and fruits and the risks of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:2527–38.
Abnet CC, Corley DA, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Diet and upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:1234–43.
Zhang FF, Cudhea F, Shan Z, Michaud DS, Imamura F, Eom H, et al. Preventable cancer burden associated with poor diet in the United States. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2019;3:pkz034.
Cranganu A, Camporeale J. Nutrition aspects of lung cancer. Nutr Clin Pract. 2009;24:688–700.
Bougnoux P, Hajjaji N, Maheo K, Couet C, Chevalier S. Fatty acids and breast cancer: sensitization to treatments and prevention of metastatic re-growth. Prog Lipid Res. 2010;49:76–86.
Syed DN, Suh Y, Afaq F, Mukhtar H. Dietary agents for chemoprevention of prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2008;265:167–76.
Khan N, Afaq F, Mukhtar H. Cancer chemoprevention through dietary antioxidants: progress and promise. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10:475–510.
Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Antioxidant supplements for preventing gastrointestinal cancers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;2008:CD004183.
Anand P, Sundaram C, Jhurani S, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB. Curcumin and cancer: an "old-age" disease with an "age-old" solution. Cancer Lett. 2008;267:133–64.
Aronson JK. Defining 'nutraceuticals': neither nutritious nor pharmaceutical. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83:8–19.
Gupta S, Sharma A, Mishra S, Awasthee N. Nutraceuticals for the prevention and cure of cancer. Cham: Springer; 2019. p. 603–610.
Gupta SC, Kim JH, Prasad S, Aggarwal BB. Regulation of survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis of tumor cells through modulation of inflammatory pathways by nutraceuticals. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010;29:405–34.
Aggarwal BB, Van Kuiken ME, Iyer LH, Harikumar KB, Sung B. Molecular targets of nutraceuticals derived from dietary spices: potential role in suppression of inflammation and tumorigenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009;234:825–49.
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2014;383:1490–502.
White A, Ironmonger L, Steele RJC, Ormiston-Smith N, Crawford C, Seims A. A review of sex-related differences in colorectal cancer incidence, screening uptake, routes to diagnosis, cancer stage and survival in the UK. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:906.
Jess T, Rungoe C, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:639–45.
Ma Y, Yang Y, Wang F, Zhang P, Shi C, Zou Y, et al. Obesity and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review of prospective studies. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e53916.
Jiang Y, Ben Q, Shen H, Lu W, Zhang Y, Zhu J. Diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011;26:863–76.
Liang PS, Chen TY, Giovannucci E. Cigarette smoking and colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:2406–15.
Fedirko V, Tramacere I, Bagnardi V, Rota M, Scotti L, Islami F, et al. Alcohol drinking and colorectal cancer risk: an overall and dose-response meta-analysis of published studies. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1958–72.
Chan DS, Lau R, Aune D, Vieira R, Greenwood DC, Kampman E, et al. Red and processed meat and colorectal cancer incidence: meta-analysis of prospective studies. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e20456.
Taylor DP, Burt RW, Williams MS, Haug PJ, Cannon-Albright LA. Population-based family history-specific risks for colorectal cancer: a constellation approach. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:877–85.
Sonnenberg A, Genta RM. Helicobacter pylori is a risk factor for colonic neoplasms. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:208–15.
Lin KJ, Cheung WY, Lai JY, Giovannucci EL. The effect of estrogen vs. combined estrogen-progestogen therapy on the risk of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:419–30.
Rothwell PM, Fowkes FG, Belch JF, Ogawa H, Warlow CP, Meade TW. Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk of death due to cancer: analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;377:31–41.
Boyle T, Keegel T, Bull F, Heyworth J, Fritschi L. Physical activity and risks of proximal and distal colon cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1548–61.
Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Seiler CM, Rickert A, Hoffmeister M. Protection from colorectal cancer after colonoscopy: a population-based, case-control study. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154:22–30.
Elmunzer BJ, Hayward RA, Schoenfeld PS, Saini SD, Deshpande A, Waljee AK. Effect of flexible sigmoidoscopy-based screening on incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med. 2012;9:e1001352.
Wu S, Feng B, Li K, Zhu X, Liang S, Liu X, et al. Fish consumption and colorectal cancer risk in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.01.022.
Aune D, Lau R, Chan DS, Vieira R, Greenwood DC, Kampman E, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:37–45.
Aune D, Chan DS, Lau R, Vieira R, Greenwood DC, Kampman E, et al. Dietary fibre, whole grains, and risk of colorectal cancer: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ. 2011;343:d6617.
Aune D, Lau R, Chan DS, Vieira R, Greenwood DC, Kampman E, et al. Nonlinear reduction in risk for colorectal cancer by fruit and vegetable intake based on meta-analysis of prospective studies. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:106–18.
Cicero AF, Baggioni A. Berberine and its role in chronic disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;928:27–45.
Wang K, Feng X, Chai L, Cao S, Qiu F. The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects. Drug Metab Rev. 2017;49:139–57.
Li Z, Geng YN, Jiang JD, Kong WJ. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of berberine in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:289264.
Feng X, Sureda A, Jafari S, Memariani Z, Tewari D, Annunziata G, et al. Berberine in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Theranostics. 2019;9:1923–51.
Yuan NN, Cai CZ, Wu MY, Su HX, Li M, Lu JH. Neuroprotective effects of berberine in animal models of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review of pre-clinical studies. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19:109.
Hengartner MO. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature. 2000;407:770–6.
Tait SW, Green DR. Caspase-independent cell death: leaving the set without the final cut. Oncogene. 2008;27:6452–61.
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY, et al. Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature. 2001;410:549–54.
Hsu WH, Hsieh YS, Kuo HC, Teng CY, Huang HI, Wang CJ, et al. Berberine induces apoptosis in SW620 human colonic carcinoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species and activation of JNK/p38 MAPK and FasL. Arch Toxicol. 2007;81:719–28.
Li W, Hua B, Saud SM, Lin H, Hou W, Matter MS, et al. Berberine regulates AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathways and inhibits colon tumorigenesis in mice. Mol Carcinog. 2015;54:1096–109.
Dai W, Mu L, Cui Y, Li Y, Chen P, Xie H, et al. Berberine promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer via regulation of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) cancer susceptibility candidate 2 (CASC2)/AU-binding factor 1 (AUF1)/B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) axis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:730–8.
Wang L, Liu L, Shi Y, Cao H, Chaturvedi R, Calcutt MW, et al. Berberine induces caspase-independent cell death in colon tumor cells through activation of apoptosis-inducing factor. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e36418.
Mehrgou A, Akouchekian M. Therapeutic impacts of microRNAs in breast cancer by their roles in regulating processes involved in this disease. J Res Med Sci. 2017;22:130.
Pardini B, De Maria D, Francavilla A, Di Gaetano C, Ronco G, Naccarati A. MicroRNAs as markers of progression in cervical cancer: a systematic review. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:696.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Feng M, Luo X, Gu C, Li Y, Zhu X, Fei J. Systematic analysis of berberine-induced signaling pathway between miRNA clusters and mRNAs and identification of mir-99a approximately 125b cluster function by seed-targeting inhibitors in multiple myeloma cells. RNA Biol. 2015;12:82–91.
Chen Q, Qin R, Fang Y, Li H. Berberine sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through miR-93/PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36:956–65.
Wang Y, Zhang S. Berberine suppresses growth and metastasis of endometrial cancer cells via miR-101/COX-2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1287–93.
Liu H, Huang C, Wu L, Wen B. Effect of evodiamine and berberine on miR-429 as an oncogene in human colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:4121–7.
Yousefi B, Samadi N, Ahmadi Y. Akt and p53R2, partners that dictate the progression and invasiveness of cancer. DNA Repair. 2014;22:24–9.
Sun Y, Shen S, Liu X, Tang H, Wang Z, Yu Z, et al. MiR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;390:19–30.
Huang C, Liu H, Gong XL, Wu LY, Wen B. Effect of evodiamine and berberine on the interaction between DNMTs and target microRNAs during malignant transformation of the colon by TGF-beta1. Oncol Rep. 2017;37:1637–45.
Vaira V, Faversani A, Dohi T, Montorsi M, Augello C, Gatti S, et al. miR-296 regulation of a cell polarity-cell plasticity module controls tumor progression. Oncogene. 2012;31:27–38.
Su YH, Tang WC, Cheng YW, Sia P, Huang CC, Lee YC, et al. Targeting of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways by Hsp90 inhibitor alone or in combination with berberine for treatment of colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1853:2261–72.
Huang G, Wu X, Li S, Xu X, Zhu H, Chen X. The long noncoding RNA CASC2 functions as a competing endogenous RNA by sponging miR-18a in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26524.
Saha SK, Khuda-Bukhsh AR. Berberine alters epigenetic modifications, disrupts microtubule network, and modulates HPV-18 E6–E7 oncoproteins by targeting p53 in cervical cancer cell HeLa: a mechanistic study including molecular docking. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;744:132–46.
Zhang J, Cao H, Zhang B, Cao H, Xu X, Ruan H, et al. Berberine potently attenuates intestinal polyps growth in ApcMin mice and familial adenomatous polyposis patients through inhibition of Wnt signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17:1484–93.
Casimiro MC, Velasco-Velazquez M, Aguirre-Alvarado C, Pestell RG. Overview of cyclins D1 function in cancer and the CDK inhibitor landscape: past and present. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014;23:295–304.
Beildeck ME, Gelmann EP, Byers SW. Cross-regulation of signaling pathways: an example of nuclear hormone receptors and the canonical Wnt pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:1763–72.
Dawson MI, Zhang XK. Discovery and design of retinoic acid receptor and retinoid X receptor class- and subtype-selective synthetic analogs of all-trans-retinoic acid and 9-cis-retinoic acid. Curr Med Chem. 2002;9:623–37.
Yousefi B, Samadi N, Baradaran B, Shafiei-Irannejad V, Zarghami N. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands and their role in chronic myeloid leukemia: therapeutic strategies. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2016;88:17–25.
Ruan H, Zhan YY, Hou J, Xu B, Chen B, Tian Y, et al. Berberine binds RXRalpha to suppress beta-catenin signaling in colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 2017;36:6906–18.
Jacobs ET, Martinez ME, Campbell PT, Conti DV, Duggan D, Figueiredo JC, et al. Genetic variation in the retinoid X receptor and calcium-sensing receptor and risk of colorectal cancer in the Colon Cancer Family Registry. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:1412–6.
Egan JB, Thompson PA, Ashbeck EL, Conti DV, Duggan D, Hibler E, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in vitamin D receptor VDR/RXRA influence the likelihood of colon adenoma recurrence. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1496–504.
Yamazaki K, Shimizu M, Okuno M, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kanemura N, Araki H, et al. Synergistic effects of RXR alpha and PPAR gamma ligands to inhibit growth in human colon cancer cells–phosphorylated RXR alpha is a critical target for colon cancer management. Gut. 2007;56:1557–633.
Duvic M, Hymes K, Heald P, Breneman D, Martin AG, Myskowski P, et al. Bexarotene is effective and safe for treatment of refractory advanced-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: multinational phase II-III trial results. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2456–71.
Guldenschuh I, Hurlimann R, Muller A, Ammann R, Mullhaupt B, Dobbie Z, et al. Relationship between APC genotype, polyp distribution, and oral sulindac treatment in the colon and rectum of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001;44:1090–7.
Kolluri SK, Corr M, James SY, Bernasconi M, Lu D, Liu W, et al. The R-enantiomer of the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug etodolac binds retinoid X receptor and induces tumor-selective apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:2525–30.
Todoric J, Antonucci L, Karin M. Targeting inflammation in cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2016;9:895–905.
Eiro N, Vizoso FJ. Inflammation and cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;4:62–72.
Watanabe T, Konishi T, Kishimoto J, Kotake K, Muto T, Sugihara K, et al. Ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer shows a poorer survival than sporadic colorectal cancer: a nationwide Japanese study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:802–8.
Zhen Y, Luo C, Zhang H. Early detection of ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2018;6:83–92.
Chen J, Pitmon E, Wang K. Microbiome, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Semin Immunol. 2017;32:43–53.
Meira LB, Bugni JM, Green SL, Lee CW, Pang B, Borenshtein D, et al. DNA damage induced by chronic inflammation contributes to colon carcinogenesis in mice. J Clin Investig. 2008;118:2516–25.
Francescone R, Hou V, Grivennikov SI. Cytokines, IBD, and colitis-associated cancer. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21:409–18.
Lucas C, Barnich N, Nguyen HTT. Microbiota, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(6):1310.
Tai WP. Luo HS [The inhibit effect of berberine on human colon cell line cyclooxygenase-2]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2003;42:558–60.
Liu X, Ji Q, Ye N, Sui H, Zhou L, Zhu H, et al. Berberine inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via COX-2/PGE2 mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0123478.
Li D, Zhang Y, Liu K, Zhao Y, Xu B, Xu L, et al. Berberine inhibits colitis-associated tumorigenesis via suppressing inflammatory responses and the consequent EGFR signaling-involved tumor cell growth. Lab Investig. 2017;97:1343–53.
Zhu L, Gu P, Shen H. Protective effects of berberine hydrochloride on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;68:242–51.
Carini F, Mazzola M, Rappa F, Jurjus A, Geagea AG, Al Kattar S, et al. Colorectal carcinogenesis: role of oxidative stress and antioxidants. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:4759–66.
Gothai S, Muniandy K, Gnanaraj C, Ibrahim IAA, Shahzad N, Al-Ghamdi SS, et al. Pharmacological insights into antioxidants against colorectal cancer: a detailed review of the possible mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:1514–22.
Ke F, Yadav PK, Ju LZ. Herbal medicine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:3–10.
Cui L, Feng L, Zhang ZH, Jia XB. The anti-inflammation effect of baicalin on experimental colitis through inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;23:294–303.
Lee IA, Hyun YJ, Kim DH. Berberine ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting lipid peroxidation, enterobacterial growth and NF-kappaB activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;648:162–70.
Yan F, Wang L, Shi Y, Cao H, Liu L, Washington MK, et al. Berberine promotes recovery of colitis and inhibits inflammatory responses in colonic macrophages and epithelial cells in DSS-treated mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302:G504–G514514.
Li R, Chen Y, Shi M, Xu X, Zhao Y, Wu X, et al. Gegen Qinlian decoction alleviates experimental colitis via suppressing TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling and enhancing antioxidant effect. Phytomedicine. 2016;23:1012–20.
Zhang LC, Wang Y, Tong LC, Sun S, Liu WY, Zhang S, et al. Berberine alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13:3374–82.
Giordano CR, Roberts R, Krentz KA, Bissig D, Talreja D, Kumar A, et al. Catalase therapy corrects oxidative stress-induced pathophysiology in incipient diabetic retinopathy. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:3095–102.
Park YS, Uddin MJ, Piao L, Hwang I, Lee JH, Ha H. Novel role of endogenous catalase in macrophage polarization in adipose tissue. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8675905.
Younus H. Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018;12:88–93.
Ndrepepa G. Myeloperoxidase—A bridge linking inflammation and oxidative stress with cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;493:36–51.
Nguyen NH, Tran GB, Nguyen CT. Anti-oxidative effects of superoxide dismutase 3 on inflammatory diseases. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020;98:59–69.
Piechota-Polanczyk A, Fichna J. Review article: the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014;387:605–20.
Bourgeais J, Gouilleux-Gruart V, Gouilleux F. Oxidative metabolism in cancer: a STAT affair? JAKSTAT. 2013;2:e25764.
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1171:59–76.
Guaman Ortiz LM, Tillhon M, Parks M, Dutto I, Prosperi E, Savio M, et al. Multiple effects of berberine derivatives on colon cancer cells. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:924585.
Wu K, Yang Q, Mu Y, Zhou L, Liu Y, Zhou Q, et al. Berberine inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells by inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:292–8.
Yu M, Tong X, Qi B, Qu H, Dong S, Yu B, et al. Berberine enhances chemosensitivity to irinotecan in colon cancer via inhibition of NFkappaB. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9:249–54.
Chidambara Murthy KN, Jayaprakasha GK, Patil BS. The natural alkaloid berberine targets multiple pathways to induce cell death in cultured human colon cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;688:14–211.
Piyanuch R, Sukhthankar M, Wandee G, Baek SJ. Berberine, a natural isoquinoline alkaloid, induces NAG-1 and ATF3 expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2007;258:230–40.
Xu LN, Lu BN, Hu MM, Xu YW, Han X, Qi Y, et al. Mechanisms involved in the cytotoxic effects of berberine on human colon cancer HCT-8 cells. Biocell. 2012;36:113–20.
Ghareeb AE, Moawed FSM, Ghareeb DA, Kandil EI. Potential prophylactic effect of berberine against rat colon carcinoma induce by 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018;19:1685–90.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JH and PMD contributed in conception, design, and drafting of the manuscript. MM, ZA, MAM, MS, and BY contributed in data collection and manuscript drafting. All authors approved the final version for submission. BY oversaw the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallajzadeh, J., Maleki Dana, P., Mobini, M. et al. Targeting of oncogenic signaling pathways by berberine for treatment of colorectal cancer. Med Oncol 37, 49 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-020-01367-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-020-01367-9